Coughing up phlegm is usually considered a sign of improvement. As a cold or acute respiratory disease develops, a dry barking cough that appears at the very beginning is replaced by a wet one, active coughing up of mucus begins and then the disease disappears. But this is not always the case. There are situations when the cough with phlegm does not go away for a month or longer. And this is already a very bad sign that cannot be ignored.
Main reasons
It is impossible to say unequivocally what sputum is. Depending on the disorder, it can be accumulated mucus in the throat, blood with pus, or plasma effusion.  blood. In order to accurately establish this, it is necessary to undergo an examination and pass a sputum test. And only then the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment.
blood. In order to accurately establish this, it is necessary to undergo an examination and pass a sputum test. And only then the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment.
Causes of cough with phlegm can be as follows:
- acute respiratory diseases (infectious or viral);
- obstructive bronchitis;
- chronic pneumonia;
- severe allergic reactions;
- bronchial asthma;
- chronic rhinitis;
- inflammation of the sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis);
- lung abscess;
- tuberculosis.
All these diseases require intensive drug treatment in the acute phase, and then medical supervision until complete recovery. With proper therapy, the expectorant cough at the first stage intensifies - the lungs begin to actively cleanse themselves, doctors call this "productive cough". Everything is fine, so you shouldn't be intimidated.
Improvement begins in a few days. A severe cough with phlegm is replaced by a milder one, and the discharge itself usually changes color. A cough with white sputum can already be considered a symptom of recovery. A slight cough can persist for up to 3-4 weeks - these are residual effects that go away without additional treatment.
A harmless cough
 Indeed, a sign of recovery is an expectorant cough that appears after an acute respiratory illness, a cold, or treated bronchitis. In this case, a cough with phlegm usually begins in the morning, since a certain amount of mucus has time to accumulate during the night, which the body needs to remove.
Indeed, a sign of recovery is an expectorant cough that appears after an acute respiratory illness, a cold, or treated bronchitis. In this case, a cough with phlegm usually begins in the morning, since a certain amount of mucus has time to accumulate during the night, which the body needs to remove.
Such a wet cough in an adult usually lasts for several days. And at this time, it is important to help the body to quickly remove all excess mucus. Expectorant syrups and various folk remedies will be good helpers. They help thin the phlegm and help cough up the phlegm.
But if, despite treatment, a severe wet cough persists for more than 1-2 weeks, this is already bad. Then you need to closely monitor the general condition and consult a doctor. Perhaps he will make some adjustments to the treatment or prescribe additional physiotherapy procedures.
Purulent sputum
An alarming signal is when the phlegm changes color when coughing. If it is transparent or white at first, it becomes yellow or green over time, this is a bad sign.
Purulent sputum also has an unpleasant characteristic odor and a sweetish aftertaste, and may include clots of fresh or clotted blood. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, especially if other dangerous symptoms are present:
 a feeling of suffocation during an attack;
a feeling of suffocation during an attack;- persistent or recurrent chest pain;
- wheezing, whistling, or gurgling sounds when breathing;
- increase in body temperature (especially sharp and strong);
- shortness of breath even with minimal exertion or after an attack;
- general weakness, loss of appetite, unreasonable weight loss.
In addition to the fact that a purulent cough in itself is a bad sign, it is also an additional source of infection, which constantly enters the oral cavity. This provokes persistent inflammation and sore throat, which must be treated separately.
Other types of sputum
Not only purulent sputum can be coughing up. Depending on the disease, it can be of a different color and consistency. Already on these grounds, an experienced doctor often makes a preliminary diagnosis:
- Gray or brown - indicates a hard-core smoker whose lungs are clogged with tobacco tar. It happens in people working in dusty rooms, on construction sites, with wool or fleecy fabrics - such a wet cough in an adult can be considered professional.
- Black is often also a professional sign for miners, builders, excavators. If there is such a wet cough, and there is no fever, then this is a natural process of cleansing the lungs.
