Many parents are concerned about the question of whether it is necessary to remove adenoids when clear signs of pathology appear. This topic causes a lot of controversy. To understand it, you should understand where the adenoids come from and how dangerous they are. The tonsils are located in the nasopharynx, forming a lymphoid ring. Like other formations of the lymphatic system, the tonsils are immune structures and must protect the body from microbes. On the way of penetration, pathogens encounter tonsils, which ensure their neutralization.
 Normally, lymphoid tissue is able to grow in size to increase protection against infection. However, after the destruction of the pathogens, its size is restored, and the symptoms of nasal congestion and runny nose disappear. In the case of frequent attacks of infectious microbes, the lymphoid tissue does not have time to return to its previous size, since it is necessary to constantly keep the defense.
Normally, lymphoid tissue is able to grow in size to increase protection against infection. However, after the destruction of the pathogens, its size is restored, and the symptoms of nasal congestion and runny nose disappear. In the case of frequent attacks of infectious microbes, the lymphoid tissue does not have time to return to its previous size, since it is necessary to constantly keep the defense.
As a result, the hypertrophied lymphoid tissue of the pharyngeal tonsil, called adenoids, leads to the appearance of symptoms typical of the disease:
- nasal congestion:
- breathing through the mouth;
- snoring during sleep;
- nasal voice.
Note that adenoids are terrible not for their symptoms, but for complications, therefore, with a complicated course of pathology, the question arises whether it is worth removing the adenoids for the child. Otolaryngologists recommend postponing surgery in children under three years of age. This is due to the formation of immunity and accelerated regeneration processes, which often leads to the re-proliferation of lymphoid tissue. On the other hand, the tonsils are part of the immune system, therefore, by removing them, a small child loses additional protection against infection.
At what age are adenoids removed?
The tonsils can grow up to 8 years old, after which the lymphoid tissue undergoes sclerotic changes and gradually decreases in volume.
The problem in adults with adenoids does not arise because of their absence. Their operation can be performed due to malignant degeneration of tissue.
Indications for surgery
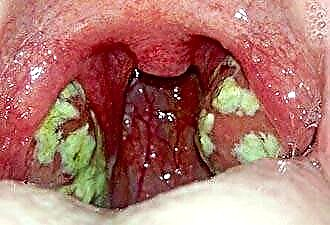
When the adenoids in children are removed or not, the otolaryngologist decides on the basis of the diagnostic results. To establish the indications, rhinoscopy, pharyngoscopy and X-ray examination are required. This makes it possible to determine the degree of proliferation of lymphoid tissue and assess the condition of the tonsils:
 the presence of mucus and purulent discharge on the surface of the tonsil;
the presence of mucus and purulent discharge on the surface of the tonsil;- the shade of the mucous membrane of lymphoid growths;
- smooth and shiny mucous membrane indicates tissue edema and the presence of an inflammatory process. In this case, drug treatment is prescribed to reduce the severity of inflammation, after which the diagnosis is repeated and the question of the operation is resolved.
The third degree of adenoids is not always an indication for surgery, but the presence of serious complications in the second degree requires surgical intervention.
