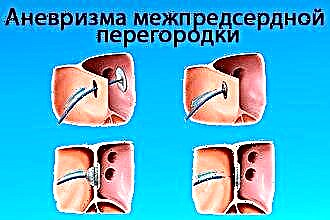
Atrial septal aneurysm in children is rarely diagnosed. Until now, modern medicine cannot name the exact causes of this pathology. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the disease has no characteristic symptoms and can be confirmed only after a comprehensive diagnosis.
What it is?
 Atrial septal aneurysm is a dangerous pathology that can lead to a rapid death. That is why a child who has been diagnosed with a disease must be constantly monitored by a cardiologist. After the patient reaches the age of 1 year, the pathology is eliminated by surgery.
Atrial septal aneurysm is a dangerous pathology that can lead to a rapid death. That is why a child who has been diagnosed with a disease must be constantly monitored by a cardiologist. After the patient reaches the age of 1 year, the pathology is eliminated by surgery.
Atrial septal aneurysm refers to small cardiac abnormalities. This pathology causes a change in the structure of the walls of a large vessel, against the background of which a protrusion of a separate part of the heart is formed. Bulging is observed from the right or left atrium.
Medicine has not yet established the exact causes of the disease. One of the main assumptions regarding the development of this deviation in the work of the heart is the abnormal formation of connective tissues in a child during his intrauterine development, caused by an infection. In addition to this version, doctors do not exclude a hereditary factor in the transmission of the disease.
Atrial septal aneurysm in children almost never causes heart failure. This is due to the fact that with the disease there are no serious disruptions in the blood supply system through the heart arteries. The aneurysm is connected to the left ventricle of the heart using a small muscle reservoir. That is why there are no visual disturbances in the child's condition, he does not experience pain, discomfort.
But over time, the pathological protrusion becomes thinner and can lead to rupture. The aggravation of the situation can provoke great physical exertion, unhealthy diet, stressful situations. After the rupture of the atrial septal aneurysm, heart failure occurs, which leads to the death of the child.
The disease can manifest itself as follows:
- Pathological pulsation in the area of the third intercostal space. If you listen to the baby in a supine position, the pulsation will be like the sound of a swinging wave. You can determine it even without listening. Feeling the heart area with your fingers, you can find pathological shocks caused by an aneurysm in a small patient.
- Parietal blood clots, which occur as a result of impaired blood circulation. Their formation leads to the disappearance of pathological pulsation.
- Violation of the heart rhythm. This manifestation is most often observed in adolescents who actively play sports or lead an unhealthy lifestyle, smoke and drink alcohol.
Currently, there are three forms of aneurysm. The most common is the protrusion of the vessel wall from the left to the right atrium. The second form of pathology is less common and manifests itself in the form of bulging of the walls from right to left. The third is S-shaped.
Dangerous signs
An aneurysm of the left ventricle of the heart in an uncomplicated course may not manifest itself in any way. Very often, the defect is found only during research.
At the site of the formation of the aneurysm, a hole appears on the septum, which disrupts blood flow through the vessels and arteries. Each systolic contraction leads to the ingress of blood not only into the left ventricle, but also partially into the right one. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the load on the right atrium, where compensatory hypertrophy begins to develop over time. Gradually, it affects the entire ventricle.
An aneurysm of the interventricular septum of the heart provokes the release of a large volume of blood into the lungs, which leads to an increase in the load on the vessels and the onset of symptoms of pulmonary hypertension.
With this ailment, young patients may experience the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath, causing asthma and pulmonary edema.
- Painful sensations in the chest, which are characterized by a pulling, aching character.
- Recurrent chest pain. This symptom should be the reason for immediate medical attention.
- Fatigue, weakness. Children constantly want to rest, lie down, they do not have the strength to play and do ordinary things.
- In newborns, a symptom of the disease is frequent regurgitation, which occurs as a result of the protrusion of the heart vessel onto the digestive tract.
- Child sweats profusely, even when in a cool room.
- Headache. This symptom is noted in older children during sports or active games.
Dangerous signs that should alert a parent and induce an ambulance call include:
- a sudden change in the color of the skin - from pale to cyanotic;
- severe coughing up blood;
- swelling of the veins in the neck;
- severe vomiting, along with which blood clots come out;
- sudden loss of consciousness.
All these dangerous symptoms may indicate a ruptured aneurysm, which in most cases leads to heart failure and rapid death.
Features of pathology in a newborn
An aneurysm of the interatrial septum in a newborn is primarily manifested by a weak cyanosis of the skin. The rest of the symptoms occur in a child at the age of 3-4 months. The final diagnosis can be made to the patient upon reaching 2 years of age. The small size of the defect in the heart vessel does not give symptoms, so the disease can only be determined through diagnosis.
With an increase in the defect, the size of which becomes more than 15 mm, an aneurysm of the MPP in a newborn may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Lagging in physical development. The patient may be underweight and delayed in psychomotor development.
- A decrease in the body's defenses, which is the cause of frequent viral diseases.
