Persistent tonsillitis is increasingly seen in adults. Pathology easily affects a person and is painful with constant relapses. Everyone is well aware of the main causes of frequent sore throats, but an effective way to reduce their occurrence has not been found.
Conservative treatment is applied using antibacterial and immunomodulatory agents. There is an operative technique for eliminating the provoking agent of anginal inflammation. And yet, most experts agree that the priority task is to increase the body's nonspecific defenses.
Causes of frequent sore throat
The main and predetermining reason for the frequent occurrence of angina is a decrease in the immune status of a person and the development of streptococcal infection in the body.
With a high resistance of the body, local defense mechanisms and general resistance successfully cope with the aggressive action of bacteria. When the pathogenic effect prevails over immunity, the inflammatory process develops as an adequate reactivity of the body.
A significant cause of frequent tonsillitis is a tendency to hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue (palatine and pharyngeal tonsils) and the ineffectiveness of previous conservative treatment, which reduces the likelihood of subsequent recovery.
The infection process increases in the presence of some factors:
- Exogenous
- Frequent visits to public places and prolonged stays in them, which promotes long-term contact and potentially contributes to infection.
- Rare stay in the fresh air, physical inactivity.
- Bad habits - smoking, alcohol abuse, drugs and sedatives.
- Inadequate nutrition and harsh living conditions (stress, malnutrition, dry food).
- Endogenous
- Reduced resistance.
- Sensitization of the body (hypersensitivity to allergens of various origins).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Major chronic diseases.
With weakened immunity, there is frequent angina in adults - the causes of persistent tonsillitis will indicate what to do to eliminate the disease.
Frequent sore throats can be associated with diseases:
- viral respiratory infection;
- flu;
- adenoiditis;
- sinusitis and sinusitis;
- caries, periodontitis.
Some experts argue that a tense psycho-emotional state, and constant stress take the second place among the factors provoking the frequent occurrence of angina in the adult population in terms of importance (in the first place - coccal infection). After all, the tension of immunity is corrected not only by the internal physiological state, but also by the emotional state of a person (a sense of mental balance or pessimism, self-sufficiency or dissatisfaction).
The main symptoms
The clinical manifestation of angina depends on the nature of the pathogenic agent and the state of the body at the time of the onset of the disease. It is necessary to analyze the previous treatment, its success, the duration of remission and clearly define the etiology of the disease. This will allow faster and more correct determination of the course and direction of the new treatment.
Inflammation provokes the development of scars in the lacunar lumen, which leads to difficulty in drainage of the tonsils. The viciousness of the pathological process develops - tonsillitis-inflammation-tonsillitis.
Signs of a sore throat:
- discomfort in the throat (perspiration, dryness);
- sore throat (increases with swallowing and during the development of the disease);
- dysphagia;
- febrile fever (38-39 ° C);
- signs of general weakness and intoxication (headache, chills, myalgia).
When examining the throat, there is a hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the tonsils, swelling. Palpation reveals an increase in the submandibular, behind-the-ear lymph nodes, their compaction and soreness.
Relapse control measures
 Frequent sore throats in an adult require an integrated approach to treatment. Consultation needed:
Frequent sore throats in an adult require an integrated approach to treatment. Consultation needed:
- otolaryngologist;
- allergist;
- therapist;
- cardiologist;
- immunologist.
Experts may advise to examine the pharynx for the presence of pathogenic microflora (smear test), blood and urine tests. It is advisable to conduct a blood test for the presence of antibodies to chronic viral infections. The PCR method (polymerase chain reaction) is not an adequate diagnosis in this matter.
With frequent tonsillitis, it is necessary to exclude:
- cytomegalovirus;
- Epstein-Bar virus.
When diagnosing them in the laboratory, qualified help from an immunologist, virologist and treatment in a specialized clinic are required.
Conservative and radical (surgical) treatment of frequent tonsillitis is generally accepted. Conservative treatment involves the use of medications and a treatment regimen that is used to eliminate the usual streptococcal sore throat.
Conservative treatment:
- antipyretic drugs;
- analgesics;
- antibiotics of the penicillin series, macrolides;
- immunoprotectors;
- vitamin and mineral complex products.