Indications for the removal of adenoids in children are complications such as:
- hearing loss. Deterioration of auditory function occurs due to a decrease in the lumen of the auditory tube due to lymphoid growths. Air is not able to pass in full, thereby inhibiting the vibrations of the eardrum. As a result of this, parents may notice that the child often asks again or does not react to the appeal to him the first time. Hearing impairment is fraught with both a decrease in school performance and a threat to life on the road from passing cars;
- adenoid face, when, due to the prolonged absence of nasal breathing, the shape of the facial skeleton changes. At the same time, the upper jaw is lengthened, the nasal voice is noted, the bite is disturbed, and the child cannot pronounce some letters. The expression on the face is bleak and tired;
- spread of infection to surrounding healthy tissues with the development of pharyngitis, sinusitis or tracheitis. Disruption of air permeability through the nasopharynx, stagnation of mucus and swelling of the mucous membrane lead to the preservation of pathogenic microbes in the folds of the mucous membrane and lacunae, which supports chronic inflammation. The examination can reveal hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils, hyperplasia or atrophy of the mucous membrane of the pharyngeal wall and purulent deposits. With an exacerbation of the disease, a violent clinic develops with a cough, runny nose, sore throat and high fever;
- apnea. Children with adenoids may temporarily stop breathing while sleeping, causing their parents' heart to beat faster. Frequent periods of apnea not only impair brain function, but are also life-threatening;
- chronic otitis media. Lymphoid growths lead to a deterioration in the patency of the auditory tube, impaired ventilation function and activation of opportunistic flora in the middle ear cavity. The multiplication of microbes contributes to the release of inflammatory fluid and the development of otitis media. The disease acquires a chronic course due to the constant presence of pathogens and favorable conditions for their life. In addition, we note that otitis media develops much faster in children due to nasal congestion than in adults. In childhood, the diameter of the Eustachian tube is smaller, so even a slight swelling of the mucous membrane leads to hearing impairment;
- frequent adenoiditis (4-6 times a year). Their development is due to the constant presence of infection in the pharyngeal tonsil, which, at the slightest decrease in immunity, is activated and begins to multiply, provoking an exacerbation of inflammation. It is not difficult to suspect adenoiditis, because it is manifested by febrile fever, nasal congestion and pain when swallowing;
 fast fatigue, inattention and forgetfulness. Changes in the functioning of the nervous system, including the brain, occurs due to insufficient oxygen supply to the body, due to which the organs suffer from hypoxia. The child complains of dizziness, constantly yawns, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, and also refuses to attend sports sections;
fast fatigue, inattention and forgetfulness. Changes in the functioning of the nervous system, including the brain, occurs due to insufficient oxygen supply to the body, due to which the organs suffer from hypoxia. The child complains of dizziness, constantly yawns, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, and also refuses to attend sports sections;- frequent allergies. The increased sensitivity of the immune system to various allergens develops due to chronic infection, which increases the sensitization of the body and reduces the protective properties of the immune system.
If parents do not agree with the opinion of the otolaryngologist about the need for surgery, they can consult with another specialist or even two.
Preparatory stage for surgery
For an ENT doctor, adenotomy is a routine, simple operation. It lasts no longer than 15 minutes and can be performed even on an outpatient basis. Already 4-5 hours after surgery, parents can take the little patient home, of course, provided that there are no complications.
The adenoids are removed under local or general anesthesia. Before the operation, an anesthesiologist is consulted, who, based on the results of diagnostics, taking into account the age and mental characteristics of the child, chooses the type of anesthesia. The doctor talks about all possible complications and the postoperative period when the patient wakes up.
It is better to perform adenotomy at the beginning of autumn, when the child's body is full of vitamins, and the immune system is in good condition.
In winter, there is a high risk of developing ARVI, against the background of which surgical interventions are not allowed.
In children with adenoids, recovery after ARVI takes about a month, so it is rather difficult to choose the date of the operation.As for the summer time, in hot weather, the risk of infection and purulent complications in the postoperative period is increased, since these are the best conditions for bacteria to reproduce. On the other hand, high fever increases bleeding, so there is a risk of bleeding.
Thanks to the preoperative examination, contraindications are revealed that impede the conduct of adenotomy. These include:
 exacerbation of chronic infectious and inflammatory pathology (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis);
exacerbation of chronic infectious and inflammatory pathology (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis);- acute stage of an infectious disease (ARVI, influenza);
- the first month after vaccination, as immunological reactions occur in the body, temporarily reducing the level of immune defense;
- severe bronchial asthma and allergic reactions;
- blood pathology, when its coagulability decreases, predisposing to increased bleeding.
Parents should know the possible complications of the operation, so as not to panic without reason, but if necessary, consult a doctor in time:
- a temporary decrease in immunity associated with stress and surgery;
- nasal congestion, snoring for two weeks;
- nasal mucus streaked with blood and bloody crusts.
