The difference between tonsils, tonsils and adenoids remains a mystery to many. Some people think that they are one and the same, believing that they are synonymous words.
In fact, every person has an accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx, it is called tonsils, tonsils, and even adenoids. They are the periphery of the lymphatic system - this is a kind of protective barrier against harmful microorganisms from the environment.
What are the differences
 The tonsils or tonsils come from the same embryonic tissue rudiment - lymphoid tissue with a porous structure.
The tonsils or tonsils come from the same embryonic tissue rudiment - lymphoid tissue with a porous structure.
They are formed by lymphoid follicles, consisting of lymphocytes of different "ages". The follicles are separated by tissue layers (many blood vessels pass through these tissues, for example, the tonsillar artery), they cover the entire surface of the tonsils. It is due to the work of these follicles that the body produces lymphocyte cells, which are responsible for performing a protective function.
Due to their porous structure, the tonsils have depressions called lacunae. On the tonsils of each type, their number reaches twenty. Their task is to help the immune system recognize harmful microorganisms among the incoming foreign elements. On their surface, pathogenic bacteria are captured and further destroyed. Thus, the body protects itself from further spread of the inflammatory process downstream into the respiratory tract.
Tonsils are of several types:
- Paired: these include the palatine and tubal tonsils. Tubal tonsils are the smallest in volume, based on diffuse lymphoid tissue and nodules. Their work is aimed at protecting the hearing aid.
 Unpaired: pharyngeal and lingual. Pharyngeal - visually representing several balls from the mucous membrane, the epithelium of which is covered with the so-called cilia. The lingual amygdala appears to be split in two due to a line running down the middle, which can be seen if the tongue is pushed out strongly - the obvious tuberosity at the base of the tongue is the lingual amygdala.
Unpaired: pharyngeal and lingual. Pharyngeal - visually representing several balls from the mucous membrane, the epithelium of which is covered with the so-called cilia. The lingual amygdala appears to be split in two due to a line running down the middle, which can be seen if the tongue is pushed out strongly - the obvious tuberosity at the base of the tongue is the lingual amygdala.
Glands and tonsils are words that have different roots, origins, but the same meaning. The word "tonsils" come from the Latin word meaning "gland". The word "amygdala" has an ancient Greek origin and in translation sounds practically the same - "almond" due to the fact that it visually resembles them.
What is the difference between tonsils and glands? It lies only in the fact that the tonsils (a common name for medical institutions, academia) are often called glands by the people. This causes confusion and unnecessary questions, but these are just different names for the same organ.
What are adenoids
One of the types of tonsils, that is, tonsils, is the pharyngeal tonsil. This is an unpaired gland, covered with ciliary epithelium, located just above the back of the pharynx, near the fornix of the nasopharynx. With a disease, the development of an inflammatory process, the pharyngeal tonsil changes and increases in size.
It is such a hypertrophied inflamed gland that is called adenoid, and the process of inflammation itself is adenoiditis. Often the appearance of adenoids occurs due to diseases of the nasopharynx. It is difficult to see them without the help of special equipment, which makes it difficult to diagnose. They can be seen only with severe hypertrophy.
If a person is not infected, then he does not have adenoids either - the tonsils function normally and do not increase in size.

There are three levels of the inflammatory process of adenoiditis:
- The first level is a slight increase in the size of the amygdala. At this stage, the disease is problematic to diagnose due to the fact that this level practically does not cause discomfort, remaining unnoticed. Snoring may occur - due to sleep in one position, in which the lumens of the nasal passages overlap.
- The second level is the average enlargement of the glands. Overlapping of half of the nasal passages, which may cause asthma attacks, difficulty breathing through the nose. A person begins to breathe through his mouth more and more often, which increases the chances of getting any disease.
- The third level is rarely seen. Complete overlapping of the nasal passages. Breathing is possible through the mouth, which again creates additional opportunities for infection. The pressure in the middle ear changes, which leads to the development of otitis media, hearing problems. The problem is solved only with the help of a surgical operation - removal of the adenoids.
Causes of diseases and their symptoms
 Inflammation of the tonsils can occur for many reasons. Knowing them, one can assume the development of the disease and take due precautions.
Inflammation of the tonsils can occur for many reasons. Knowing them, one can assume the development of the disease and take due precautions.
