If a person has a cold ear, an otolaryngologist will be able to suggest what to do first, as well as how and how to treat otitis media to prevent complications. He correctly diagnoses the disease and develops adequate treatment depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, and also explains to the patient how to cure the ear from a cold. But anti-inflammatory drops and antibiotics in the patient's medicine cabinet will help relieve pain and relieve the condition before going to the doctor.
The main directions of treatment of catarrhal otitis media
 Therapy for acute otitis media is mainly aimed at relieving the inflammatory process and relieving pain. In the case of a cold of the ears, treatment should be started as early as possible, then the measures taken give the best effect and do not allow the inflammation to go into a much more dangerous and unpleasant purulent stage. This will affect the eustachian tubes and eardrum. How to treat a cold ear, we will consider further.
Therapy for acute otitis media is mainly aimed at relieving the inflammatory process and relieving pain. In the case of a cold of the ears, treatment should be started as early as possible, then the measures taken give the best effect and do not allow the inflammation to go into a much more dangerous and unpleasant purulent stage. This will affect the eustachian tubes and eardrum. How to treat a cold ear, we will consider further.
Pain relief of the hearing organs with catarrhal otitis media is performed most often with the help of topical preparations:
- Ear drops Normax, Sofradex, Otinum, Otipax contain anti-inflammatory components or antibiotics in their composition, which allows you to quickly relieve pain. You need to drip them several times a day according to a doctor's prescription, before using them, warming them up in your hand to a temperature of 35-37 degrees. After the ear canal is closed with cotton or gauze turunda.
- In the absence of special drops, you can use novocaine, 70% alcohol or carbolic glycerin, heated vodka or liquid paraffin.
- Pain-relieving ointments and compresses, such as a compress of 1% or 2% salicylic alcohol. The cotton wool impregnated with it is inserted into the ear canal.
- Nasal drops, which have a vasoconstrictor effect (Naphthyzin, Galazolin, Sanorin), help reduce swelling and improve the outflow of fluid from the affected organ. Apply 5 drops 3 times a day.
In addition, with the help of medicines and physiotherapy, the fight against inflammation is carried out:
- Normalization of body temperature with antipyretic drugs. The most common of these are paracetamol, aspirin, ibuprofen, and analgin. They should be taken if the temperature has risen above 38.5 degrees, as well as at night.
- In the absence of purulent discharge, local heating is applied. For this, an ultraviolet lamp, UHF, vodka compresses, and a heating pad are used.
- The suppression of the activity of pathogenic microflora is carried out using bactericidal drops (Kallorgol, Protargol).

- In complex or advanced cases, in addition to drops, specialized antibiotics in tablets (Flemoxin Solutab, Flemoklav, Tsifran) or sulfonamides are used.
If it is a catarrhal ear cold, treatment at home after consultation with a doctor is the best option in most cases.
Features of therapy for purulent otitis media
How to treat a purulent ear cold can only be determined by an ENT doctor. A purulent form of otitis media requires mandatory antibiotic therapy; in severe cases, hospitalization and round-the-clock supervision of a medical worker may be required. In particular, this applies to the pre-perforative stage, when the pain is especially strong, and the purulent contents are in the tympanic cavity.
After the eardrum breaks through, exudate flows out, which, in combination with the action of antibiotics, quickly improves the patient's condition. Small holes in the eardrum soon overgrow without a trace, and in place of large ones, scars can form, which negatively affect the functioning of the entire auditory system. At the same time, it is categorically not recommended to use any folk remedies. The secreted pus and mucus are odorless. They should be wiped off with a cotton swab soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Disinfectants and astringents are also used.
With a prolonged (over several months) presence of fluid in the tympanic cavity, as well as with relapses of the disease, the doctor may decide to perform a myringtomy operation.
It is used for both adults and children. In this case, the tympanic membrane is dissected under general anesthesia, the pus is removed and a special tube made of plastic or metal is inserted, which facilitates the withdrawal of fluid to the outside. The tube is worn from several months to one and a half years, after which it falls out on its own.
Sometimes the question arises of what to do if the ear has a cold (chill), and the treatment does not help. Then you need to see a doctor, since sometimes inflammation can be caused by fungal diseases. At the same time, the fungus does not externally manifest itself in any way, but it develops very quickly and clogs the passage, as a result of which local drugs do not get inside. In this case, after examination, the otolaryngologist flushes the ear canal with a special solution and prescribes the necessary drugs.
With a neglect of the disease or improper therapy (self-medication), serious complications are possible:
- the appearance of scars on the eardrum;
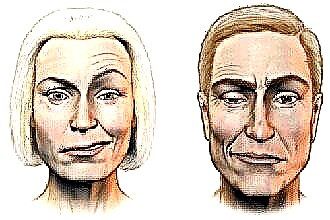 the transition of inflammation to the cochlea of the inner ear and the potential development of labyrinthitis and adhesive otitis media;
the transition of inflammation to the cochlea of the inner ear and the potential development of labyrinthitis and adhesive otitis media;- mastoiditis;
- meningitis;
- significant impairment or complete loss of hearing;
- paralysis of the facial nerve;
- in children, speech development delay.
Using traditional medicine recipes
If a person has a cold ear, traditional medicine can tell how to treat it at home. A large number of plants can alleviate the condition of the patient with acute otitis media. Below are some time-tested recipes:
- Tincture of calendula. A cotton swab is moistened in it and inserted into the ear canal, covered with dry cotton on top. Keep as long as possible, lying on your side.
- Geranium leaf. The edge of the sheet is cut off, which is then rolled up into a tube and the cut end is introduced into the course, laid with a cotton swab and fixed with a scarf or bandage.
- Garlic oil. In 100 g of highly heated vegetable oil, 2 cloves of crushed garlic are added, infused for an hour, then filtered. 2-4 drops of oil are applied to the bandage and placed in the ear canal for 10 minutes.
- Propolis tincture. 10 g of beekeeping product is cooled in the form of a bar in the freezer, then grated and poured into an opaque container. The powder is poured with wine alcohol (70%), closed tightly and infused in a dark place for about a week, cooled in the refrigerator and filtered. In a pipette, equal shares of water and tincture are mixed, all this is dripped onto a cotton swab and inserted into the diseased organ for 10 minutes or until the burning sensation begins.
- Linseed oil with onions. Onion juice and linseed oil are mixed in a 1: 1 ratio, a gauze swab is moistened in the mixture and placed for 3 hours, then the procedure is repeated with fresh oil.
- Horseradish juice. Freshly squeezed juice is dripped into the organ of hearing three times a day, 2 drops. It helps well at the initial stage of the disease.
All folk recipes should be used only after consulting a doctor and making an accurate diagnosis.
Prevention methods
You can reduce the risk of getting middle acute otitis media by observing some rules regarding yourself or your child:
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract and influenza should be avoided, it is optimal to be regularly vaccinated against influenza with drugs that are relevant in this season;
- vaccinate a child against pneumococcal infection;
- go to the clinic in time for symptoms of an allergy and take appropriate measures to eliminate it or ease the course;
- monitor the baby's breathing (nasal or oral) to prevent overgrowth of the adenoids;
- feed the baby, holding him at an angle of 45 degrees, in order to avoid flowing milk or formula into the Eustachian tubes;
- to exclude as much as possible contact with tobacco smoke, which provokes and complicates the course of inflammatory processes.


 the transition of inflammation to the cochlea of the inner ear and the potential development of labyrinthitis and adhesive otitis media;
the transition of inflammation to the cochlea of the inner ear and the potential development of labyrinthitis and adhesive otitis media;