Symptoms and varieties
 According to ICD 10, a hemangioma of any localization has a code D18.0.
According to ICD 10, a hemangioma of any localization has a code D18.0.
The tumor consists of vascular tissue. It is localized on the outer surface of the nose and inside it. It is a tangle of vascular-type cavities filled with blood. At an early age, the neoplasm progresses rapidly and grows not only in width, but also deep into the tissues.
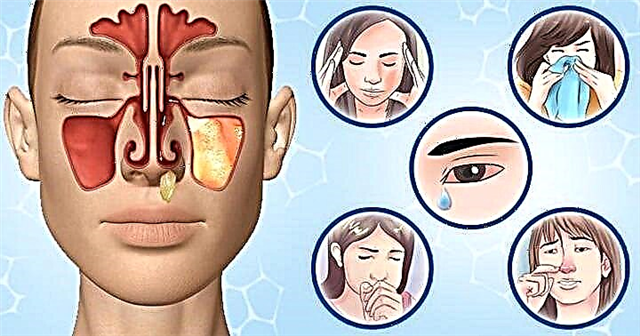
If a tumor forms inside the nasal passages, then the pathology manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- violation of nasal breathing;
- congestion;
- sensation of a foreign body in the nasal passage;
- frequent bleeding.
Outside neoplasms are visible to the naked eye. Their external characteristics depend on which type of hemangioma prevails. There are such forms of tumor:
- Simple or capillary. They are red or blue-purple in color, their borders are clearly delineated. The tumor grows evenly, increases in size only in width. It is located superficially and captures only a few millimeters of subcutaneous fat. Localization sites - side walls, the tip of the nose, paranasal sinuses and organ septa. The surface of simple hemangiomas is smooth, slightly protruding above the level of the skin. The diameter of such a neoplasm is no more than 2-3 cm.
- Cavernous. Hemangiomas of this type are located under the skin, have a soft elastic structure. Such tumors are localized in cartilaginous and bone tissues. The neoplasm affects large vessels. It consists of cavities or cavities filled with blood. The color of the tumor as it develops changes from bluish to blue-purple.
- Mixed. This type of benign neoplasm combines the signs of both cavernous and capillary hemangiomas. That is, both large and small vessels are intertwined in the hemangioma. Mixed tumors are considered the most dangerous, since they grow rapidly and are capable of affecting nearby organs.
Depending on the prevalence of hemangiomas on the nose, they are single or multiple. Pathology is also congenital, if it is detected after birth in a child, or acquired, if it occurs in adulthood.
It is necessary to distinguish hemangioma from angioma and lymphangioma. Angioma, despite the fact that it is in many respects similar to the first indicated type of tumor, is represented by such tumor-like neoplasms as polyps or cysts. Angioma grows slowly.
Lymphangioma is a rare congenital tumor, the development of which occurs even during intrauterine development.
Causes
 The exact reasons that could cause the appearance of vascular tumors in newborns have not been established. It is assumed that this phenomenon is associated with factors such as:
The exact reasons that could cause the appearance of vascular tumors in newborns have not been established. It is assumed that this phenomenon is associated with factors such as:
- taking certain medications by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- smoking;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- serious viral or infectious diseases suffered by a woman during gestation;
- hormonal disorders;
- living of a pregnant woman in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- late pregnancy (the age of the woman in labor is 38 years and older).
The risk group includes newborns who were born prematurely. An underweight baby and multiple pregnancies also put the baby at risk for nasal vascular tumors.
In an adult, hemangioma develops under the influence of the following reasons:
- pathologies of internal organs that cause dysfunctions of the vascular system;
- damage to the structures of the nose, trauma to the nasal passages;
- taking drugs;
- allergic reactions;
- harmful working conditions (work in the field of woodworking, metallurgy, flour-grinding industry);
- polyps in the nose;
- chronic sinusitis and rhinitis;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays.
The risk of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one is low. In children, such neoplasms can disappear on their own. Despite this, hemangioma requires examination and therapeutic measures.
Diagnostics
 The disease can be identified using the following diagnostic measures:
The disease can be identified using the following diagnostic measures:
- radiography;
- angiographic examination;
- endoscopy;
- CT scan.
After assessing the features of the location and structure of the neoplasms, the specialist determines the optimal course of treatment.
Treatment methods
Treatment of vascular nasal hemangioma depends on the location of the tumor, as well as the age of the patient.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment is acceptable for capillary hemangiomas, which are small. Most often, with this type of neoplasm, propranolol is prescribed, a drug that causes spasm of the arteries. The tool has the greatest effect on areas where the proliferation of vascular tissue is observed. Hemangioma, left without power sources, gradually dies off.
For external tumors, topical hormonal agents are prescribed. Usually, for this type of disease, Timolol drops are recommended, which should be applied to the affected area.
Surgical methods
Radical methods of removing a neoplasm can be both extensive and less invasive.
A surgical method of removing a hemangioma with a scalpel is carried out if the neoplasm grows rapidly and, due to its large size, exerts pressure on the nearby nerves and vessels.
Surgical intervention is contraindicated if the patient is in old age, as well as in the presence of such serious diseases as renal failure, cirrhosis of the liver, diabetes mellitus.
 Less invasive treatments include:
Less invasive treatments include:
- laser removal. Under the influence of rays, the tumor is resorbed. Such an operation can be prescribed for an infant. To completely remove the neoplasm, 2-3 procedures will be required;
- the introduction of sclerosing substances. With this method, small neoplasms can be eliminated. Sclerosants are injected into the tumor;
- moxibustion with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation;
- radiosurgical method.
Folk remedies
There are folk remedies that are aimed at eliminating hemangiomas.
The most popular methods are:
- compress based on kombucha. The composition should be applied to the affected areas daily. Leave to act for 30-60 minutes;
- solution with copper sulfate. A tablespoon of the substance must be dissolved in half a glass of water, mixed. Use the resulting product to wipe external hemangiomas;
- antitumor collection for oral administration. It is necessary to prepare a mixture of yarrow, burdock leaf, plantain, sweet clover and St. John's wort, which must be taken in an amount of 50 g of each item. You should also add 30 g of highlander bird, coltsfoot, cinquefoil, calendula flowers, as well as 10 g of dried cress, white willow bark, geranium and hazel leaves. Take a tablespoon of the resulting collection, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, put in a water bath and stand for 5 minutes. Insist collection for an hour, then strain.Take 120 ml of the product 4 times a day, warming it up before taking.
It must be borne in mind that traditional medicine does not replace the main methods of treatment..
Complications
The most common complications of nasal hemangiomas are bleeding and ulceration on their surface.
In the most severe cases, when the tumor grows deep into the tissues, the hemangioma located on the face can cause compression of the trachea. Under such conditions, the patient has a severe cough, hoarseness.
Since hemangioma is a vascular tumor, it can cause blood clots.
In some cases, a vascular tumor contributes to the development of inflammatory processes that cause further growth of the neoplasm.
Hemangioma can occur at any age, but infants and the elderly are more likely to suffer from it. Pathology rarely causes serious complications, but requires mandatory treatment.