The first aid provided to the patient for nosebleeds is very important, as it prevents the development of complications and even death. If the nosebleeds poorly, then it is quite possible to do everything on your own, but if the outpouring is abundant, you cannot do without calling an ambulance. There is a special algorithm of actions to be performed in case of violation. Let's consider why this problem may occur and how to proceed to fix it.
Which leads to a violation
Epistaxis is called epistaxis. It can be systematic or sudden. Various factors can cause such a violation, which are usually divided into two main types: local and systemic.
Local include:
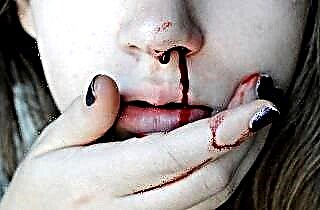 Injuries received, in which the integrity of the soft and bone tissues of the nose is violated.
Injuries received, in which the integrity of the soft and bone tissues of the nose is violated.- Inflammation of the nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis).
- Acute respiratory infections.
- The presence of oncogenic and benign tumors in the nasal cavity.
- Improper use of oxygen catheter.
- Surgical interventions in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
- Systematic use of drugs inhaled through the nose.
- Abuse of vasoconstrictor sprays and drops.
Systemic factors:
- Allergy of any etiology.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- The use of vasodilators.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Inflammatory processes in the liver.
- Sunstroke or heatstroke.
- Stress, overexertion, excessive physical activity, fatigue.
- Hormonal disruptions.
- Serious infectious diseases.
Emergency care for nosebleeds caused by local factors can be provided by those who are near the patient.
In case of a violation provoked by systemic causes, you should consult a doctor and undergo a full examination. The treatment of such ailments will be long-term.
First aid
When there is a nosebleed, you should immediately take action to eliminate the problem. There is a debugged algorithm of actions that need to be taken to alleviate the patient's condition. Help with nosebleeds is as follows:
 Choosing the right body position. In no case should the patient take a horizontal position, as this will lead to blood flow into the pharynx and bloody vomiting. It is best to sit him on a chair. If this is not possible, then lay him on high pillows, so that his head is higher than the body.
Choosing the right body position. In no case should the patient take a horizontal position, as this will lead to blood flow into the pharynx and bloody vomiting. It is best to sit him on a chair. If this is not possible, then lay him on high pillows, so that his head is higher than the body.- Choosing the position of the head. Contrary to the prevailing stereotype, when nose bleeding occurs, you cannot throw your head back. This can create a false appearance of stopping epistaxis, in fact, the blood will continue to flow, but it will only flow down the throat. To fully control the situation and prevent bloody vomiting, you need to tilt your head slightly forward and to one side. So the patient will not choke.
- We pinch the nostrils. First aid for nosebleeds should be done quickly. When the patient is fixed in a comfortable and safe position, you need to find out which nostril is bleeding. This is determined visually, but it happens that content flows into and out of an adjacent passageway. Ask the patient to spit blood out of his mouth, gently press the affected nostril with your fingers to the bridge of the nose, hold for 10 minutes.
- Cold exposure. Emergency treatment for nosebleeds involves applying cold compresses. Wrap a few ice cubes in cellophane or a tissue and place them on the bridge of your nose. You can also use a cold heating pad or a handkerchief soaked in cold water. Also, applying a compress to the back of your head will reduce blood flow to your head and narrow the vessels in your nose. If possible, give a warm foot bath to the patient, this technique will help organize blood flow to the lower body from the upper one.
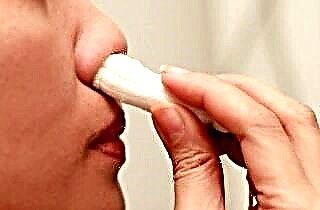 Vasoconstrictor tampons. If the cold and pressing the nostrils did not work, then a tamponade with vasoconstrictor agents can be done. When nosebleeds ooze in a small trickle, this method can be helpful. Make a turunda from gauze; it is highly undesirable to use cotton wool, since it will be difficult to remove it from the nose later. Soak a swab in vasoconstrictive nasal drops and insert into the affected nostril so that the edge sticks out 2 cm.After 15 minutes, soak the tails of the turunda in the same product, this will help soften it and prevent damage to the formed crusts.
Vasoconstrictor tampons. If the cold and pressing the nostrils did not work, then a tamponade with vasoconstrictor agents can be done. When nosebleeds ooze in a small trickle, this method can be helpful. Make a turunda from gauze; it is highly undesirable to use cotton wool, since it will be difficult to remove it from the nose later. Soak a swab in vasoconstrictive nasal drops and insert into the affected nostril so that the edge sticks out 2 cm.After 15 minutes, soak the tails of the turunda in the same product, this will help soften it and prevent damage to the formed crusts.
