The main complaint of a child in the presence of an inflammatory process in the ear is the development of pain syndrome. Depending on the localization of the lesion, the severity, prevalence, the nature of the pain may be different. In some pathological conditions localized in the parotid region, it may be itching, which is an analogue of pain. In other cases of lesions of the ear, proceeding with the involvement of its internal parts in the process, pain sensations can be replaced by a feeling of heaviness in the ears, and also be accompanied by nausea, vomiting. The most common variant described by patients is intense, acute ear pain, which is described as “shooting in a child's ear”.
Symptoms and Causes

Pain in the pathology of the ear can be of such intensity that children toss and turn in bed, periodically scream, cry. As for other complaints from the ear, tinnitus is also a concern of patients. There is a decrease in hearing, but with a unilateral lesion, it is less noticeable. Additional signs are hyperthermia up to 38-39 degrees, general malaise, decreased appetite.
The combination of these symptoms indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the ear. Inflammation of the middle ear is a pathology that requires immediate treatment. The earlier treatment is started, the faster the recovery will come, and the less likely to develop severe dangerous complications of otitis media.
In order to determine what to do when a child's ear is shooting, it is necessary to understand the causes of the disease and its development mechanism. The child's ear shoots if the middle ear is involved in the pathological process. As a result of a violation of the drainage function of the auditory tube, stagnation occurs in the tympanic cavity, leading to the development of catarrhal inflammation in it. It is at this stage that the pain syndrome appears, the child shoots in the ear. What to do in this case depends on the presence of other additional signs.
First of all, we are talking about the condition of the eardrum. Only an otolaryngologist can clarify the integrity of the tympanic membrane. Therefore, if a child's ear shoots, what to do and what treatment to prescribe, the specialist decides. The doctor should conduct an otoscopy, and with the help of a special instrument, draw a conclusion about the condition of the tympanic membrane.
First aid
However, at the stage of pre-medical consultation, parents should also know what to do if the ear shoots child. Since the development of the process is due to edema and impaired patency of the auditory tube, when the first signs of otitis media of the middle ear appear, vasoconstrictor drops must be instilled into the nose. In many cases, carrying out such actions contributes to the regression of the disease in the near future.
child. Since the development of the process is due to edema and impaired patency of the auditory tube, when the first signs of otitis media of the middle ear appear, vasoconstrictor drops must be instilled into the nose. In many cases, carrying out such actions contributes to the regression of the disease in the near future.
The child's condition is accompanied by severe pain syndrome, as well as symptoms of general intoxication. Under these conditions, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects is shown. Among all the variety of drugs in this group in children, the safest drugs with a smaller spectrum of side effects are preferred. Based on this, paracetamol or ibuprofen is the priority. Depending on the age, they can be used in tablets, syrups or suppositories.
It is necessary to refrain from taking ear drops before being examined by a specialist.
This is due to the fact that many of them contain ototoxic components. With an intact tympanic membrane, they are absolutely safe and, due to their composition, are effective. In cases where there is an opening in the eardrum, and drugs can easily enter the middle ear cavity, the use of such drugs can be very dangerous.
The next direction of therapeutic measures required when pain in the ear appears, are actions aimed at immobilizing the ear and maintaining the thermal regime. To do this, it is recommended to lay a cotton swab or tampon in the external auditory canal. It will be even more effective to put on a hat on top or tie a scarf.
In adults and older children, it is possible to carry out warming procedures using dry heat, as well as wet compresses. However, these procedures may be feasible only at the very initial signs of ear damage. The transformation of catarrhal otitis media into purulent otitis media can take only a few hours in children.
Carrying out any warming procedures with a purulent course of the process is an absolute contraindication.
Such actions can lead to the further spread of purulent exudate to the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the lining of the brain. In addition, when prescribing physiotherapy procedures, it must be remembered that they are contraindicated in children.
- with an increase in body temperature over 37.3 degrees;
- before reaching the age of five;
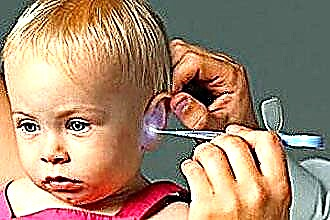
- in the presence of concomitant serious diseases.
In the case when the otolaryngologist examined the patient, performed an otoscopy, strict adherence to his recommendations is necessary. If a doctor's consultation is postponed for some time, the child's parents should
- Instill vasoconstrictor drops in his nose. Tizine, galazolin, naphthyzine are the most popular drugs in this regard.
- Next, you should close the external auditory canal with a cotton turunda;
- Make sure paracetamol is taken.
Despite these measures, in the near future the patient should be consulted by an ENT doctor.
Correction of treatment
In this case, the task of the otolaryngologist will be not only in the abolition of drugs containing ototoxic components, if necessary. After clarifying the diagnosis, the doctor can decide on the prescription of antibiotics.
In the case of the development of purulent inflammation of the middle ear, antibiotics cannot be dispensed with. These drugs should be prescribed as early as possible.
It is their use that prevents the development of severe complications of otitis media.
Since ear inflammation is a complication of such pathologies as influenza, other acute respiratory viral infections, childhood infections, and pathology of the ENT organs, it is necessary to carry out all measures aimed at treating the underlying disease. In addition, sufficient attention must be paid to actions aimed at restoring the patency of the auditory tube. In this regard, the child should be taught to blow his nose correctly, alternately with each half of the nose, in the same way, sneeze without covering his nose. In newborns, it is periodically necessary to mechanically cleanse the nasal cavity from the crusts that have accumulated there, which interfere with free breathing. In addition, drinking plenty of fluids, recommended for any infectious processes, as a detoxifying agent, antipyretic, also helps to reduce the viscosity of mucus, which means it improves the patency of the auditory tube.
Correction of treatment carried out by a specialist will improve the situation in the near future. In addition, at the stage of the recovery stage, the use of tools and procedures will be required to help restore the integrity of the tympanic membrane.
Examinations by an otolaryngologist should be carried out regularly, until the function of the hearing organ is fully restored.