Tonsillitis is an acute infectious disease characterized by the defeat of the main components of the pharyngeal ring by viral or bacterial pathogens. The foci of inflammation are often localized in the palatine tonsils, resulting in inflammation of the lymphadenoid tissues.
 In 95% of cases, the causative agents of infection are gram-positive bacteria, such as staphylococci, meningococci and streptococci. How to quickly stop inflammation? The elimination of pathogenic flora involves the use of drugs for etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy. Late diagnosis and treatment of pathology can cause the spread of foci of inflammation in the surrounding tissues and organs. Generalization of catarrhal processes is fraught with the emergence of not only local, but also systemic complications, characterized by damage to the heart muscle, joints, kidneys, meninges, etc.
In 95% of cases, the causative agents of infection are gram-positive bacteria, such as staphylococci, meningococci and streptococci. How to quickly stop inflammation? The elimination of pathogenic flora involves the use of drugs for etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy. Late diagnosis and treatment of pathology can cause the spread of foci of inflammation in the surrounding tissues and organs. Generalization of catarrhal processes is fraught with the emergence of not only local, but also systemic complications, characterized by damage to the heart muscle, joints, kidneys, meninges, etc.
General rules
How to treat a sore throat in a child? To reduce the risk of complications when the first symptoms of pathology occur, you need to be examined by a specialist. As a rule, preschool children do not complain of discomfort in the throat, which somewhat complicates the diagnosis. The development of an infectious disease is evidenced by:
- malaise;
- apathy;
- subfebrile fever;
- hyperemia of the pharynx;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- nausea;
- sweating
After a visual examination of the patient and the results of bacterial culture, the specialist will be able to accurately determine the type of pathology and the optimal course of treatment. To accelerate the regression of inflammation in the throat, during the first 7 days, the patient needs to create optimal conditions for recovery:
- strict bed rest - prevents the creation of large loads on the cardiovascular system in the presence of hyperthermia;
- plentiful drinking - ensures the removal of toxic substances from the body, which contributes to detoxification;
- rational nutrition - minimizes the load on the digestive system, which prevents the occurrence of intestinal syndrome, accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, etc.
Important! Solid food high in coarse fiber can injure the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and thereby aggravate the patient's well-being.
Lack of appetite in the first two to three days after infection is the norm, so you should not force the patient to eat. To prevent dehydration, provide your child with plenty of fluids in the form of salted meat broths on lean meat.
Treatment principles
How to cure a sore throat at home? Conservative treatment of an infectious disease in children is carried out with the help of pharmaceutical preparations. They must have pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic and immunostimulating properties. The choice of medicines is determined by the etiological factors in the development of tonsillitis. For the treatment of a viral infection, antiviral drugs are used, microbial - antibiotics, candidal - antifungal agents.
In pediatric practice, symptomatic drugs with analgesic and antiseptic properties are used to relieve local manifestations of the disease. To prevent relapses of pathology, the attending pediatrician prescribes to the patient the intake of vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants.

What types of medications are included in the conservative treatment of acute tonsillitis?
- antipyretics;
- rinsing solutions;
- analgesics;
- sprays and aerosols;
- antibiotics;
- probiotics;
- antimycotics;
- antihistamines;
- immunostimulants.
Important! To reduce the likelihood of irritation of the gastric mucosa, antipyretics and pain relievers are best used in the form of rectal suppositories.
Etiotropic therapy
Etiotropic therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the development of infectious-allergic reactions in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx. Antiviral and antibacterial treatment of angina in children contributes to the destruction of pathogens in the foci of inflammation, which leads to regression of pathological processes in the ciliated epithelium. Due to this, the process of detoxification of the body is accelerated, which entails a gradual improvement in well-being.
 The treatment regimen for acute tonsillitis in children includes only those drugs that have the least toxicity. Of the antibiotics, penicillins and macrolides are considered the safest. The latter practically do not cause allergic reactions, therefore they can be used in the treatment of acute tonsillitis in children aged 1 year and older. The most effective drugs of etiotropic action include:
The treatment regimen for acute tonsillitis in children includes only those drugs that have the least toxicity. Of the antibiotics, penicillins and macrolides are considered the safest. The latter practically do not cause allergic reactions, therefore they can be used in the treatment of acute tonsillitis in children aged 1 year and older. The most effective drugs of etiotropic action include:
- "Flemoxin Solutab" is a broad-spectrum drug with bactericidal properties against gram-positive and gram-negative microbes;
- "Amoxiclav" is an antibacterial agent of combined action, the components of which are capable of inhibiting the synthesis of beta-lactamase; used in the treatment of complicated angina, which prevents the development of a pharyngeal abscess, otitis media, bone infection, etc.;
- "Ecoclave" is a semi-synthetic antibiotic that destroys most strains of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria that provoke inflammation of the mucous membranes of the ENT organs;
- "Hemomycin" is an azalide antibiotic, the components of which form stable compounds with the ribosomes of pathogenic bacteria, which prevents their further development; quickly relieves inflammation in soft tissues, which prevents the spread of infection;
- "Pancef" is a broad-spectrum agent that promotes the destruction of the cell walls of pathogenic microbes; the antibiotic is effective in the treatment of bacterial diseases of the upper respiratory tract: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, etc.
