In the first months of life, the baby adapts to new living conditions. Organs and systems continue to form, ensuring the vital activity of the whole organism. The mucous membrane of the nasal cavities is also at the developmental stage, due to which mucus can be produced in large volumes and be regarded as snot. Treatment of a common cold in infants at 1 month should be carried out by a pediatrician, taking into account the severity of the disease and concomitant pathology.
Only a doctor, based on the results of the examination, will be able to differentiate between physiological rhinitis and rhinitis of pathological origin. It is not necessary to treat a runny nose in a month-old baby if it is of a physiological type and does not interfere with nasal breathing. In other cases, therapy is needed from the first days of the disease.
 With a negligent attitude towards rhinitis, a child may develop complications associated with oxygen starvation of the body, the spread of inflammation, infection, and the progression of an allergic reaction. Let's highlight the most common complications:
With a negligent attitude towards rhinitis, a child may develop complications associated with oxygen starvation of the body, the spread of inflammation, infection, and the progression of an allergic reaction. Let's highlight the most common complications:
- otitis. It develops as a result of swelling of the mucous membrane of the Eustachian tube, impaired airway function, sanitation of the ear cavity, which causes opportunistic pathogenic microbes of the flora in the ear to be activated;
- sinusitis. The accumulation of mucus and a violation of nasal breathing leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses, which is manifested by green snot and pain in the area of the nasal cavities;
- pharyngitis. The coverage of the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall is accompanied by nasopharyngitis, coughing and sore throat;
- bronchitis - may result from mucus flowing from the nasopharynx into the trachea. The child begins to be bothered by coughing, and hyperthermia is recorded;
- laryngitis - manifested by hoarseness, difficulty breathing, coughing;
A life-threatening complication is croup, which occurs against the background of pronounced edema of the vocal cords, due to which an attack of suffocation develops.
- bronchospasm is the result of prolonged contact with an allergen. The risk of developing bronchial asthma also increases;
- dacryocystitis, conjunctivitis. They arise as a result of a violation of the outflow of tear fluid into the nasal cavities and the spread of inflammation to the conjunctiva;
- weight loss. Lack of nasal breathing makes feeding difficult. When trying to grab the nipple and start sucking, the newborn stops breathing, abandons the breast and begins to cry. Insufficient food intake leads to a decrease in body weight.
Causes of discharge
The mucus, which is in the nasal cavities, is the protection of the mucous membrane from the effects of environmental factors. By regularly removing dust and microbes, the risk of developing rhinitis is reduced. What can cause increased mucus production?
- colds should be put in the first place among the causes of the common cold. Snot may appear after hypothermia in frost or draft;
- physiological characteristics of the first months of life, when the mucous membrane adapts to new conditions;
- infectious pathogens. It can be influenza virus, rhinovirus, streptococcus, staphylococcus. Usually, infectious rhinitis in an infant rarely develops, due to the presence of protective immunoglobulins, which are transmitted from the mother;
- allergens. Frequent allergic factors include pollen, hygiene products, household chemicals and animal hair. Sometimes short-term rhinorrhea can be observed after vaccination;
- unfavorable living conditions. The child will find it difficult to breathe if the air in the room is dry or dusty. In response to irritation, the nasal mucosa begins to intensively produce mucus, trying to remove dust particles and moisturize the surface.
Characteristic features of the flow
The main symptom of a runny nose is snot. At the beginning of the disease, they are transparent and differ in a watery consistency. As the disease progresses, the mucus becomes thicker, acquires a yellowish tint. Note that with allergic rhinitis, the discharge is always colorless and watery.
If the discharge is green, sinusitis is suspected.
Among other clinical symptoms, it is worth highlighting:
- hyperthermia up to 38 degrees and above;
- Difficulty nasal breathing, due to which the baby has to breathe through the mouth;
- refusal of breasts, pacifiers;
 shortness of breath;
shortness of breath;- lacrimation, itching of the eyes, nose, sneezing, conjunctival hyperemia, which is characteristic of allergic rhinitis;
- irritability, tearfulness, lethargy;
- poor sleep;
- dyspeptic disorders. The appearance of diarrhea, vomiting is caused by swallowing air during feeding.
Usually, snot bothers for 10 days, but with immunodeficiency, it is possible for a longer persistence of symptoms of the disease.
Therapeutic tactics
How to treat a runny nose? Before starting drug therapy, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. If snot of allergic origin, they can be eliminated only by stopping the effect of the allergic factor on the body. For this it is recommended:
- regularly carry out wet cleaning in the children's room, which will reduce the concentration of allergens;
- refuse to walk outside and not ventilate the room in windy weather during the flowering period, if the allergy is related to pollen;
- household chemicals with a pungent odor, air fresheners should be abandoned;
- you need to use special hypoallergenic hygiene products;
- stop contact with animals, give them to neighbors or friends;
- laundry should be washed only with baby powder;
- to facilitate breathing, it is necessary to maintain the humidity at 70%. The temperature in the room should not exceed 20 degrees.