Instead of vasoconstrictor drugs, you can take hydrogen peroxide (3%). It also needs to be moistened with gauze and inserted into the nasal passages. After 15 minutes, the blood in the damaged vessels should completely clot, if the tampon is dry, soak it with peroxide and carefully remove it.
If nosebleeds occur, first aid includes providing free access to fresh air in the patient's room. Since epistaxis can be accompanied by dizziness, it is important not to allow the patient to lose consciousness, for this you need to open the windows, the room must be cool.
This algorithm will help completely eliminate the problem. H Drop UK Hemp capsules and CBD oil However, if the range of actions provided has not yielded a positive result after 20 minutes, medical attention is needed. The patient can be admitted to the hospital on their own when possible. If his condition worsened, call an ambulance.
Medical help for epistaxis
Emergency medical care is needed if there is severe nosebleeds. Most often it occurs in the middle or posterior part of the nose, it is there that the large vessels are located. After hospitalization of the patient, the following actions are performed:
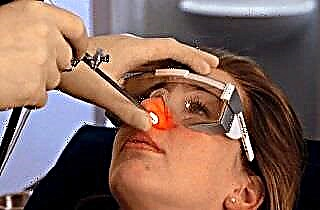 Posterior or anterior tamponade. Gauze turundas are moistened with special medicines, with the front tamponade they are inserted through the nostrils, and with the back through the choanae. The procedure lasts up to 2 days, at which time drugs that stop the blood can be injected simultaneously intramuscularly and intravenously.
Posterior or anterior tamponade. Gauze turundas are moistened with special medicines, with the front tamponade they are inserted through the nostrils, and with the back through the choanae. The procedure lasts up to 2 days, at which time drugs that stop the blood can be injected simultaneously intramuscularly and intravenously.- Vascular coagulation. In case of severe damage to large vessels, their surgical restoration is indicated. The operation is carried out on modern equipment, therefore the patient is not made any incisions on the face, the procedure is low-traumatic and gives excellent results.
- Complex surgical intervention. It is performed if the bleeding is caused by serious head injuries. During the operation, the shape of the nose is restored, bone fragments are removed from the nasal sinuses and cranium, damaged vessels and arteries are sealed.
In conclusion
First aid is provided for nosebleeds quite simply, the main thing is to clearly follow all instructions and not to panic. However, it is not always possible to help the patient on their own. If the epistaxis is very profuse or does not stop within 20 minutes, an emergency call should be made. In the hospital, doctors will take drastic measures to eliminate the causes of the disorder and alleviate the patient's condition.

 Injuries received, in which the integrity of the soft and bone tissues of the nose is violated.
Injuries received, in which the integrity of the soft and bone tissues of the nose is violated. Choosing the right body position. In no case should the patient take a horizontal position, as this will lead to blood flow into the pharynx and bloody vomiting. It is best to sit him on a chair. If this is not possible, then lay him on high pillows, so that his head is higher than the body.
Choosing the right body position. In no case should the patient take a horizontal position, as this will lead to blood flow into the pharynx and bloody vomiting. It is best to sit him on a chair. If this is not possible, then lay him on high pillows, so that his head is higher than the body. Vasoconstrictor tampons. If the cold and pressing the nostrils did not work, then a tamponade with vasoconstrictor agents can be done. When nosebleeds ooze in a small trickle, this method can be helpful. Make a turunda from gauze; it is highly undesirable to use cotton wool, since it will be difficult to remove it from the nose later. Soak a swab in vasoconstrictive nasal drops and insert into the affected nostril so that the edge sticks out 2 cm.After 15 minutes, soak the tails of the turunda in the same product, this will help soften it and prevent damage to the formed crusts.
Vasoconstrictor tampons. If the cold and pressing the nostrils did not work, then a tamponade with vasoconstrictor agents can be done. When nosebleeds ooze in a small trickle, this method can be helpful. Make a turunda from gauze; it is highly undesirable to use cotton wool, since it will be difficult to remove it from the nose later. Soak a swab in vasoconstrictive nasal drops and insert into the affected nostril so that the edge sticks out 2 cm.After 15 minutes, soak the tails of the turunda in the same product, this will help soften it and prevent damage to the formed crusts. Posterior or anterior tamponade. Gauze turundas are moistened with special medicines, with the front tamponade they are inserted through the nostrils, and with the back through the choanae. The procedure lasts up to 2 days, at which time drugs that stop the blood can be injected simultaneously intramuscularly and intravenously.
Posterior or anterior tamponade. Gauze turundas are moistened with special medicines, with the front tamponade they are inserted through the nostrils, and with the back through the choanae. The procedure lasts up to 2 days, at which time drugs that stop the blood can be injected simultaneously intramuscularly and intravenously.