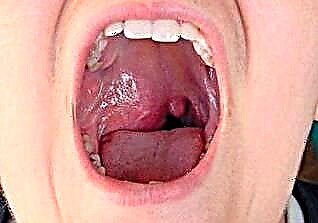
Adenoids are too strong growth of the unpaired tonsil, located on the back wall of the nasopharynx. This organ is part of the immune system and is part of the so-called pharyngeal ring of the tonsils, which protects the body from foreign particles entering through the mouth and nose. In childhood, there is a violation associated with the pathologically enhanced multiplication of cells of the pharyngeal tonsil, which leads to an increase in its size.
 Inhalation for adenoids in children will help to cope with this disease at an early stage of development. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between the adenoids themselves (growth of the tonsil) and adenoiditis, which is the most frequent complication and consequence of this violation.
Inhalation for adenoids in children will help to cope with this disease at an early stage of development. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between the adenoids themselves (growth of the tonsil) and adenoiditis, which is the most frequent complication and consequence of this violation.
Adenoiditis is an inflammation of the tissues of the pharyngeal tonsil. It can be of both bacterial and autoimmune nature, characterized by a number of pathological symptoms and provoking the occurrence of other diseases of the respiratory system.
Inhalation action
The effect of inhalation of drugs on a pathologically enlarged amygdala is mainly symptomatic. Restraining the progression of the disease improves the general condition of the child, reduces the severity of the manifestations of this disorder. This is achieved through the following inhalation effects:
- improvement of lymphatic outflow and blood microcirculation;
- decrease in the severity of edematous phenomena on the mucous membrane of the tonsils;
- prevention of inflammatory lesions;
- strengthening and stimulation of local immune defense.
If the inflammatory process has already joined the proliferation of the tonsils, the disease is characterized as adenoiditis. Inhalation in this case is also used quite widely, but now their main task is to combat the symptoms caused by inflammation:
- suppression of too frequent coughing attacks;
- moisturizing periodically drying out mucous membranes;
- softening it, which relieves tissue irritation;
- decreased production of nasal mucus;
- liquefaction and stimulation of the removal of already formed mucous deposits;
- prevention of the transition of the inflammatory process to other parts of the respiratory system.
How and with what to carry out inhalation?
Steam inhalation is not used for adenoids. The high temperature of the drugs leads to local vasodilation, which increases the edema of the mucous membrane and stimulates further growth of the tonsil tissue.
The optimal technique for inhalation administration of drugs to children with adenoids is the use of nebulizers. Here are some recipes to help with adenoids in children:
- Sodium chloride solution. It is easier to buy it in a ready-made form at the pharmacy. For 1 inhalation, you will need 5 ml of liquid, which does not need to be heated or additionally diluted with water before filling the nebulizer.
- Saline solution is easy to prepare yourself at home. To do this, take 1 large spoonful of kitchen salt for 300 ml of warm boiled water. It is useful to replace it with commercial sea salt. But salt with iodine potassium compounds (iodized) is not recommended to be used - these substances irritate the mucous membrane.
- Soda-saline solution for inhalation contains half a teaspoon of baking soda and a small spoonful of salt in 200 ml of water. It is also useful to drop 1 drop of iodine there. Make sure to completely dissolve the salt and baking soda. These solutions cannot be used in membrane nebulizers - they will disable the device.
- It is recommended to inhale mineral waters to soften the mucous membrane. Use slightly alkaline brands (for example, Essentuki and Narzan), but first get rid of the bubbles of carbon dioxide that may be contained in these and other mineralized waters.
- Pharmacological drugs, the action of which is aimed at thinning and removing mucus in inflammation of the adenoids. These are drugs such as Lazolvan, ACC, Ambrobene, etc. Mucolytics and expectorants are often sold in disposable nebulizer bottles, but if the child uses a personal device, then before refueling, the drug must be diluted with an equal volume of saline.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Shown here are inhalations with pharmacy extracts of medicinal herbs. An example is the drug Rotokan - a mixture of chamomile, yarrow and calendula, which gently relieves intense inflammation on the amygdala.
