Inflammation of the sinuses today are in one of the first places among other respiratory diseases. This is due primarily to the constantly deteriorating ecology and its direct consequence - reduced immune protection in the majority of the population. All sinusitis, if untreated, easily becomes chronic and can cause serious complications. But acute frontal sinusitis due to the anatomical location of the inflamed sinuses is one of the most dangerous diseases and requires immediate treatment.
A bit of anatomy
The group of sinusitis includes all types of inflammation of the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses, of which a person usually has 4 types:
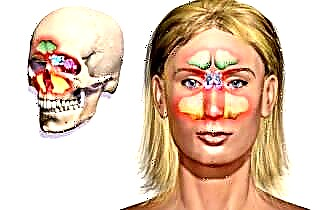 frontal - paired sinuses located above the brow ridges practically in the middle of the forehead;
frontal - paired sinuses located above the brow ridges practically in the middle of the forehead;- lattice labyrinth - also a paired cellular formation to the right and left of the upper part of the bridge of the nose, in the interorbital zone;
- the maxillary sinuses are the largest paired cavities located on both sides of the wings of the nose, and the lower wall separates them from the bones of the upper jaw;
- The sphenoid sinus is a small space within the sphenoid bone, which is located at the base of the skull.
Some people have congenital sinus underdevelopment, either genetically determined or caused by intrauterine damage to the fetus. The small size of the sinuses increases the risk of developing sinusitis, as they interfere with normal air circulation. But about every tenth of the frontal sinuses are absent at all and then it is impossible to get sick with frontal sinusitis. This feature is easy to see on an X-ray image of the skull.
The structure of the frontal sinuses is quite simple. They are pyramidal cavities with tops located on the sides of the upper edge of the bridge of the nose. The cavity is lined with epithelial cells from the inside, which constantly produce mucus. The frontal sinus communicates with the nasal cavity through a narrow passage through which excess mucus is removed to the outside.
The posterior wall of the frontal sinus separates it from the cranial cavity, and the lower one from the orbit. With the development of active inflammatory processes, they can quite easily move to neighboring organs. Therefore, it is very important to recognize acute frontal sinusitis in time and begin its correct treatment. Otherwise, very serious complications may appear.
Causes of frontal sinusitis
The development of most sinusitis, including frontal sinusitis, is most often provoked by pathogens: viruses, bacteria, fungi. Once on the nasal mucous membranes, they spread further and penetrate into the sinuses, causing increased mucus production and swelling. Because of the swelling, the narrow passages connecting the sinuses to the nasal cavity are blocked and excellent conditions are created for the development of anaerobic bacteria. Pus forms and accumulates in the sinuses. The liquid presses on the nerve endings of the already irritated mucous membranes and causes pain.
 With sinusitis of an allergic nature, not complicated by infection, it is not pus that accumulates in the sinuses, but a transparent secret that has no outlet, since the ducts are blocked by edematous mucous membranes. This form is easier to treat, since it is enough just to relieve swelling and reduce secretion. But it quickly turns into a chronic one, since in allergy sufferers, the nasal mucosa is almost constantly inflamed.
With sinusitis of an allergic nature, not complicated by infection, it is not pus that accumulates in the sinuses, but a transparent secret that has no outlet, since the ducts are blocked by edematous mucous membranes. This form is easier to treat, since it is enough just to relieve swelling and reduce secretion. But it quickly turns into a chronic one, since in allergy sufferers, the nasal mucosa is almost constantly inflamed.
Additional factors contributing to the development of the disease and complicating its course are:
- reduced immunity for any reason: vitamin deficiency, previous operations, etc.;
- chronic respiratory diseases, including inflammation of the adjacent sinuses;
- the formation and growth of polyps in the nasal cavity and adjacent paranasal sinuses;
- bruises and / or fractures of the bones of the nose and skull;
- congenital or acquired after injuries and operations curvature of the nasal septum;
- polluted air, exposure to physical or chemical irritants;
- ingress of a small foreign body into the nasal cavity.
As a result of the negative impact of external or internal factors, the edema of the mucous membranes increases, and the disease begins to develop actively.
But if, with the non-infectious nature of the disease, the elimination of provocative factors is usually sufficient to quickly improve the condition, then in the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, they will have to be fought with medication.
