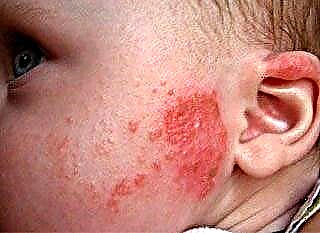
Angina is called inflammation of the tonsils and the mucous membrane of the pharynx. In preschool children, the disease occurs very often, which is associated with a low reactivity of the body. How does doctor Komarovsky treat sore throat in children?
 The renowned practicing pediatrician is convinced that the therapy of ENT diseases can only be carried out after an accurate diagnosis.
The renowned practicing pediatrician is convinced that the therapy of ENT diseases can only be carried out after an accurate diagnosis.
Local and general symptoms of tonsillitis are similar to the manifestations of scarlet fever, measles and other pathologies. To find out the nature of the inflammation, you need to be examined by an experienced specialist. Only by the results of bacterial culture from the throat can the causative agent of the infection be identified and the optimal course of treatment can be determined. The earlier therapy is started, the lower the risks of developing post-infectious complications will be.
What is Immunity?
Immunity is the body's ability to resist pathogenic viruses, protozoa and bacteria. Human body tissues are made up of several groups of cells that perform specific functions. For example, lymphadenoid tissues are involved in the formation of immune defenses. They are localized in the thymus gland, small intestine, and bone marrow. You can visually see lymphadenoid formations (palatine tonsils) in a child in the throat behind the palatine arches.
Absolutely all substances that enter the body with air or food are "controlled" at the level of the tonsils. The pale pink paired organs regularly encounter foreign agents, some of which are harmful. Tonsillitis is a disease that occurs when the tonsils (tonsils) are damaged by pathogenic bacteria or viruses.
Common pathogens include:
- rhinoviruses;
- streptococci;
- herpes viruses;
- staphylococci;
- adenoviruses;
- pneumococci.
As a result of the active reproduction of pathogens in the ENT organs, inflammatory processes occur, accompanied by hyperemia and tissue edema. The child has general signs of intoxication and an increase in lymph nodes, which indicates the development of a pathogenic flora in the body.
Catarrhal sore throat
 Catarrhal sore throat is one of the most common infectious diseases found in children. A relatively mild form of pathology with timely and competent treatment passes without complications within 5-7 days. The infection is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets and by contact through household items, toys, etc.
Catarrhal sore throat is one of the most common infectious diseases found in children. A relatively mild form of pathology with timely and competent treatment passes without complications within 5-7 days. The infection is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets and by contact through household items, toys, etc.
Dr. E.O. Komarovsky claims that the clinical manifestations of ENT disease in children are more pronounced than in adults. This is due to the sensitization of the child's body, i.e. a tendency to allergic reactions. The main symptoms of inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa include:
- an increase in the palatine tonsils;
- sore throat and head;
- hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- painful swallowing;
- temperature increase;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- general weakness; lack of appetite.
Important! With untimely treatment of the disease, inflammation of the salivary glands occurs, which leads to intense salivation.
How is angina treated in children? Komarovsky warns that therapy for patients under the age of 2 years should be carried out under the constant supervision of a physician, i.e. in the hospital. Self-medication often causes the progression of the disease and the development of local and sometimes systemic complications. The child may have seizures, shooting pains in the ears, rhinitis, pyelonephritis, etc.
It should be noted that catarrhal angina can provoke the development of purulent processes in the tonsils. Delayed treatment of pathology leads to an increase in the number of pathogens in the tonsils and a decrease in local immunity. If the catarrhal processes are not stopped within 3-4 days, the patient may develop follicular or lacunar tonsillitis.
Angina in infants
 Newborns and infants are more susceptible to infectious diseases than others, which is associated with the lack of adaptive, i.e. acquired immunity. It is the presence of immunological memory that allows the human body to suppress the development of pathogens. But since a baby has never previously encountered bacteria and viruses that provoke tonsillitis, he will certainly get sick.
Newborns and infants are more susceptible to infectious diseases than others, which is associated with the lack of adaptive, i.e. acquired immunity. It is the presence of immunological memory that allows the human body to suppress the development of pathogens. But since a baby has never previously encountered bacteria and viruses that provoke tonsillitis, he will certainly get sick.
Catarrhal sore throat in infants is almost asymptomatic, so it is not always possible to start treatment on time. The development of ENT disease can only be signaled by such clinical manifestations as:
- subfebrile fever;
- tearfulness and poor sleep;
- refusal to eat;
- hyperemia of the oropharyngeal mucosa.
Improper treatment of tonsillitis can lead to the development of rheumatic fever, characterized by damage to the heart muscle and joints. If the disease is not diagnosed in time, the catarrhal processes in the tonsils will turn into purulent inflammation within 2-3 days. Due to the hypersensitivity of the child's body to antibacterial drugs, it will not be possible to cure purulent sore throat immediately, but within at least 7-10 days.
