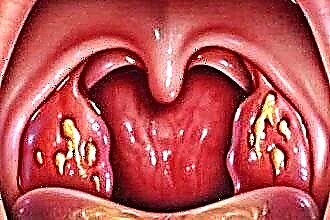
Most often, fluid in the ear behind the eardrum accumulates during inflammation in the middle ear. In addition to the unpleasant sensation and squelching sounds in the ears, the liquid, as it collects, presses on the eardrum and causes severe pain. In severe cases, the eardrum may rupture and fluid may leak out. The consequences of such inflammatory processes, which were not paid due attention to in time, can be quite serious.
Inflammation of the middle ear in a child
 Most often, for no apparent reason, middle ear inflammation occurs in children, especially small ones. According to statistics, every baby under the age of 1 year suffers this disease. Unfortunately, in young children, it is difficult to diagnose it at an early stage, since the child cannot yet convey his feelings in words. Therefore, mothers usually notice the disease only after a persistent increase in temperature and constant long-term crying of the child.
Most often, for no apparent reason, middle ear inflammation occurs in children, especially small ones. According to statistics, every baby under the age of 1 year suffers this disease. Unfortunately, in young children, it is difficult to diagnose it at an early stage, since the child cannot yet convey his feelings in words. Therefore, mothers usually notice the disease only after a persistent increase in temperature and constant long-term crying of the child.
By this time, the liquid behind the eardrum in the child has time to accumulate in such an amount that constant strong pressure is created on it, due to which the child experiences severe pain. When the body temperature rises above 38 degrees, children's antibiotics are usually prescribed. But in most cases, childhood middle ear infections go away without them. Therefore, the most common treatment is to relieve pain symptoms.
It is very important to constantly closely monitor the condition of the child until he is completely cured and regularly show him to the doctor in order to prevent the occurrence of serious complications.
Children with otitis media are rarely admitted to the hospital, as treatment consists mainly of maintaining dry heat (cotton wool) and, if necessary, pain relief.
During this period, it is necessary to somewhat limit the child's mobility and make sure that there are no drafts in the room. But this does not mean that the room in which the baby is located should not be ventilated. If possible, it is advisable to quartz the room to reduce the risk of ear infection. It is the ingress of infections that leads to the fact that otitis media passes into a purulent stage. The illness usually goes away within 2-3 weeks.
Causes and symptoms of the disease in adults
 There are many more reasons for the appearance of otitis media in adults, although in general they are less likely to suffer from this disease than children. Some of the most common reasons include:
There are many more reasons for the appearance of otitis media in adults, although in general they are less likely to suffer from this disease than children. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Severe hypothermia due to lack of headgear in the cold season.
- Constant presence in a draft.
- Complication after upper respiratory tract infections.
- Complication after ear barotrauma.
- Blockade of the ear canal with a sulfur plug.
The main symptom that there is fluid in the ear behind the eardrum is an unpleasant squelching sound that occurs when the ear tragus is pressed. Pain occurs as fluid builds up.
With infection and the development of purulent otitis media, the pain increases and the body temperature rises. In severe cases, it can reach 400C and hold on very steadfastly. Such patients are immediately admitted to the hospital. When purulent fluid has accumulated behind the eardrum, home treatment can have very serious consequences.
How to treat otitis media in adults
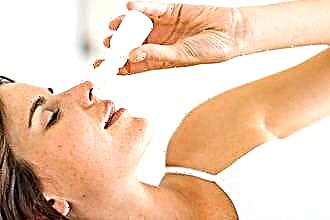
When an adult has accumulated fluid in the ear behind the eardrum, treatment depends on the presence of an infection, which only a doctor can reliably determine. If there is no infection, then the fluid gradually dissolves on its own and the use of antibiotics is impractical. In this case, there should be dry heat on the ear at all times (a woolen band or cotton wrap). For pain, it is necessary to use anti-inflammatory drops with analgesic components.

Purulent otitis media is treated only with antibiotics, which should be prescribed by a doctor. Its danger is that the infection through the Eustachian tube can penetrate further and cause serious complications.
If severe pain persists within a few days, you may need to undergo minor surgery, during which the eardrum is opened with sterile surgical instruments and a small tube is inserted into it to drain fluid.
Eardrum rupture can occur spontaneously under natural fluid pressure. Usually, immediately after this, the pain subsides and the patient begins to recover. This can be seen by spotting from the ear and temporary hearing loss. In this case, it is extremely important to carefully monitor so that an infection does not enter the wound, which leads to additional complications.
It is impossible to insert cotton wool and gauze turundochka into the ear on your own - the liquid should flow out. But it is simply necessary to cover the auditory opening with a sterile bandage.
Possible complications
 With timely detection and treatment of otitis media, severe complications are extremely rare. They are mainly caused by the entry and further spread of pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci and others. The consequences of untreated purulent otitis media can be:
With timely detection and treatment of otitis media, severe complications are extremely rare. They are mainly caused by the entry and further spread of pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci and others. The consequences of untreated purulent otitis media can be:
- meningitis - inflammation of the outer lining of the brain;
- labyrinthitis - acute inflammation of the inner ear;
- mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid process of the ear.
If the tympanic membrane is hardened or completely ruptured, partial or complete hearing loss is possible. In this case, surgery may be required to restore it. With a small perforation, the tympanic membrane usually heals on its own within 2-3 weeks and does not require additional treatment.
Prevention
Everyone knows that ears should be protected from childhood. But many adults ignore the elementary rules that can serve as an excellent prevention of middle ear inflammation with the subsequent accumulation of fluid behind the eardrum:
- do not go without a hat during the cold season;
- do not stay in a draft or under an air conditioner for a long time;
 in a very strong wind, in the absence of a headdress, cover your ears with your hands or a scarf;
in a very strong wind, in the absence of a headdress, cover your ears with your hands or a scarf;- regularly free the ear canal from the sulfur accumulated there;
- clean your ears very carefully and only with clean cotton swabs;
- if water gets into your ears, especially after swimming in open water, be sure to remove it with cotton swabs or tampons.
These simple rules apply equally to both adults and children. They will allow you to avoid a very unpleasant disease or minimize the risk of its occurrence. But if squelching sounds were found in the ear, which, in the absence of pain, do not disappear within 3-4 days, it is necessary to consult a specialist. He will be able to diagnose the degree of development of the disease in time and adjust the treatment so that complications do not arise.

 in a very strong wind, in the absence of a headdress, cover your ears with your hands or a scarf;
in a very strong wind, in the absence of a headdress, cover your ears with your hands or a scarf;