Diseases of the ENT organs can be characterized by an acute course or chronic, when clinical symptoms are present for more than 3 weeks. As for the leading symptom, it depends on the localization of the inflammatory process.
 A symptom when the throat hurts for a long time may be due to the defeat of the corresponding parts of the throat cavity or the development of diseases that are not associated with the pathology of the ENT organs.
A symptom when the throat hurts for a long time may be due to the defeat of the corresponding parts of the throat cavity or the development of diseases that are not associated with the pathology of the ENT organs.
To clarify the nature of the lesion, when the sore throat does not go away for 3 weeks, it is necessary to identify additional symptoms, collect an anamnesis of the disease, and find out what is the reason for the appearance of these signs.
The most typical reasons why a patient has had a sore throat for a month are as follows:
- The presence of hazardous substances in the inhaled air;
- Hypothermia;
- Exposure to pathogens;
- Long-term use of medications;
- Accidental or deliberate use of concentrated solutions, acid, vinegar;
- Traumatic injury;
- The presence of diseases accompanied by a decrease in immunity, dry mouth, and also characterized by a pain syndrome that radiates down the throat.
Pathology of ENT organs
Among the pathology of the ENT organs, manifested by the fact that the throat hurts for a long time, there are:
- Pharyngitis;
- Laryngitis;
- Tonsillitis;
- Sinusitis.
If your throat hurts for two weeks, this is usually not a cause for concern. This course of colds is most common among children, and is largely due to the patient's insufficient immunity. Prolonged course of ARVI or other diseases of the upper respiratory tract is quite widespread. In this case, the only danger is the development of complications, bronchitis, pneumonia, otitis media. However, in this case, other symptoms that are not related to the pathology of the throat come to the fore.
 If the throat hurts for three to four weeks, the second month there are unpleasant sensations when swallowing, you need to go to an appointment with an otolaryngologist and find out the reasons for this condition. In patients with chronic laryngitis and pharyngitis, besides the fact that the sore throat does not go away for a long time, there is a dry, barking, persistent cough. It is present both day and night, interfering with the patient's proper rest.
If the throat hurts for three to four weeks, the second month there are unpleasant sensations when swallowing, you need to go to an appointment with an otolaryngologist and find out the reasons for this condition. In patients with chronic laryngitis and pharyngitis, besides the fact that the sore throat does not go away for a long time, there is a dry, barking, persistent cough. It is present both day and night, interfering with the patient's proper rest.
Moreover, despite the severity of such a symptom, an objective examination of the throat cavity with pharyngitis reveals only minor changes that are manifested by hyperemia of the throat mucosa.
An additional symptom of laryngitis is a change in the timbre of the voice. He gets hoarse. With a severe course of the process, sound reproduction can be impaired so much that the disease is accompanied by a lack of voice. The reasons for this condition are damage to the vocal cords.
With the hypertrophic form of laryngitis, the so-called "singer's nodules" are formed on them, the growth of the epithelium the size of a pinhead, which interfere with the full-fledged work of the ligaments. Such changes can be caused by constant exposure to some unfavorable environmental factors, smoking, smoke content in the air, and the presence of dangerous impurities in it. Employees of certain workshops of chemical production, cement plants are exposed to such hazardous substances all day long.
The causes of laryngitis may be due to overstrain of this part of the larynx.
Most often, this symptom develops in vocalists, lecturers. As for the pain in the throat, patients describe it as tickling, scratching, rawness, and worsening at the end of the day. Over time, the condition of such patients worsens.
In this case, the symptomatology will be noted for as long as the provoking factors will be present for a long time. Quite often, the only way to improve the situation is to change professional activity. At the same time, rehabilitation processes can take a lot of time.
Chronic tonsillitis is a consequence of an acute process, when untimely incorrect treatment led to the fact that the throat hurts for more than 3 weeks. In this case, the picture is characteristic with pharyngoscopy. The tonsils are enlarged, covered with a greyish-dirty coating.
In chronic tonsillitis, the sore throat is not constant. Its presence is associated with the stage of the disease, remission or exacerbation. Most often, the deterioration of the patient's condition occurs in the autumn-winter period of time, it can be provoked by hypothermia, exacerbation of concomitant pathology. However, in a state of remission, there are changes in the throat cavity, characteristic of the inflammatory process in the tonsils, purulent plugs.
The inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses is accompanied by the presence of viscous discharge. When the patient is in a horizontal position, it flows down the back of the pharynx, irritating it. The result of such actions is the development of pain in the throat, cough. Without appropriate treatment, sinusitis is characterized by a long course. The throat may be sore for 3 to 4 weeks.
Local treatment and cough suppressants used in this situation do not improve the situation. Patients complain that nothing is helping. At the same time, procedures aimed at sanitizing these foci of infection will lead to a decrease in sore throat and coughing in the near future after appropriate treatment.
Infectious diseases
 Some infectious diseases can also cause long-term sore throat. The most common of these is infectious mononucleosis. In this case, the throat can hurt for 2 weeks or longer. It is the presence of pronounced symptoms during such a period that makes it possible to differentiate the disease from other acute viral respiratory infections, which can also be contracted by airborne droplets from an infected patient.