Baby care
Drug therapy is only one of the components of the treatment of infectious-allergic sore throat. So that later the child does not have serious complications, he needs to provide special care. Compliance with the pediatrician's recommendations does not guarantee instant elimination of the symptoms of the disease, but minimizes the risks of post-infectious consequences:
- bed rest - prevents serious stress on vital systems and organs during an exacerbation of inflammatory processes;
- plentiful drinking - prevents dehydration of the body and intensification of symptoms of general intoxication;
- regular ventilation and cleaning - minimizes the risks of irritation of the mucous throat with dry air;
- rubbing the breast with menthol ointment - helps to relieve discomfort in the throat.
Important! The principles of treating infants with folk remedies must first be agreed with the pediatrician.
It is recommended to give children fortified drinks, the use of which makes it possible to replenish the lack of nutrients in the body. Warm tea with honey, herbal decoction, fresh fruit juice and milk are the best immune stimulants.
Principles of therapy
To eliminate catarrhal processes in a child's throat, it is necessary to provide comprehensive treatment with the use of pathogenetic and palliative drugs, i.e. symptomatic action. The drugs of the first group are aimed at destroying the pathogenic flora, and the second - at stopping the general and local symptoms of pathology.
Treatment of children under the age of 2 years is best carried out in stationary conditions under the supervision of a specialist.
As part of the drug therapy, the patient is prescribed the following types of drugs:
- antibiotics - destroy pathogenic microbes;
- antiviral agents - prevent the multiplication of viruses;
- local antiseptics - disinfect the throat mucosa;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - accelerate the regeneration of lymphadenoid tissues;
- antipyretics - eliminate subfebrile and febrile fever.
Only the attending physician can prescribe medications, based on the patient's history and the results of bacterial culture from the pharynx. An overdose of antibiotics can lead to a deterioration in health and the development of late post-infectious complications, 50% of which are systemic.
Choosing an antibiotic
 What antibacterial drugs should be used to treat angina in children? According to E.O.Komarovsky, at the initial stages of the development of the disease, it is more expedient to use penicillins. They are highly resistant to streptococcal infections, which often cause serious post-infectious complications. In about 70% of cases, angina in children is provoked by beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
What antibacterial drugs should be used to treat angina in children? According to E.O.Komarovsky, at the initial stages of the development of the disease, it is more expedient to use penicillins. They are highly resistant to streptococcal infections, which often cause serious post-infectious complications. In about 70% of cases, angina in children is provoked by beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
The dosage of drugs is determined by the patient's weight, the form of sore throat and the degree of spread of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx.
On average, the course of antimicrobial therapy is 7-10 days. The most effective and safest antibiotics include:
- "Amoxicillin";
- Augmentin;
- Ecoclave.
Speaking about angina, you need to remember that it occurs against the background of the development of nonspecific bacteria. Some of them are capable of producing a special enzyme that protects them from the effects of penicillin drugs. In the presence of allergies or ineffectiveness of the drug, penicillins are replaced with macrolides: "Hemomycin", "Sumamed", "Macropen", etc.
If, before the development of tonsillitis, the child was repeatedly treated with the drugs of the above groups, the pathogens could develop resistance to the active components of antibiotics. In case of ineffectiveness of penicillins and macrolides, the child is prescribed cephalosporins: "Suprax", "Cefurus" and "Zinnat". They are quite toxic and therefore often cause allergic reactions. However, it is cephalosporins that have a wide spectrum of action and are insensitive to beta-lactamases and penicillinases - enzymes that inactivate penicillin drugs.
Local treatment
Catarrhal inflammation of the throat is characterized by damage to only the superficial layers of lymphadenoid tissues. According to E.O. Komarovsky, it is possible to stop pathological processes with the help of local antiseptic solutions. They contribute to the regression of inflammation and the acceleration of the processes of epithelialization of the mucous membrane, due to which discomfort in the throat, hyperemia and swelling pass away.
Important! Do not gargle and irrigate the throat for children under the age of 2-2.5 years.
 In pediatric therapy, the most effective and safe topical drugs include: "Chlorfillipt"; Miramistin; "Normoflorin"; Furacilin; Stopangin.
In pediatric therapy, the most effective and safe topical drugs include: "Chlorfillipt"; Miramistin; "Normoflorin"; Furacilin; Stopangin.
In the absence of pharmacy products, you can prepare a soda rinse solution. Irrigation of the throat with soda increases the concentration of alkali in the mucous membrane, which is an unfavorable environment for the development of bacteria. Regular rinsing with a non-concentrated soda solution for 2-3 days will eliminate local manifestations of the disease.