The duration of a sore throat usually does not exceed 7 days. In addition, the catarrhal form proceeds quite easily and is accompanied by a low-grade fever. Often, other forms of acute tonsillitis are characterized by a mild course. At the same time, acute tonsillitis caused by hemolytic streptococcus A or staphylococcus is isolated in a separate group and is considered a very dangerous pathology. This is due to the peculiarities of the course of the disease, as well as its predictions. With incorrect, untimely treatment, as well as in the presence of other predisposing factors, such a sore throat can lead to the development of serious complications, and subsequently even disability.
Early complications
 Complications after angina in children can be early and delayed, developing a few weeks after suffering from acute streptococcal tonsillitis. Early complications of angina are usually local in nature. In this case, the consequences of a sore throat are most often the following:
Complications after angina in children can be early and delayed, developing a few weeks after suffering from acute streptococcal tonsillitis. Early complications of angina are usually local in nature. In this case, the consequences of a sore throat are most often the following:
- paratonsillar abscess;
- purulent lymphadenitis;
- phlegmon;
- laryngeal edema;
- bleeding from the tonsils;
- otitis;
- laryngitis.
Like any purulent process, the development of angina can be accompanied by a generalization of the process, leading to the development of sepsis. It is in this way that the meninges may be involved in the process, which results in the development of purulent meningitis. Such complications are extremely rare, but they develop in the early stages or directly against the background of angina, in the first few days after the onset of the disease.
Purulent complications
The lacunar or follicular form of angina is characterized by a lesion of the tonsils of a purulent nature. With the spread of such a process, the involvement of nearby tissues, it is purulent complications that develop. The most common complication of angina is paratonsillar abscess. This disease is a defeat of loose tissue surrounding the amygdala, and the development of a purulent process in it.
The first signs of an abscess begin to appear 2-7 days after the development of angina. Its presence can be suspected by changes in the clinical picture, when, after some improvement in the general condition in acute tonsillitis, there is an increase in sore throat and a new temperature rise. The painful sensations increase sharply when swallowing, as well as when trying to pronounce sounds. At the same time, the patient's voice changes, becomes more hoarse.
The development of pain syndrome is due to the forced position of the body: the patient's head is tilted to the side, towards the development of the pathological focus.
 The temperature rise reaches 40 degrees. There may be chills, as well as other signs of intoxication, weakness, headache, lack of appetite. Pharyngoscopy, carried out in this situation, allows you to detect the absence of plaque and abscesses, which are a typical symptom of follicular or purulent sore throat. At the same time, there is a sharp increase in the amygdala from one side. She is brightly hyperemic. Swelling of the tongue is also characteristic. In this case, an enlarged purulent formation shifts it somewhat to the side. The most typical one-sided development of the process.
The temperature rise reaches 40 degrees. There may be chills, as well as other signs of intoxication, weakness, headache, lack of appetite. Pharyngoscopy, carried out in this situation, allows you to detect the absence of plaque and abscesses, which are a typical symptom of follicular or purulent sore throat. At the same time, there is a sharp increase in the amygdala from one side. She is brightly hyperemic. Swelling of the tongue is also characteristic. In this case, an enlarged purulent formation shifts it somewhat to the side. The most typical one-sided development of the process.
If, despite antibiotic therapy, the patient's condition continues to deteriorate, sore throat increases, and intoxication increases, then the most appropriate method of treatment in this case is surgery.
Puncture or opening of an abscess, evacuation of purulent contents contributes to the rapid normalization of the situation.
A radical method of treatment is characterized by bilateral tonsillectomy, that is, excision of the infectious focus, which is the cause of the formation of an abscess.
Another complication that needs immediate consultation with a surgeon is purulent lymphadenitis. Swelling and soreness of the lymph nodes is one of the constant symptoms of sore throat. With incorrect treatment, insufficient immunity, the development of a purulent process in them may be noted. Clinically, such a pathology is characterized by an increase in the morbidity of these formations. The skin over them becomes red, swollen, hot to the touch. In cases where antibiotic therapy does not work, surgical intervention is also performed.
 A severe purulent complication of angina is the development of phlegmon, inflammation of the soft tissues of the neck. An objective examination reveals swelling of the neck and redness of the skin above it, a local increase in temperature. The phenomena of intoxication are pronounced.
A severe purulent complication of angina is the development of phlegmon, inflammation of the soft tissues of the neck. An objective examination reveals swelling of the neck and redness of the skin above it, a local increase in temperature. The phenomena of intoxication are pronounced.
The temperature is kept within 40 degrees, the patient is lethargic, confusion, delirium, severe headache, vomiting may be noted. It is difficult for a child to open his mouth. There is an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth, severe salivation. In cases where antibiotic therapy does not work, surgery is performed to facilitate the outflow of pus.
Laryngeal edema
Laryngeal edema is a dangerous complication. It can occur in any severe course of angina, but this development is most typical in acute tonsillitis caused by a diphtheria bacillus. The first symptom of such a pathology, which allows one to suspect the development of laryngeal edema, is a change in the patient's voice and the appearance of a cough.
Within a short time, these symptoms increase and are accompanied by shortness of breath, first on inspiration, then on expiration. In this case, the face becomes cyanotic, the neck increases in size. Due to the increase in edema, the risk of developing suffocation becomes more and more real. This condition requires urgent measures in the intensive care unit, for which the ambulance team must immediately deliver the child to the hospital.