 Pink - this shade is obtained if there is a small amount of blood in the liquid mucus. This usually happens with severe attacks of coughing due to which small capillaries burst. If the color doesn't change to bright red, don't worry too much.
Pink - this shade is obtained if there is a small amount of blood in the liquid mucus. This usually happens with severe attacks of coughing due to which small capillaries burst. If the color doesn't change to bright red, don't worry too much.- Red or dark brown - This is evidence of internal bleeding. You should see a doctor immediately. May be life threatening. It happens with an open form of tuberculosis, oncology, etc.
- Foamy - this consistency indicates a very serious disease. It happens with anthrax or pulmonary edema. Lack of treatment in both cases is fatal.
- Vitreous - not to be confused with transparent! It is thick, dense, coughs hard, irritates the larynx, spits out as if in whole pieces. Typical for bronchial asthma.
Since the color and consistency of sputum is of great diagnostic value, it is imperative to pay attention to them.
How to treat
Only a doctor should decide how to treat a cough with phlegm and fever. With its infectious nature, broad-spectrum antibiotics are usually prescribed. They are able to quickly kill pathogenic microorganisms, after which the cough with pus usually disappears.
In order for the mucus to come out faster, expectorant drugs are used. And the use of antitussives is strictly prohibited. Antitussive pills suppress the cough reflex, and as a result, mucus will stagnate in the bronchi and lungs, and pathogenic microflora will flourish, increasing inflammation.
 Antihistamines are capable of stopping a severe wet cough and reducing the amount of mucous secretions. After taking them, breathing is easier, spasms are relieved, and shortness of breath goes away. But in this case, this is not a treatment, but only a way to temporarily get rid of a painful cough.
Antihistamines are capable of stopping a severe wet cough and reducing the amount of mucous secretions. After taking them, breathing is easier, spasms are relieved, and shortness of breath goes away. But in this case, this is not a treatment, but only a way to temporarily get rid of a painful cough.
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory sprays are unable to penetrate deeply into the lungs or bronchi. But their use helps prevent infection from spreading to the upper respiratory tract, relieve irritation of the larynx and reduce pain. Gargling gives the same effect, only weaker.
Folk remedies
If a cough with profuse sputum is not accompanied by a high fever, there is no pus and traces of blood in the discharge, or they disappeared after treatment, you can use traditional folk remedies:
- Black radish juice with honey is almost a real medicine, has expectorant, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic properties. Cut off a tail from a large black radish, gouge out the middle and pour honey over it. After several hours, a healing juice is formed, which must be taken in a teaspoon several times a day.
- Aloe pulp or juice with honey - quickly heals an irritated throat, helps to drain mucus, has antibacterial properties (but you cannot use it with purulent mucus or damaged capillaries!). Cut the bottom leaf of a three-year-old plant and peel it off. Chop the pulp or squeeze the juice, mix with the same amount of honey. Take a teaspoon 3-4 times a day.
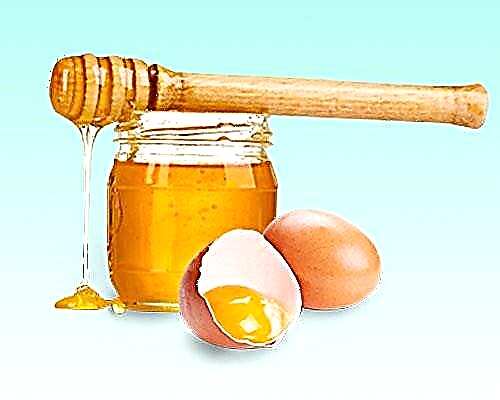 Crushed garlic with honey is a powerful antibacterial agent, previously it was even used to treat tuberculosis, it helps to eliminate foci of inflammation, kills microbes, and reduces the amount of mucus. Chop the garlic cloves thoroughly, pour in an equal amount of honey, leave for several hours, use half a teaspoon 5-6 times a day.
