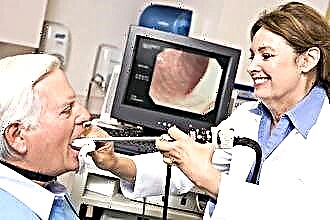
The external auditory canal of a healthy ear contains sulfur. Other content is not typical. Certain pathological processes in the ear are accompanied by bloody or purulent discharge. This symptom can be observed in both adults and children. In this case, purulent discharge is more common in childhood.

The presence of blood in the ear can be caused by traumatic damage to the auricle, other parts of the outer ear, or even the eardrum.
In this case, discharge from the ear in a child may be due to careless actions during the toilet of the ear, attempts to clean it of sulfur, or when a foreign body is deliberately introduced into the external auditory canal, which is typical for children aged 2 to 5 years. In this case, the development of pain syndrome of varying severity is possible.
Causes of suppuration
Purulent discharge from a child's ear is a viscous, sticky, off-white or yellowish liquid, the presence of which is caused by the development of acute purulent ear inflammation. Otitis media in children is usually a complication of another pathology, such as
- ARVI;
- sinusitis;
- adenoiditis;
- scarlet fever;
- measles.
With all these pathological processes, edema and the formation of mucus in the auditory tube occur. Subsequently, the contents are thrown into the middle ear cavity, which causes the development of a pathological process in it. At first the inflammation is catarrhal. With untimely, incorrect treatment, the presence of other predisposing factors, it transforms into purulent inflammation.
The mucous exudate in the middle ear cavity thickens and becomes purulent under the influence of infectious agents. The pressure exerted on the walls of the tympanic cavity leads to a rupture of the tympanic septum. As a result, a yellow liquid, that is, pus, flows from the child's ear.
The pathognomonic symptom of ear inflammation is the presence of pain. There may also be congestion in the ears, hearing loss. The typical course of acute otitis media is characterized by an increase in temperature up to 38-39 degrees.
The appearance of suppuration is accompanied by changes in the clinical picture of otitis media. Improvement noted the general condition of the child, a decrease in pain syndrome, a decrease in temperature indicators. At the same time, discharge from the ear in a child without pain is the most typical development of the pathological process.
the general condition of the child, a decrease in pain syndrome, a decrease in temperature indicators. At the same time, discharge from the ear in a child without pain is the most typical development of the pathological process.
The value of paracentesis
Most often, the exudate is a yellow viscous liquid with a characteristic odor. If the tympanic membrane is severely injured, the child may have brown discharge from the ear. Despite the frightening appearance, the appearance of otorrhea is a natural development of acute purulent otitis media. Moreover, in a certain situation, it may be necessary to surgically perforate the tympanic membrane. The indications for paracentesis are the following factors:
- deterioration of the child's condition;
- increased pain in the ear;
- an increase in the phenomena of intoxication;
- the appearance of symptoms indicating the spread of the process, such as dizziness, lack of coordination, nausea, vomiting.
Surgical procedures help prevent infection from spreading to the temporal mastoid bone and meningeal membranes.
Conservative treatment
When suppuration occurs, subsequent measures should be aimed at combating the bacterial causative agent of the disease, include the toilet of the external auditory canal. Since the use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops helps to improve the outflow of pus from the middle ear cavity, their use must be continued.
The most correct method of prescribing antibiotics is to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to them. However, such a study takes several days.
Antibiotic therapy should begin immediately after clarifying the diagnosis of purulent otitis media.
As a result, the drugs of choice are antibiotics that are most active against the likely causative agents of the disease. They are drugs from the amoxicillin group:
- Flemoxin solutab;
- Zinnat;
- Amoxiclav;
 Amoxil;
Amoxil;- Amosin;
- Hikontsil;
- Ecobol.
In addition to drugs of systemic action, used in the form of tablets, ear drops containing an antibiotic are also used.
Features of the use of ear drops
The use of ear drops when a child has ear pain and fluid flows has its own characteristics. They consist in the fact that in order to reduce pain, dosage forms in the form of drops should be used in a heated form, since thermal procedures have the property of masking pain sensations. To do this, before using the drops, you must hold them in your hand, or dip the bottle in hot water for a few seconds.
Before using the drops, the external auditory canal must be cleared of the contents.
Discharge from the ear in infants must be removed with cotton swabs and flagella. It is not recommended to use other devices for these purposes. This applies to ear sticks, hairpins and other items that can injure the skin if handled carelessly. To facilitate the absorption of exudate, you can pre-moisten the cotton filaments in 3% hydrogen peroxide or saline.
Having removed the yellow discharge from the ear in infants, it is recommended to carry out instillation by the injection method. This method increases the effectiveness of the procedure, allowing you to increase the concentration of the drug in the desired place. The field of instillation of the external auditory canal should be covered with a cotton swab, which will provide rest to the damaged organ.
Pain relievers
Such a popular remedy as Sofradex cannot be used due to the presence of neomycin in its composition, which has an ototoxic effect. The use of Otinum, Otipax is also contraindicated due to the hazardous components present in their composition. These funds can be approved for use only in the early stage of otitis media, before the fluid appears in the child's ears.
What kind of treatment with an analgesic component can be used in this case depends on the severity of the clinical manifestations and the age of the patient.
In those cases when, despite the development of suppuration, a pronounced pain syndrome persists, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in children is indicated.
The drugs of this group, in addition to the antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect, also have an analgesic effect. Depending on the age of the child, paracetamol, ibuprofen can be used in the form of tablets, syrup or suppositories.
At the first sign of ear inflammation, thermal treatments are quite effective. However, if a yellow fluid flows out of the child's ear, then this is an absolute contraindication to its conduct. In addition, any physiotherapy procedure is considered dangerous before the age of five.
If ear inflammation has taken the form of purulent otitis media, this should not cause panic in the child or his parents. Qualified specialist advice, timely and correct treatment will help to normalize the patient's condition in a short time.

 Amoxil;
Amoxil;