Important! You can not shorten the course of antibiotic treatment while improving the well-being of the child.
The duration of antibiotic therapy is determined only by a specialist; on average, one course takes 7-10 days. During this time, you cannot refuse to take the prescribed drugs, which is due to the possibility of recurrence of inflammation. Often, relapses of tonsillitis lead to complications, in particular rheumatic heart disease.
Local sulfonamides
Complex therapy of ENT disease involves the use of local antibacterial drugs. Unlike systemic antibiotics, they quickly penetrate into the lesions, which helps to destroy the pathogenic flora in the hyperemic mucous membrane of the oropharynx. In pediatrics, to stop pathological processes in the palatine tonsils and nearby tissues, use:
- "Bioparox" is a drug for inhalation, which has a pronounced antiphlogistic
 and fungistatic action; the components of the drug are quickly incorporated into the cellular structures of microbes, which leads to their death;
and fungistatic action; the components of the drug are quickly incorporated into the cellular structures of microbes, which leads to their death; - "Bactrim" is a combined action drug with anti-edematous and antimicrobial properties; prevents the generalization of inflammatory processes and blood poisoning during the development of chronic tonsillitis;
- "Biseptol" is a bacteriostatic and bactericidal drug that prevents the replication of RNA and DNA of pathogens; helps to eliminate toxic substances and relieve symptoms.
Topical drugs cannot replace systemic antibiotics.
As a rule, sulfa drugs are used only in cases where an infectious disease is complicated by purulent inflammation in the lacunae of the tonsils (lacunar tonsillitis). They help to eliminate local manifestations of pathology, but approximately 40% of known pathogens of angina are resistant to the effects of drugs in this group. It is for this reason that they are used only with the parallel use of systemic antibiotics.
Gargles
To speed up the healing process, in children, the treatment of acute tonsillitis should be accompanied by a debridement of the oropharynx. The physiotherapeutic procedure is carried out in combination with pharmacotherapy, which allows you to quickly destroy pathogens in the lacunae of lymphadenoid formations. Removal of parasitic bacteria helps to increase local immunity, thereby accelerating the epithelialization of the affected tissues.
It is undesirable to use the same drug if it has recently been used to treat ARVI and other colds.
High-performance rinsing solutions include:
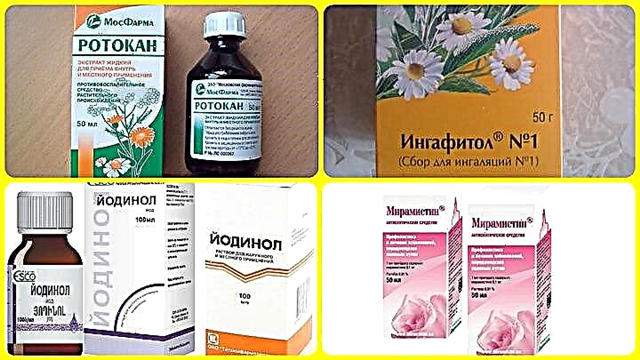
- Miramistin is an antiseptic that has a hydrophobic effect on pathogenic microbes, which leads to the destruction of cell membranes and the death of pathogens;
- "Iodinol" is a disinfectant that inhibits the development of pathogenic bacteria, thereby increasing the tissue reactivity of the affected ENT organs;
- Ingafitol is a herbal preparation with a pronounced antiphlogistic and antimicrobial effect; accelerates the regeneration of the ciliated epithelium, which prevents the penetration of pathogenic flora deep into the tissues;
- Rotokan is a solution with antiphlogistic, hemostatic and regenerative effects; quickly eliminates hyperemia and inflammation in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx;
- "Evkarom" - a drug based on chamomile and eucalyptus, which prevents the synthesis of inflammatory mediators; accelerates the regression of pathological processes in the lesions.
Home treatment can be accompanied by the use of medicinal solutions based on "Hydrogen peroxide" or "Furacilin" tablets. To prepare a rinse solution, it is enough to dissolve two tablets of the drug or 2 tbsp. l. 3% "Hydrogen peroxide" in 250 ml of water.