Crushed garlic with honey is a powerful antibacterial agent, previously it was even used to treat tuberculosis, it helps to eliminate foci of inflammation, kills microbes, and reduces the amount of mucus. Chop the garlic cloves thoroughly, pour in an equal amount of honey, leave for several hours, use half a teaspoon 5-6 times a day.- Yolks with honey - soothes an irritated throat, relieves coughing attacks, and promotes the discharge of phlegm. Separate two yolks from the whites, beat with a tablespoon of honey until white foam. Soften a tablespoon of ghee in a water bath and add to the yolks. You can pour in a teaspoon of brandy. Mix everything well and take a teaspoon 3-4 times a day.
- Onion syrup - coats the throat, soothes irritated mucous membranes, has expectorant properties. Peel half a kilogram of onions and chop finely. Place in an enamel saucepan and cover with two glasses of sugar. When the onion starts up the juice, add 3 tbsp. tablespoons of honey, mix and put on low heat. Cook for 2-3 hours until the juice thickens and acquires a pleasant amber color. Express the syrup, drink a teaspoon several times a day.
The throat must be constantly rinsed with a solution of sea salt. If there is no sea salt, take the usual rock salt (1 tsp per glass) and pour in a few drops of iodine. You can buy ready-made rinses at the pharmacy or use herbal teas.
Inhalation and warming up
 Inhalation has an excellent therapeutic effect when an expectorant cough begins. It is better to do inhalation with a nebulizer. It converts the medicine into a finely dispersed solution, which penetrates deeply into the bronchi or lungs and significantly speeds up the treatment process.
Inhalation has an excellent therapeutic effect when an expectorant cough begins. It is better to do inhalation with a nebulizer. It converts the medicine into a finely dispersed solution, which penetrates deeply into the bronchi or lungs and significantly speeds up the treatment process.
Steam inhalations with soda solution dilute phlegm well and soften dry cough, facilitating its discharge. For inhalation, you can use eucalyptus, chamomile, calendula, thyme, elecampane, sage, essential oils: tea tree, pine, cedar, thuja. If you don't have an inhaler at home, you can just breathe over the steam.
One must be careful with warming up procedures. They are categorically contraindicated if the expectorant mucus with pus or traces of blood. Do not warm up even at elevated body temperature, as well as infectious diseases in the acute phase.
So if you are not sure that the procedure will benefit you and not harm you, be sure to consult your doctor before starting treatment.
Remember that a wet cough is only a protective reflex reaction of the body. And it is better than dry or barking, as in most cases it is easier to diagnose and treat. It is important not to miss the moment of the onset of a serious illness or the transition of the respiratory to a chronic form. And then, with the right actions, you can cope with the problem pretty quickly.

 a feeling of suffocation during an attack;
a feeling of suffocation during an attack; Pink - this shade is obtained if there is a small amount of blood in the liquid mucus. This usually happens with severe attacks of coughing due to which small capillaries burst. If the color doesn't change to bright red, don't worry too much.
Pink - this shade is obtained if there is a small amount of blood in the liquid mucus. This usually happens with severe attacks of coughing due to which small capillaries burst. If the color doesn't change to bright red, don't worry too much. Crushed garlic with honey is a powerful antibacterial agent, previously it was even used to treat tuberculosis, it helps to eliminate foci of inflammation, kills microbes, and reduces the amount of mucus. Chop the garlic cloves thoroughly, pour in an equal amount of honey, leave for several hours, use half a teaspoon 5-6 times a day.
Crushed garlic with honey is a powerful antibacterial agent, previously it was even used to treat tuberculosis, it helps to eliminate foci of inflammation, kills microbes, and reduces the amount of mucus. Chop the garlic cloves thoroughly, pour in an equal amount of honey, leave for several hours, use half a teaspoon 5-6 times a day.