Some infectious diseases can also cause long-term sore throat. The most common of these is infectious mononucleosis. In this case, the throat can hurt for 2 weeks or longer. It is the presence of pronounced symptoms during such a period that makes it possible to differentiate the disease from other acute viral respiratory infections, which can also be contracted by airborne droplets from an infected patient.
An important role in the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus is played by the presence of additional signs:
- Enlargement of the cervical, axillary, inguinal lymph nodes;
- Prolonged fever;
- The presence of skin rashes;
- Enlargement of the liver and spleen;
- Detection of abnormal cells in blood tests;
Some signs of infectious mononucleosis can be detected within six months. Children's infections, measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever, rubella, transmitted by airborne droplets, can also be accompanied by an inflammatory process in the throat for several weeks.
Some sexually transmitted infections can cause this symptom to develop.
Syphilis, damage to the mucous throat with chlamydia, a gonococcal pathogen are pathological conditions that must also be taken into account when conducting differential diagnostics of conditions accompanied by a sore throat.
It is possible to diagnose this pathology only with the use of laboratory diagnostics, since the clinical manifestations are nonspecific. As for HIV infection, the weakening of immunity, characteristic of this disease, leads to the development of fungal, viral, bacterial lesions of the mucous membranes, including the throat.
Pathology of other organs

Diseases of other organs and systems can also be the reasons for the development of a sore throat.
Most often, the development of such a symptom is noted with such pathologies:
- reflux esophagitis;
- angina pectoris;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypothyroidism;
- hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the spine;
- anemia.
In addition, any pathology that requires prolonged use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, chemotherapy, leads to the development of an inflammatory or atrophic process in the mouth and throat. The consequence of this is the appearance of pain syndrome.
When the contents of the stomach are thrown back into the esophagus, the mucous membrane of the esophagus and pharynx is irritated with acidic contents. This irritating effect is characterized by a persistent sore throat that occurs after eating and when the patient takes a horizontal position. An esophagoscopy will reveal existing inflammatory diseases or birth defects.
Additional symptoms confirming the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract are the presence of dyspeptic complaints, belching, heartburn, abdominal pain, and stool disorder. Treatments prescribed for chronic gastritis, duodenitis, cholecystitis, or hiatal hernia will also reduce sore throat.
The first signs of diabetes mellitus are dry mouth, constant thirst. The consequence of this may be an inflammatory process in the pharynx, accompanied by the development of unpleasant sensations, perspiration and scratching. Very often, dry skin and mucous membranes are noted in patients with hypothyroidism. In this case, the swallowing process may be disrupted, which is also accompanied by the development of pain syndrome and a feeling of a lump in the throat.
Leukemia, as well as blood diseases, manifested by anemia, are accompanied by atrophic, ulcerative-necrotic processes of the oral mucosa, palatine tonsils.
 Additional symptoms are the flatness of the papillary layer of the tongue, burning pain in the tongue, a feeling of creeping, weakness, pallor of the skin. In all cases, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo a laboratory examination.
Additional symptoms are the flatness of the papillary layer of the tongue, burning pain in the tongue, a feeling of creeping, weakness, pallor of the skin. In all cases, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo a laboratory examination.
Similar symptoms can develop with chronic bleeding due to ulcerative processes in the intestines or heavy menstruation. Forced fasting or mental disorders, accompanied by refusal to eat, lead to hypovitaminosis and the development of a pathological process in the mouth and throat.
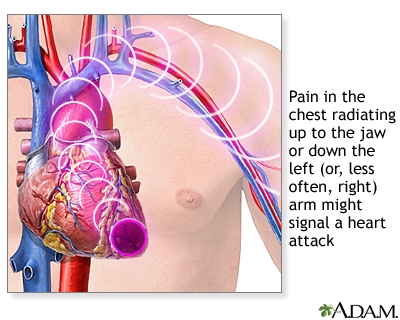
Angina pectoris or myocardial infarction can also be atypical and be accompanied by pain syndrome not behind the sternum or in the region of the heart, but characterized by a sore throat.
In the case of severe pain, deterioration, shortness of breath, such patients are subject to hospitalization and appropriate examination.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, radiculitis can also manifest themselves with a similar pain syndrome. At the same time, there is a crunch when turning the neck, an increase in pain syndrome when moving, turning the head. The pathology of the gums, the process of teething and inflammatory processes in them also do not exclude the appearance of prolonged pain in the throat or oral cavity.
Tumor processes localized in the larynx, pharynx, thyroid gland are characterized by a feeling of a lump in the throat or the presence of a foreign body. Often, the first symptom of such diseases is a change in the timbre of the voice, the appearance of its hoarseness. Additional symptoms in this case may be emaciation, weakness, sweating, prolonged subfebrile condition. Similar symptoms are present when the mucous membrane of the throat is affected by a tuberculous pathogen. At the same time, there is an increase in regional lymph nodes, confirming the bacterial nature of the pathogen.
The nature of the lesion, in which a sore throat may occur for 2 months, must be clarified, even if this condition is not accompanied by a significant deterioration in the general condition. To do this, you need to consult with an otolaryngologist who will conduct an objective study of the pathology of the ENT organs. In the absence of such diseases, the therapist will help determine the necessary examinations. Depending on the alleged pathology, they will include laboratory and apparatus examinations.