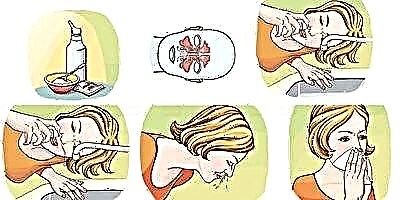
Ear bleeding is an alarming symptom that may indicate damage to the skin in the ear canal or perforation of the membrane. Blood in the ear after brushing is a good reason for seeking help from an otolaryngologist. Mechanical tissue damage leads to a decrease in local immunity, which is fraught with the development of opportunistic microorganisms.
According to experts, the occurrence of a problem in 95% of cases is due to non-compliance with the technique of carrying out hygienic procedures. If blood appears on the cotton swab when cleaning the ears, this indicates damage to the blood vessels in the tissues being treated. To restore the integrity of the skin and membranes, it is necessary to use local antiseptic preparations that have analgesic, decongestant and regenerating properties.
Causes of injury

Improper hygiene practices are often the cause of injury, as a result of which blood appears in the ear when cleaning. The causes of hemorrhage lie in damage to the network of small capillaries located in the upper layers of the skin. Less often, spotting accumulates in the outer ear when the integrity of the membrane is violated, which is associated with injury with sharp objects or cotton swabs.
Non-stopping ear bleeding may indicate damage to benign tumors in the outer ear.
When tissue is injured, hemorrhages are extremely rarely profuse. However, experts warn that if a problem arises, it is necessary to undergo simple treatment using topical agents. Thus, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of complications caused by the penetration of pathogens into the middle ear cavity through the damaged ear membrane.
The harm of cleaning
The ears do not need regular care due to the ability of the ear canal to cleanse itself. Most often, blood from the ear occurs after cleaning with a cotton swab, which experts do not recommend using for hygiene procedures. Cleansing the ear canal with hard sticks leads to injury, which is due to the specific structural features of the outer ear.
The auditory canal is conventionally divided into two sections:
- bone - a narrow canal located in front of the tympanic membrane;
- membranous-cartilaginous - the external part of the auditory canal, which contains more than 2000 glands of external secretion.

Sulfur is excreted exclusively in the membranous-cartilaginous section, from where it is easily evacuated to the outside due to the superficial growth of epidermal cells. Self-cleaning ability eliminates the need for regular ear toilet in the absence of ear diseases accompanied by exudation from the tympanic cavity.
Why does blood appear in my ear when cleaning? Hygienic use of cotton swabs can damage the eardrum or the thin skin in the bony ear canal. Mechanical trauma contributes to a decrease in local immunity, as a result of which there is an uncontrolled reproduction of opportunistic microorganisms.
Damage symptoms
Perforation of the ear membrane is evidenced not only by blood in the ear during cleaning, but also by a sharp pain that quickly subsides. Untimely treatment can lead to the development of complications, which may be signaled by the following symptoms:
- hearing loss;
- dizziness;
- vomiting;
- aching pains;
- tinnitus.
In the presence of large perforated holes in the membrane, patients feel air being evacuated from the sore ear during sneezing or coughing. Despite the ability of the membrane to regenerate, significant damage can only be repaired with surgery. Myringoplasty helps to restore the integrity of the membrane, as a result of which the hearing is sharpened in patients.
Important! Untimely surgical intervention can cause irreversible morphological changes in the ear membrane.
Diagnostics
If blood appears on the stick when cleaning the ear, it is advisable to be examined by an otolaryngologist. For diagnosis, palpation and otoscopy are performed. Diagnostic procedures allow:
detect puffiness;
- identify damage in the auditory canal;
- assess the degree of damage to the ear membrane;
- determine the presence of foci of inflammation;
- detect spotting.
With extensive perforation of the ear membrane using otoscopy, it is possible to determine the condition of the mucous membrane in the middle ear. The otolaryngologist conducts research using a frontal reflector and a metal funnel. If inflammatory reactions are detected in the organ of hearing, the membrane will have a reddish tint.
First aid
In case of damage to the ear after hygiene procedures, you should seek help from an ENT doctor. It is undesirable to pour alcohol solutions for disinfection into the ear canal. If there are perforated holes in the ear membrane, fluid will seep into the tympanic cavity, causing aseptic inflammation.
Important! Do not rinse your ears yourself and remove bloody discharge from them. This can cause infection of the middle ear with bacterial, fungal or viral pathogens.
First aid should be limited to the introduction into the ear canal of a sterile gauze turunda, fixed with a bandage. In case of severe pain, it is allowed to give the patient a pain reliever such as Paracetamol or Diclofenac. In the process of transporting a patient, it is advisable to ensure that he does not throw his head back. This can cause bleeding to enter the middle ear rather than the outer ear canal.
Drug therapy
The principles of pharmacological treatment are largely determined by the nature of complications arising from damage to the tissues of the outer ear. In order to relieve the symptoms of pathology and prevent the development of infectious inflammation, the following can be used:
- antibacterial drugs ("Amoxicillin", "Spiramycin") - prevent the multiplication of microbial pathogens in injured tissues;
- vasoconstrictor drops ("Tizin", "Sanorin") - eliminate puffiness in damaged skin and ear membrane;
- mucolytic agents ("Fluimucil", "ACC") - accelerate the process of evacuation of liquid secretions from the ear canal that occurs during inflammatory processes;
- anti-inflammatory drugs ("Otinum", "Fenazon") - relieve swelling and prevent the spread of foci of inflammation in the middle ear cavity.
After using ear drops, it is advisable to lay the ear canal with sterile cotton wool or gauze turunda.
Prophylaxis
Blood in the ears during cleaning occurs exclusively when the rules for conducting hygiene procedures are not followed. According to experts, it is impossible to use cotton swabs to cleanse the auditory canals. In addition, cleaning can be done no more than 1 time a month, subject to the following rules:
- dilute 3% hydrogen peroxide in boiled water in a 1: 2 ratio;
- heat the solution to 37-38 degrees;
- drip 2 drops of the prepared preparation into each ear;
- after 10 minutes, remove the liquid with gauze turundas.
Experts recommend using only hydrogen peroxide diluted in water, as the concentrated solution dehydrates the skin in the ear canal.Irritation of the tissues can cause dysfunction of the sulfur glands and the formation of plugs in the ears.