The main causes of the disease of the tonsils (tonsils):
- contact with infected people;
- hypothermia - sudden temperature changes, prolonged exposure to frost;
- inflammation of the mucous tissue of the mouth or nasal cavity due to harmful climatic conditions or work environment;
- caries;
- frequently consumed junk food;
- sinusitis;
- lack of vitamins or other necessary elements in the body;
- weakened immunity during and after illness;
- genetic predisposition to diseases of the tonsils.
Signs of the development of glandular disease:
 a change in the shape of the glands - their size increases, the pink tint changes to bright red;
a change in the shape of the glands - their size increases, the pink tint changes to bright red;- possible yellow bloom;
- the appearance on the tonsils of abscesses with a bad smell;
- sore throat due to large innervation (the presence of a large number of nerve endings in the tonsils) and when eating;
- change of state - before having hardness, they turn into loose, soft;
- the appearance of scars between the tonsils and the palate;
- enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes.
Common signs include weakness, sore throat and headache, bone aches throughout the body, and fever.
Treatment
Treatment of glandular diseases should be started immediately after their appearance, otherwise it can lead to serious complications associated not only with them, but also with other organs. With the development of the disease, problems with the kidneys, with the cardiovascular system, and inflammation of the joints are possible. Immediately, if symptoms are found, it is required to consult a doctor and begin the treatment prescribed by him.
There are several ways to treat tonsil diseases:
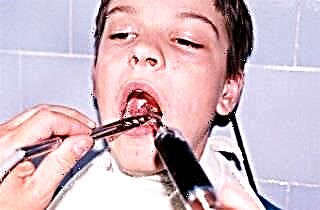 Vacuum flushing - cleansing the secretions collected in the throat. It is carried out for patients with a chronic form of the disease.
Vacuum flushing - cleansing the secretions collected in the throat. It is carried out for patients with a chronic form of the disease.- Coagulation - sealing lacunae (depressions in the structure of the amygdala). They are needed to trap harmful elements so that they do not get further into the respiratory tract. The essence of coagulation is to avoid the ingress of harmful microorganisms there. It is used in the advanced stage of the disease.
- Treatment with laser instruments.
- Treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs; vitamin course, pain relievers.
- Removal of tonsils is the most radical method of treatment used when methods without surgical intervention are impossible.
- Cryodestruction is a less radical measure of treatment than removal of the tonsil - it remains in place, only it decreases in volume.
Before proceeding to radical measures and surgical operations, it is better to take a course of taking antibiotics and vitamins. Removal of the tonsils should take place when there are no other options. The tonsils are an important part of the immune system - it is undesirable to lose it in any case.
 At the initial stage of inflammation, you can rinse your throat and nose with special antiseptic agents. An important point is the general improvement in the state of the body.Inflammatory processes often appear precisely because of reduced immunity after an illness.
At the initial stage of inflammation, you can rinse your throat and nose with special antiseptic agents. An important point is the general improvement in the state of the body.Inflammatory processes often appear precisely because of reduced immunity after an illness.
Therefore, its strengthening with the help of a vitamin course and immunostimulants will help to get rid of tonsil diseases. Also, harden the body, do not forget about good sleep, exclude harmful foods from the diet, avoid contact with infected people and sudden temperature changes. Take care of your health in advance, and take action at the first signs of illness.

 Unpaired: pharyngeal and lingual. Pharyngeal - visually representing several balls from the mucous membrane, the epithelium of which is covered with the so-called cilia. The lingual amygdala appears to be split in two due to a line running down the middle, which can be seen if the tongue is pushed out strongly - the obvious tuberosity at the base of the tongue is the lingual amygdala.
Unpaired: pharyngeal and lingual. Pharyngeal - visually representing several balls from the mucous membrane, the epithelium of which is covered with the so-called cilia. The lingual amygdala appears to be split in two due to a line running down the middle, which can be seen if the tongue is pushed out strongly - the obvious tuberosity at the base of the tongue is the lingual amygdala. a change in the shape of the glands - their size increases, the pink tint changes to bright red;
a change in the shape of the glands - their size increases, the pink tint changes to bright red; Vacuum flushing - cleansing the secretions collected in the throat. It is carried out for patients with a chronic form of the disease.
Vacuum flushing - cleansing the secretions collected in the throat. It is carried out for patients with a chronic form of the disease.