To improve nasal breathing, the child can be given antihistamines for systemic (Fenistil in the form of drops) or topical (Delufen).
For other forms of the disease, treatment may include the use of vasoconstrictor drugs, such as Otrivin 0.05% or Nazol baby. These medicines are allowed for infants, but one should remember about the risk of overdrying the mucous membrane and developing addiction. Their action is to reduce mucosal edema and rhinorrhea due to spasm of blood vessels.
It is not recommended to use vasoconstrictor drugs for nasal use more than twice a day for more than five days.
A prerequisite for therapy is regular cleansing of the nasal cavities from mucus. To cure a runny nose, you need to use saline solutions, for example, Marimer, Humer, Dolphin. They are allowed from the first days of life.
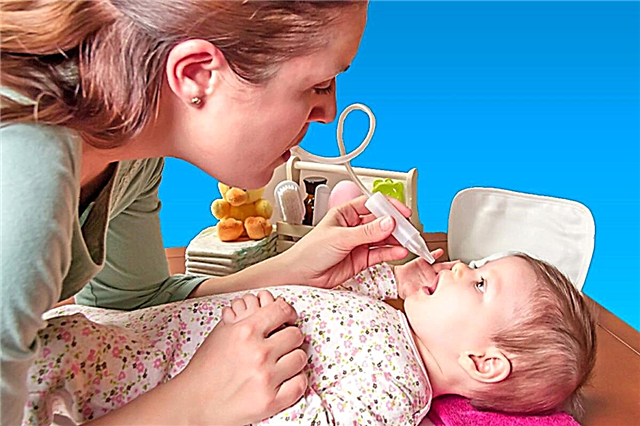
For infants, saline solutions are recommended in the form of drops. Using a spray increases the risk of developing otitis media. The nose should be buried 3-4 times a day, after which it is necessary to clean the nasal cavities using a special aspirator or a small pear.
Remember, the introduction of the solution into the nasal passages with the help of a pear is prohibited due to the high pressure of the water jet. It is necessary to remove snot from the nose with a syringe with great care.
You can prepare a solution for rinsing the nasal passages at home. To do this, carefully dissolve salt (2 g) in boiled warm water (270 ml).
Regardless of the cause of rhinitis, it is necessary to provide optimal conditions for a speedy recovery:
- microclimate in the children's room (humidity, temperature);
- nutritious diet. Babies should be getting enough breast milk or formula. If snot interferes with sucking, you must choose a different feeding method, such as with a spoon.After six months, the child is introduced to complementary foods, which allows you to slightly expand the diet with juices or compotes;
- walks in the fresh air allow for the physiological sanitation of the nasal cavities and prevent the accumulation of mucus. With hyperthermia above 37.5 degrees, as well as the child's poor health, the walk should be postponed;
- healthy sleep. During the period of illness, the body needs strength to fight microbes, so children need to be provided with proper rest.
It is forbidden to use nasal preparations with an antiseptic and hormonal composition without a medical prescription.
If a pediatrician recommends inpatient treatment, one should not refuse.
This means that the child's condition is serious and requires medical supervision.
If the pediatrician has allowed home treatment, do not forget to regularly visit the doctor's office to assess the dynamics of therapy and its correction. When is home treatment prohibited?
- when wheezing, barking cough appears;
- with weight loss due to poor nutrition and dehydration;
- when bloody snot appears;
- if the runny nose does not go away within 10 days;
- if the hyperthermia remains at a high level (above 38 degrees);
- with a deterioration in the general condition.
Preventive Tips
To reduce the incidence of respiratory illness as much as possible, prevention is essential from birth. It includes:
- breastfeeding, which allows you to form a strong immunity of the child;
- ensuring optimal living conditions;
- limiting contact with possible allergens and sick people;
- prevention during the epidemic. For this, the drug Nazoferon can be used in the form of nasal drops. It increases the production of interferons, increasing the level of protection. You can also use the herbal remedy Derinat. It is allowed from birth, it is prescribed to strengthen the immune system;
- regular rinsing of the nasal cavities;
- daily walks in the fresh air, choosing for this place with clean air (park, forest zone). Children should be dressed according to the weather for a walk.
Don't forget about climate change. Sea air is especially important for the immunity of children. It has a beneficial effect on the immune system, which makes it possible to protect the child not only from respiratory diseases, but other serious diseases.

 shortness of breath;
shortness of breath; If a pediatrician recommends inpatient treatment, one should not refuse.
If a pediatrician recommends inpatient treatment, one should not refuse.