Topical sprays and lozenges
 Comprehensive treatment is the main requirement that must be observed during the treatment of an infectious disease. To ease the course of tonsillitis and eliminate local manifestations of inflammation, it is necessary to use symptomatic drugs. With their help, it is possible to stop painful sensations in the oropharynx, tissue edema, hyperemia, etc.
Comprehensive treatment is the main requirement that must be observed during the treatment of an infectious disease. To ease the course of tonsillitis and eliminate local manifestations of inflammation, it is necessary to use symptomatic drugs. With their help, it is possible to stop painful sensations in the oropharynx, tissue edema, hyperemia, etc.
With severe inflammation of the palatine tonsils, it is undesirable to lubricate the oropharynx with antiseptic gels and ointments. Careless carrying out of the procedure is fraught with the destruction of the protective layer on the surface of the mucous membrane.
To speed up recovery, it is more advisable to use sprays, lozenges and lozenges:
- "Lugol spray" - a local antiseptic with bactericidal and fungicidal action, which prevents the growth of pathogenic microbes and yeast-like fungi;
- "Geksoral spray" is a local anesthetic, antiphlogistic, antimicrobial and antimycotic drug; inhibits the synthesis of cyclooxygenase, which contributes to the regression of catarrhal processes in the throat;
- "Strepsils" - lollipops of combined action, the components of which inhibit the development of bacterial and fungal flora;
- "Faringosept" is a pathogenetic drug that destroys all types of coccal infections; can be used in monotherapy for acute tonsillitis.
Important! Sprays and aerosols should not be used to treat children under 3 years of age.
The main rule of local therapy is the use of drugs after meals. Some drug components negatively affect the intestinal and stomach lining, which can cause flatulence, pain and nausea. To prolong the effect of the medication, do not give your child a drink for 20-30 minutes after cleansing the throat.
Antihistamines
Angina in children is accompanied by severe allergic reactions, which are caused by an increase in the concentration of toxic substances to the blood. This is evidenced by hyperemia of the palatine arches, swelling of the tonsils and inflammation of the back of the throat.
 To eliminate allergic manifestations, it is necessary to use antihistamines. Antihistamines are drugs that competitively block specific receptors that respond to histamine. In turn, histamine is the main neurotransmitter of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. To eliminate swelling and tissue hyperemia, antihistamines are used, which either reduce the sensitivity of histamine receptors or suppress histamine synthesis.
To eliminate allergic manifestations, it is necessary to use antihistamines. Antihistamines are drugs that competitively block specific receptors that respond to histamine. In turn, histamine is the main neurotransmitter of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. To eliminate swelling and tissue hyperemia, antihistamines are used, which either reduce the sensitivity of histamine receptors or suppress histamine synthesis.
What types of antihistamines can be used in pediatric therapy?
- "Fenistil" is an anti-allergic drug that has an antiserotonin effect on the hyperemic tissues of the oropharynx; reduces capillary permeability, which helps to eliminate puffiness;
- "Zodak" is a long-acting antihistamine drug that inhibits the release of histamine from mast cells; accelerates the regression of catarrhal processes in the ciliated epithelium;
- "Peritol" is an anti-allergic agent that relieves discomfort in the throat caused by burning and soreness; used in the treatment of hyperreactive conditions in adults and children over 8 years old.
If a child's sore throat is accompanied by a sore throat that worsens when swallowing, antiallergic drugs must be used. Thanks to them, the risk of mechanical damage to the surface of the mucous membrane by food is reduced, which is fraught with even greater tissue inflammation.
Probiotics
As a rule, tonsillitis occurs due to the development of bacterial flora in the ENT organs. The presence of pathogens is evidenced by purulent inflammation, high fever, redness of the throat, etc. It is possible to completely eliminate the pathology only with the help of antibacterial drugs. However, many of them negatively affect the state of the intestinal microflora, which reduces the body's reactivity.
How to treat infantile angina at home? When undergoing a course of antibiotic therapy, it is advisable to give probiotics to children. The drugs stimulate the intestinal microflora, which promotes the synthesis of beneficial bacteria. The safest probiotics include:
 Biobacton;
Biobacton;- Linex;
- "Bifiform";
- "Acipol".
The composition of the above drugs includes lacto- and bifidobacteria, which have a beneficial effect on the endogenous microflora of the body. Their use increases nonspecific immunity, which prevents the development of infectious diseases of various etiologies.

 and fungistatic action; the components of the drug are quickly incorporated into the cellular structures of microbes, which leads to their death;
and fungistatic action; the components of the drug are quickly incorporated into the cellular structures of microbes, which leads to their death; Biobacton;
Biobacton;