Typical symptoms
Fortunately, in an acute form, frontal sinusitis gives quite characteristic symptoms, according to which the disease is easy to recognize already at the initial stage. And the main one is a painful sensation in the middle of the forehead, which intensifies when pressing on the forehead, tilting the head forward and is especially pronounced in the morning.
 If one or more of the following symptoms join the pain, then frontal sinusitis can be diagnosed with almost 100% probability:
If one or more of the following symptoms join the pain, then frontal sinusitis can be diagnosed with almost 100% probability:
- a feeling of fullness in the middle of the forehead;
- redness and inflammation of the inner corner of the eye;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva, lacrimation;
- gritty or gritty eyes, photophobia;
- persistent nasal congestion;
- difficulty breathing through one nostril is expressed;
- swelling of the upper part of the face on one side;
- overhanging and / or swelling of the upper eyelid;
- pronounced change in skin color in the area of inflammation;
- increased body temperature;
- profuse nasal discharge, often purulent;
- signs of general intoxication: weakness, dizziness, etc.
With unilateral frontitis, the signs are clearly manifested on one side. With two-sided - on both. But the bilateral form does not arise suddenly - it usually develops as a consequence of bilateral ethmoiditis (inflammation of the ethmoid labyrinth) or passes from one frontal sinus to another with improper treatment or its absence.
Usually acute frontal sinusitis immediately gives a high body temperature, sometimes the thermometer crosses the mark at 39OC. This is not bad: firstly, it is easier to recognize the disease in time, and secondly, high body temperature creates extremely unfavorable conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which means it performs protective functions.
Too high a temperature greatly weakens the patient and it is necessary to lower it a little with the help of antipyretic drugs. But often it keeps within the limits of 37.5-38OC, and in this case, you do not need to knock it down.
Diagnostics
Only an otolaryngologist can diagnose frontal sinusitis after an examination. Based on the patient's complaints and the initial examination, one can only make a preliminary diagnosis, which in the case of acute frontal sinusitis is almost always confirmed. The examination also reveals the nature of the disease and the degree of damage to the frontal and adjacent sinuses. All this helps to individually select the most effective course of treatment.
 To diagnose frontal sinusitis, the following is used:
To diagnose frontal sinusitis, the following is used:
- general blood test - to accurately establish the presence and activity of the course of inflammatory processes in the body;
- rhinoscopy - a visual examination of the nasal cavity using the introduction of a special instrument: allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membranes of the nose and nasal septum;
- endoscopy - internal examination of the nasal sinus by introducing an endoscope with a miniature camera into it, allows you to examine the mucous membranes in detail and detect polyps and other neoplasms;
- Ultrasound - ultrasound examination, which helps to see the localization of lesions, the area of spread of inflammation, neoplasms;
- thermography - examination using a thermal imager, which displays the temperature map of the nasal sinuses on the monitor, the inflamed areas have a higher temperature;
- X-rays - usually images of all paranasal sinuses are taken so that you can see which of them are affected by the disease, it also allows you to detect neoplasms and the degree of filling of the sinus with pus.
Computed tomography is the most informative method that helps to examine the affected areas in detail.
If you suspect the infectious nature of the disease or the presence of purulent mucous secretions, a bacterial sowing of mucus must be performed, which detects microorganisms, determines their type and checks for sensitivity to various groups of drugs.
If the cause of the development of frontal sinusitis is overgrown polyps, it is highly desirable to conduct a biopsy and examine samples of the modified tissues in order to exclude them from being malignant tumors. It is possible to take tissue for analysis during an endoscopy, if the doctor has the appropriate equipment.
Treatment regimen
At the initial stage, acute frontal sinusitis can be treated even with folk methods. But this requires constant monitoring of the patient's condition.  If it continues to deteriorate, despite the measures taken, it is necessary to connect drug therapy to avoid complications.
If it continues to deteriorate, despite the measures taken, it is necessary to connect drug therapy to avoid complications.
In acute purulent frontitis, complex treatment is used, which simultaneously eliminates the cause of the disease and its symptoms. Therefore, it is so important to pass a preliminary high-quality diagnostic examination. According to its results, the patient is prescribed drugs of several drug groups at once:
- antipyretic - only when the temperature rises above 38.5OFrom and to her persistent fall;
- anti-inflammatory - they usually have antipyretic and analgesic effects;
- antihistamines - quickly relieve mucosal edema, restore normal air and mucus circulation;
- vasoconstrictor - have a decongestant effect, reduce the amount of mucus secreted;
- antibacterial - if pathogenic microorganisms were found during sowing;
- antifungal - as a prevention of the development of candidiasis while taking antibiotics, or if the cause of the disease is fungi.