- Pathological protrusion of the heart, which can be determined by palpation.
Therapy
Before treating a child, he must undergo certain diagnostic procedures:
- Auscultation - listening to the heart with a stethoscope. This device will allow you to hear noises if there is a possibility of an anomaly;
- ECG. It is performed in order to check the work of the heart, it makes it possible to detect rhythm disturbances;
- Ultrasound. This diagnostic method is safe and informative enough. It allows you to detect bulging of the interatrial septum, as well as determine fluctuations in the cardiac cycle.
Treatment depends on the rate of growth and increase in the size of the formation. With the progression of the disease, the patient is shown surgical intervention, which involves replacing the damaged section of the vessel with an artificial graft.
Small aneurysms rarely rupture the heart vessel and can be treated with medication. Medication therapy includes antihypertensive drugs, which are also used to stabilize blood pressure. Therapeutic measures should be aimed at normalizing the work of the heart muscle, establishing a rhythm, and improving metabolic processes in the myocardium.
Treatment is not complete without magnesium preparations. The role of this trace element in the formation of collagen fibers is difficult to overestimate.Magnesium has an antiarrhythmic effect, contributes to the contraction and relaxation of heart cells. That is why it is included in complex therapy for rhythm disturbances.
 Treatment with magnesium preparations consists in taking "Magnerot" three times at a dosage of 0.5 g at a time. The duration of such therapy is 1 week. After that, take 25 g of this drug for 5 weeks. The use of "Magne B6" is also required. The course of treatment is 1.5-2 months. In this case, the dosage depends on the weight of the child.
Treatment with magnesium preparations consists in taking "Magnerot" three times at a dosage of 0.5 g at a time. The duration of such therapy is 1 week. After that, take 25 g of this drug for 5 weeks. The use of "Magne B6" is also required. The course of treatment is 1.5-2 months. In this case, the dosage depends on the weight of the child.
For antioxidant protection and membrane stabilizing effect, L-carnitine, Cyto-Mac, Coenzyme Q10 are used. Metabolic therapy can last for about 1.5 months. Moreover, it must be repeated several times a year, as a rule, two or three are enough.
To improve metabolism, it is recommended to take vitamins PP and group B. Vitamin therapy is carried out in a two-month course, with repetitions up to 3 times a year.
 It is also possible to use beta-blockers, glycosides and anticoagulants. The former help to reduce the heart rate. Glycosides and anticoagulants can be prescribed preoperatively.
It is also possible to use beta-blockers, glycosides and anticoagulants. The former help to reduce the heart rate. Glycosides and anticoagulants can be prescribed preoperatively.
Additionally, you should adhere to non-drug treatment, the essence of which is as follows:
- It is necessary to properly organize the child's day regimen, provide him with normal sleep, walks in the fresh air, and proper rest.
- Particular attention should be paid to the baby's nutrition, it should be balanced and as healthy as possible.
- It will be useful to carry out hydrotherapy or balneotherapy.
- Different types of massage have a very good effect.
- Physiotherapy will also be beneficial, especially when it comes to electrophoresis using magnesium.
Small aneurysms can be treated with folk remedies. But they must be used only under the supervision of the attending physician. In no case should you conduct experiments on your own, especially if the pathological formation has reached a large size.
From the recipes of traditional medicine, the collection of herbs such as rose hips, Valerian officinalis, hawthorn and marsh calamus has proven itself perfectly. To prepare the product, you must take 1 tbsp. spoon of each component, and pour the raw material with boiling water (0.5 l). After the infusion has stood for 2-3 hours, it is filtered, and 1 teaspoon of the broth is diluted in a glass of water. Treatment is carried out three times a day.
Forecast
In order to prevent the transition of the disease to a more severe form, you should regularly undergo an examination with the baby with a local pediatrician and cardiologist. It is also periodically necessary to do an ultrasound scan and perform an ECG. Such measures will allow you to control the dynamics of the disease, and take timely action in order to minimize possible complications.
In general, the prognosis for such an anomaly is favorable. Pathology does not affect the development of the baby, and rarely causes discomfort. Aneurysm rupture is diagnosed in 10% of patients. In this case, the survival rate after the operation is about 80%.
Many parents who have faced such a problem are concerned about the issue of their child's attendance at physical education classes and sports sections. Permission for this kind of training must be given by a cardiologist. The specialist makes a decision based on the results of the examination, taking into account the size of the anomaly and the accompanying changes in the work of the heart.
Prevention is relevant only at the time of planning and carrying a child. The expectant mother should monitor her health, undergo the necessary examinations and pass the appropriate tests to detect infections. This should be taken especially seriously by those whose relatives suffer from heart disease. During pregnancy, it is important to undergo an ultrasound scan of the fetus several times. You also need to forget about bad habits in the form of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. In the first trimester, you should do everything possible to avoid infectious diseases (ARVI or flu). For this, it is important to eat right, walk daily, and minimize the time spent in crowded places.