To reduce the risk of infection, you should make sure that your child is excused from school and sports activities in advance. He is shown to limit physical activity and stressful situations.
Operation or medication
The indications for the removal of the adenoids are given by the doctor, however, the operation cannot be performed without the consent of the parents. Of course, in the presence of severe complications, adenotomy is performed without hesitation, but in controversial situations, it should be remembered that:
- removal of adenoids leads to a partial weakening of the body's defenses, because the amygdala is part of the immune system. As a result, the child becomes more susceptible to infection and the risk of developing hay fever, allergic rhinitis and tracheitis increases;
- after adenotomy, the child will not become less sick, because the frequency of ARVI depends on the level of immunity and general health;
- surgical intervention does not guarantee the absence of the risk of re-proliferation of lymphoid tissue. The likelihood of relapse is highest in young children. Do not forget that the quality of the operation also depends on the experience of the surgeon and the method of removing the tonsil. Anglų kalbos dienos dienos stovykla vaikams Vilniuje Kaune Klaipėdoje INTELLECTUS anglų kalbos mokykla If the hyperplastic tissue is not completely removed, its remnants can cause a relapse;
- nasal congestion may not be a manifestation of adenoids, but a deviated septum, chronic sinusitis, or allergic rhinitis. The consequence of this is the lack of effect from the operation, since nasal breathing will not be restored.
Having removed the adenoids from the child, conservative treatment should not be stopped. Regular treatment courses can prevent repeated tissue hyperplasia and completely eliminate the focus of infection. In treatment, you can use:
 means for washing the nasal cavities, which can be purchased at the pharmacy (Aqua Maris, Humer) or prepared independently (sea salt solution - 3 g per 220 ml of warm water). Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, sage or eucalyptus leaves are also used;
means for washing the nasal cavities, which can be purchased at the pharmacy (Aqua Maris, Humer) or prepared independently (sea salt solution - 3 g per 220 ml of warm water). Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, sage or eucalyptus leaves are also used;- medicines for nasal instillation (Vibrocil, Collargol, Kalanchoe juice);
- solutions for rinsing the oropharynx (Miramistin, Givalex, Furacilin);
- antihistamines (Loratadin, Suprastin) to reduce mucosal edema and normalize nasal breathing;
- immunomodulators (IRS-19, Immudon), enhancing local protection.
Parents should remember that success in the treatment of adenoids directly depends on the state of the immune system. In this regard, do not forget about hardening the child, vitamin therapy, proper nutrition, exercise, breathing exercises and timely treatment of chronic infectious pathology. It is especially useful for children to stay in an area with a sea, mountain or forest climate.

 the presence of mucus and purulent discharge on the surface of the tonsil;
the presence of mucus and purulent discharge on the surface of the tonsil; fast fatigue, inattention and forgetfulness. Changes in the functioning of the nervous system, including the brain, occurs due to insufficient oxygen supply to the body, due to which the organs suffer from hypoxia. The child complains of dizziness, constantly yawns, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, and also refuses to attend sports sections;
fast fatigue, inattention and forgetfulness. Changes in the functioning of the nervous system, including the brain, occurs due to insufficient oxygen supply to the body, due to which the organs suffer from hypoxia. The child complains of dizziness, constantly yawns, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, and also refuses to attend sports sections; exacerbation of chronic infectious and inflammatory pathology (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis);
exacerbation of chronic infectious and inflammatory pathology (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis); means for washing the nasal cavities, which can be purchased at the pharmacy (Aqua Maris, Humer) or prepared independently (sea salt solution - 3 g per 220 ml of warm water). Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, sage or eucalyptus leaves are also used;
means for washing the nasal cavities, which can be purchased at the pharmacy (Aqua Maris, Humer) or prepared independently (sea salt solution - 3 g per 220 ml of warm water). Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, sage or eucalyptus leaves are also used;