To improve the general condition of the patient, a course of vitamin therapy and immunomodulators are also prescribed, which stimulate the body's defenses. The dosage of drugs and their combination are selected individually, depending on the patient's condition and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Frontal puncture and surgery
If purulent frontal sinusitis is severely neglected or develops very quickly with a large accumulation of pus in the sinuses, which does not come out on its own, the doctor may decide on the need for forced cleansing of the sinus by performing a frontal puncture.
 This procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting and requires the use of special equipment - a trepanator, since the bones that form the walls of the frontal sinus are dense enough and it will not be possible to pierce them with a regular needle. In fact, the procedure is a mini-operation, so it is assigned only in extreme cases, when all other methods have already been tried and did not bring the expected result.
This procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting and requires the use of special equipment - a trepanator, since the bones that form the walls of the frontal sinus are dense enough and it will not be possible to pierce them with a regular needle. In fact, the procedure is a mini-operation, so it is assigned only in extreme cases, when all other methods have already been tried and did not bring the expected result.
The puncture is performed under local anesthesia. The needle is inserted through the nasal passage or the frontal bone. The contents of the sinus are pumped out, an antiseptic solution is injected into its cavity for washing, which is then also removed. Finally, the mucous membrane is treated with a solution with an antibiotic, and a drainage is installed at the puncture site, or it is closed by the skin with the imposition of a micro-suture. The drain can remain in the patient's body for up to 5 days, and then it is removed and the wound is closed.
After a correctly performed procedure, the patient's condition improves rapidly. But for at least 5-7 days, he must still be in the hospital to make sure that there are no complications, and the development of the disease is suspended. Usually, after a puncture, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for at least 7 days.
At the stage of recovery, the patient can be recommended physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, UHF, quartz tube and others. Steam inhalations give a good effect - they quickly relieve swelling and moisturize mucous membranes, accelerating their recovery.
But all these procedures can be used only when pus is completely absent and the body temperature does not rise above 37.5OWITH.
Surgery sometimes becomes necessary. The most difficult form for treatment is polyposis frontitis. If the polyp that provokes it is in the nasal cavity, then the operation is quite simple and takes no more than 15 minutes - the formation is removed with a medical loop. Pre-biopsy is done to exclude oncology.
It is worse when the polyp grows in the sinus cavity. Then you have to open the frontal bone in order to get to the neoplasm and remove it. The decision to carry out such operations is used extremely rarely and only when urgently needed.
Prevention measures
Prevention of acute frontal sinusitis is much easier than its treatment. Therefore, it is better to do everything initially to prevent the development of this unpleasant disease. First of all, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system by all possible means: exercise, perform hardening procedures, and eat right. Not less important:
 prevent severe hypothermia of the forehead - in cold and very windy weather, it is necessary to wear hats;
prevent severe hypothermia of the forehead - in cold and very windy weather, it is necessary to wear hats;- completely cure all respiratory diseases, preventing them from becoming chronic;
- at least once a year to undergo preventive examinations in order to detect polyps in time;
- after a nose injury, be sure to visit an ENT doctor to make sure there is no serious damage to the nasal septum;
- monitor the cleanliness and temperature of the air in residential and work premises;
- do not allow prolonged exposure to external irritants on the respiratory system, use personal protective equipment when working in hazardous industries;
- regularly cleanse the nasal cavity from the mucus accumulated there, do not pick in the nose with fingers and other hard objects.
Quitting bad habits, especially smoking, also significantly reduces the chances of developing inflammation in the upper respiratory tract.
A good prevention of any type of sinusitis is breathing exercises, which it is advisable to do regularly. And the main thing is to see a doctor on time, without trying to cure the disease on your own. Misuse of drugs can only aggravate the disease and lead to serious complications.

 frontal - paired sinuses located above the brow ridges practically in the middle of the forehead;
frontal - paired sinuses located above the brow ridges practically in the middle of the forehead; prevent severe hypothermia of the forehead - in cold and very windy weather, it is necessary to wear hats;
prevent severe hypothermia of the forehead - in cold and very windy weather, it is necessary to wear hats;