- Chlorophyllipt is a strong herbal antiseptic that can
 used for inhalation if adenoiditis is infectious in nature. Before use, a tenfold volume of saline must be added to a 1% solution of the drug.
used for inhalation if adenoiditis is infectious in nature. Before use, a tenfold volume of saline must be added to a 1% solution of the drug. - Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs that have an anti-inflammatory, moisturizing, disinfecting effect. Monopreparations and mixtures of coltsfoot, string, perforated St. John's wort, oak bark, mint, currant leaves, calendula, viburnum color, etc. are used. Phytopreparations are not inhaled using mesh nebulizers.
Benefits of using nebulizers
- The technique for performing this procedure is very simple, and even a child aged 2-3 years can master it.
- The drug compound is delivered exactly to the site of exposure. According to the World Health Organization, 98% of the drug is consumed by nebulizer inhalation.
- The previous point also determines the economic benefits of using nebulizers. A significant reduction in the loss of the active substance during its delivery allows the use of a smaller volume of the drug to obtain the same therapeutic effect. That is, the vial with the medicine will last for a longer period of treatment.
- Nebulizers create an air suspension of the drug without the use of additional propellant substances.
Which nebulizer should you use?
The type of device (compressor, ultrasonic or membrane) is determined primarily by the drug that is planned to be inhaled. In the description of the recipes above, there are several indications of the inapplicability of certain models.
In addition, nebulizers differ in the diameter of the drug particles created in the air suspension. This parameter is called dispersion. The higher the dispersion, the smaller the size of the drug substance particles and the deeper they are able to penetrate into the deeper parts of the respiratory system.
The pharyngeal tonsil, the growth of which is called adenoids, is located at the very entrance to the respiratory tract - on the back wall of the nasopharynx. Therefore, with inhalations aimed at treating this pathology, it is necessary that the active compounds settle in the upper parts of this system.
 That is, it is preferable to use those models of nebulizers that form coarse aerosols. This feature is primarily characterized by devices that use compressor technology for air injection under pressure to create air suspension. But ultrasonic and membrane nebulizers, too, should not be rejected right away. Many modern models have an option to adjust the diameter of the particles created. It is necessary to adjust it in such a way that the size of the microdroplets of the pharmaceutical preparation in the aerosol is 10 microns or more.
That is, it is preferable to use those models of nebulizers that form coarse aerosols. This feature is primarily characterized by devices that use compressor technology for air injection under pressure to create air suspension. But ultrasonic and membrane nebulizers, too, should not be rejected right away. Many modern models have an option to adjust the diameter of the particles created. It is necessary to adjust it in such a way that the size of the microdroplets of the pharmaceutical preparation in the aerosol is 10 microns or more.
The effectiveness of nebulizer inhalation
Adenoids are an anatomical change in the nasopharyngeal tonsil.Therefore, inhalation effects in this violation do not always lead to a positive result. Everything here is determined by the degree of progression of the disease:
- Stage 1: the nasopharyngeal tonsil overlaps only the upper edge of the vomer - the bone plate, which is one of two parts that form the bony septum of the nasal passages;
- Stage 2: the amygdala covers more than 60% of the coulter height;
- Stage 3: the opener is almost completely closed by the overgrown tonsil.
Inhalation helps mainly in the first stage of the development of pathology.
At the same time, chronic tonsil hypertrophy can be compensated for by removing edematous phenomena on the mucous membrane, preventing the inflammatory process and inhibiting further increase in this organ. But, unfortunately, in most cases these measures will be effective only for some time. If the child already has a tendency to adenoids, then the progression of the disease is difficult to avoid.
Nevertheless, correct treatment, including nebulizer inhalation, begun at the earliest stage of the pathology, can significantly slow down its development. Thus, it turns out to gain time before the transition of the disease to stages 2 and / or 3. If a child reaches the age of puberty during this period and successfully passes through it, then, thanks to a serious hormonal change in his body, there are great chances for the symptoms of adenoids to subside on their own.
In the case when the pathology is already determined at 2-3 stages, adenoids and adenoiditis begin to provoke the appearance of such complications as:
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- hearing impairment;
- violations of the physical development of the child;
- difficulty breathing;
- chronic inflammation of the lungs, bronchi, sinuses;
- persistent rhinitis; sleep disorders, etc.
At this stage, nebulizer inhalations are no longer effective, and the child's treatment consists in surgical removal of the adenoids.

 used for inhalation if adenoiditis is infectious in nature. Before use, a tenfold volume of saline must be added to a 1% solution of the drug.
used for inhalation if adenoiditis is infectious in nature. Before use, a tenfold volume of saline must be added to a 1% solution of the drug.