Important! It is advisable to use antimicrobial drugs and symptomatic therapy after being examined by a doctor and receiving professional advice.
Reckless use of antibiotics often causes adaptation of pathogenic microflora. Subsequently, an increase in the dose of medication and the course of treatment is required.
The duration of the use of antimicrobial agents is 10 days for the penicillin group and 5 for macrolides. Although statistics claim that more than 50% of the sick stop taking antibiotics on their own at the first signs of improvement.
Treatment of angina at home should include:
- Compliance with all recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician.
- Bed rest until the temperature is normalized. It is strongly not recommended to carry a sore throat "on the legs". This provokes cardiovascular disorders and the development of complications.
- Adequate food and drink. Food should be light, liquid, not traumatic for a sore throat, not hot (soups, mashed potatoes, milk porridge). Drinking - warm (or room temperature) and frequent (herbal and lemon teas, dried fruit compotes, fruit drinks, juices).
After eating and every hour or two, it is worth gargling to remove food debris and sanitize the throat.
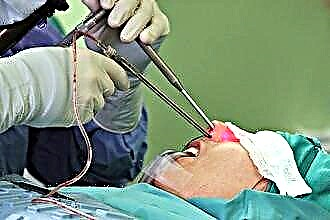
Operative treatment
Cryotonsillotomy is a method of treating tonsillitis. The essence of the therapy is the partial surgical removal of the affected areas of the narrowed lacunae of the tonsils using liquid nitrogen (t -180 ° C) in a cryoapplicator. The exposure of the procedure is 40-50 seconds.
Frozen affected areas are covered with a crust for a week and gradually regenerate after 5-10 days. It is permissible to carry out such treatment from the age of 6. Reoperation is not required, since the therapeutic and prophylactic effect is observed after the first treatment.
The method of regenerative cryotherapy according to Dorokhov is known and successfully recommended (not to be confused with cryodestruction). The therapeutic technique allows you to restore the functional ability of the affected tissue due to the effect of deep cold on the tissues of the lymphadenoid tonsillar pharyngeal ring. Lymphofollicles are restored and regain their protective function. Immune processes are activated, tonsillitis is easier to treat conservatively. The method does not force the patient to specifically prepare for the procedure. After half an hour, you can drink and eat.
In modern medicine, the removal of adenoids or tonsils is not welcomed as a preventive operation. The absence of tonsils will lead to the introduction of pathogenic agents into the body faster and aggravate the development of anginal consequences.
Prevention of frequent sore throats
 At the first discomfort in the throat, it is worth carrying out preventive debridement of the tonsils at a doctor, and not at home. In adults, with frequent tonsillitis, preventive lacunar sanitation is performed twice a year in an outpatient clinic. After the procedure, throat warming is applied. This technique is effective only if this sequence is performed during the period of remission.
At the first discomfort in the throat, it is worth carrying out preventive debridement of the tonsils at a doctor, and not at home. In adults, with frequent tonsillitis, preventive lacunar sanitation is performed twice a year in an outpatient clinic. After the procedure, throat warming is applied. This technique is effective only if this sequence is performed during the period of remission.
The main preventive direction remains activities aimed at strengthening and regulating the body's immune forces. Much has been said about this, but it is worth repeating.
Strengthening immunity means hardening, getting rid of bad habits, an active lifestyle (playing sports, adequate physical activity, if possible, visiting the pool), frequent stay in the fresh air, treatment of chronic diseases, creating an optimal microclimate at home (18-20 ° C with humidity 60-65%).
Important! It is advisable to try to correct emotional and psychological health.
Perhaps, by changing your attitude towards yourself and the phenomena of the outside world, you will be able to cope with an important component of the occurrence of frequent sore throats - stress and overwork. Following this, immunity will improve, and the body's defenses are activated.

 The main and predetermining reason for the frequent occurrence of angina is a decrease in the immune status of a person and the development of streptococcal infection in the body.
The main and predetermining reason for the frequent occurrence of angina is a decrease in the immune status of a person and the development of streptococcal infection in the body.