Other local complications
 Bleeding from the tonsils is most typical for the necrotic form of angina, when after the rejection of the necrotic film, an erosive bleeding surface remains. With a deep and extensive lesion, injury to a large vessel is possible, which is manifested by bleeding. If conservative methods of stopping bleeding are ineffective, electrocoagulation of the vessel is indicated in the conditions of the surgical department. The spread of the infectious process to nearby organs leads to the development of complications such as otitis media or laryngitis. At the same time, the treatment tactics does not have any peculiarities, it is carried out in accordance with the identified pathology.
Bleeding from the tonsils is most typical for the necrotic form of angina, when after the rejection of the necrotic film, an erosive bleeding surface remains. With a deep and extensive lesion, injury to a large vessel is possible, which is manifested by bleeding. If conservative methods of stopping bleeding are ineffective, electrocoagulation of the vessel is indicated in the conditions of the surgical department. The spread of the infectious process to nearby organs leads to the development of complications such as otitis media or laryngitis. At the same time, the treatment tactics does not have any peculiarities, it is carried out in accordance with the identified pathology.
In this case, it is important to recognize the development of complications in order to correct the treatment in time.
Delayed hazard
Delayed dangerous complications of angina in children are diseases, the first signs of which are detected after a few weeks. Their presence is due to the fact that under the influence of streptococcus in the body, autoimmune mechanisms are triggered, when antibodies begin to be produced against the cells of its own body, having a damaging effect on target organs.
Most often, cells and tissues of the heart, kidneys, blood vessels, and joints are affected. The most common diseases that develop as a result of exposure to this streptococcal pathogen are
- rheumatism;
- glomerulonephritis;
- systemic vasculitis.
Rheumatism is a pathology that over time can lead not only to disability and disability, but even the death of the patient.
As a result of the launch of autoimmune processes, the development of pathological processes in the tissues of the heart occurs with the further formation of the pathology of the valve apparatus and the development of heart defects.
 The same rheumatic lesion is noted in the articular apparatus. Swelling and redness of large joints is especially characteristic. Movement in them is limited due to pain. Such a lesion is characterized by their "volatility", that is, the transition of the pathological process from one joint to another.
The same rheumatic lesion is noted in the articular apparatus. Swelling and redness of large joints is especially characteristic. Movement in them is limited due to pain. Such a lesion is characterized by their "volatility", that is, the transition of the pathological process from one joint to another.
A dangerous process after a sore throat can develop in the kidneys. Glomerulonephritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by the development of renal failure. Its constant symptoms are the presence of edema, as well as protein and red blood cells in the urine.
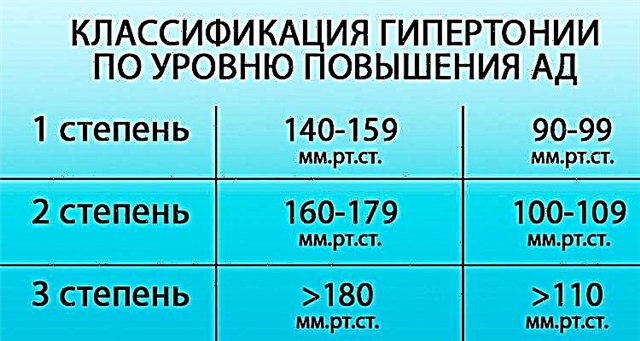
Over the next few years, a persistent increase in blood pressure develops.
Renal tissue damaged by the autoimmune process contributes to the development of infectious processes in it caused by various pathogens. Pyelonephritis, which quite often takes a chronic course, is accompanied by heaviness in the lower back, severe malaise, prolonged hyperthermia and decreased immunity, also worsening the quality of life of patients.
The clinical picture in autoimmune vascular inflammation can be very different, since the process may involve vessels of various locations and sizes. The most common signs of such a lesion are
- skin manifestations in the form of a characteristic rash;
- the development of abdominal syndrome, manifested by intestinal bleeding and abdominal pain;
- renal syndrome; articular syndrome.
Prevention measures
 The risk of developing severe complications after angina is quite high, especially in cases where there is a repeated infection with hemolytic streptococcus. In this regard, after suffering a sore throat, the child should be monitored by a pediatrician for a year. Carrying out an objective examination, laboratory examination, including a general urine analysis, a study of renal functions, acute phase reactions, an ECG, an ultrasound of the heart allows you to identify pathology in a timely manner. In order to prevent long-term dangerous complications, bicillin prophylaxis can be carried out, directed directly against this pathogen.
The risk of developing severe complications after angina is quite high, especially in cases where there is a repeated infection with hemolytic streptococcus. In this regard, after suffering a sore throat, the child should be monitored by a pediatrician for a year. Carrying out an objective examination, laboratory examination, including a general urine analysis, a study of renal functions, acute phase reactions, an ECG, an ultrasound of the heart allows you to identify pathology in a timely manner. In order to prevent long-term dangerous complications, bicillin prophylaxis can be carried out, directed directly against this pathogen.
The introduction of prolonged antibiotics of the penicillin series in children with frequent angina caused by hemolytic streptococcus is a fairly effective way to combat possible complications of the disease.
Another method of preventing complications of angina is tonsillectomy. Despite the significant role of the tonsils in maintaining immunity, this method of treatment is indicated when chronic tonsillitis becomes decompensated, accompanied by systemic disorders in the body, and conservative treatment is ineffective.