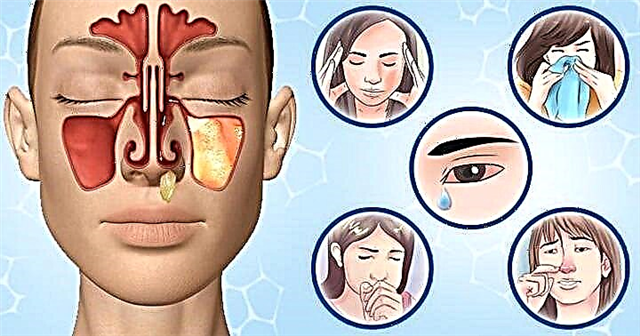
Follicular tonsillitis is an acute disease of the ENT organs, which is accompanied by purulent inflammation of the tonsils in the throat. A massive attack of pathogens against the background of a weakened organism turns off the protective function of the tonsils, as a result of which acute purulent processes rapidly develop in the follicles.
The peak incidence occurs in the cold season, when the immune system is weakened. Angina is bacterial in nature and is most often transmitted by airborne droplets.
Etiology
In the cold season, the off-season, the body's resistance is significantly reduced, which leads to an increase in the activity of pathogens.
Follicular tonsillitis can be caused by:
 group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus,
group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus,- staphylococci,
- adeno-, rhinoviruses,
- fungi Candida spp.
Purulent follicular tonsillitis in 70% of cases develops due to the activity of streptococcus in the oral cavity. A prerequisite for the rapid development of a pathogen is a decrease in immunity. Most often this happens due to:
- hypothermia;
- hypovitaminosis and anemia;
- chronic diseases;
- lack of sleep, constant stress;
- malnutrition;
- secondary immunodeficiency.
| ANGINA FOLLICULAR. ETIOLOGY | ||
| Reasons for development | Pathways of transmission of the pathogen | Infection methods |
| pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci and staphylococci); decrease in the reactivity of the body. | endogenous (the pathogen is asymptomatic in the body, after a decrease in the body's resistance it provokes the disease); exogenous (the pathogen enters from the outside). | airborne; contact and household; fecal-oral (through water or food). |
Decreased immunity in the oral cavity leads to the appearance of purulent foci in the follicles (clusters of lymph nodes) of the tonsils. The development of intoxication is accompanied by characteristic symptoms - there is a headache, body aches, a feeling of nausea.
Symptoms
In its pathogenesis, the symptoms of follicular sore throat go through several stages. Many of them resemble the clinical picture of influenza and ARVI, other types of tonsillitis, mononucleosis, oral candidiasis. Improper treatment or its absence leads to the penetration of streptococcus into the blood and intoxication of the body.
A characteristic feature is the defeat of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils, which are the least protected from environmental influences, in contrast to the subcutaneous lymph nodes. When breathing, the tonsils directly interact with microbes.
With proper treatment, the duration of the course of the disease does not exceed 10 days.
Timely referral to a therapist will help to avoid the development of complications that are fraught with angina, including:
- paratonsillar abscess;
- acute purulent lymphadenitis;
- rheumatism;
- infectious polyarthritis;
- myocarditis.
During pregnancy, follicular tonsillitis is especially dangerous for its complications. The development of purulent processes can lead to meningitis, acute otitis media, sepsis, since the immunity of women during pregnancy is reduced. For this reason, acute tonsillitis is dangerous for both the woman and the health of the unborn child.
The incubation period (from the moment of infection to the first symptoms) of the disease is from 10 hours to 2 days. Microbes begin to accumulate in the lymphatic tissue of the tonsils. The development of pathogens leads to inflammation of the surface tissues, which spreads to deeper layers. Therefore, in most cases, without timely treatment, catarrhal tonsillitis becomes follicular, which manifests itself as follows:
- fever, high temperature (39–40 degrees), which is difficult to confuse with antipyretic drugs;
- headache;
- aches in muscles, joints;
- discomfort when swallowing, increasing sore throat radiating to the ear;
- yellow and white ulcers on the tonsils;
- an increase in regional lymph nodes, pain on palpation,
- pain when turning the head.
Features of the course of the disease in children
Purulent tonsillitis in children is observed much more often than in adults due to the structural features of the lymphoid tissue. Usually in young patients, the disease is much more severe.
Most cases are characterized by a very high temperature (up to 40 degrees), feverish conditions, severe headaches. To the usual set of symptoms are also added:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- meningeal symptoms (stiff neck muscles);
- loss of consciousness.
Hypertrophied tonsils are also found in absolutely healthy children. And, on the contrary, the inflammatory process can proceed at their normal size.
Establishing diagnosis
 Most often, the history of the disease is sufficient to determine the diagnosis. To clarify the form, an examination of the oral cavity, pharynx of the patient or pharyngoscopy is carried out. In this case, a typical picture of inflamed tonsils is observed: a sharp increase, edema, bright hyperemia (redness), the surface is covered with white-yellow tubercles. Also, the soft palate swells and reddens. After maturation, the follicles are opened and films of white-yellow color are formed, which are easily removed with a spatula without bleeding marks (which distinguishes the disease from diphtheria).
Most often, the history of the disease is sufficient to determine the diagnosis. To clarify the form, an examination of the oral cavity, pharynx of the patient or pharyngoscopy is carried out. In this case, a typical picture of inflamed tonsils is observed: a sharp increase, edema, bright hyperemia (redness), the surface is covered with white-yellow tubercles. Also, the soft palate swells and reddens. After maturation, the follicles are opened and films of white-yellow color are formed, which are easily removed with a spatula without bleeding marks (which distinguishes the disease from diphtheria).
As additional research methods, a general blood test is used (a sharp increase in ESR, leukocytes, eosinophilia, an increase in the number of stab and segmented leukocytes), bacteriological examination of smears from tonsils, a blood test to determine the pathogen.
Follicular sore throat without fever
Hyperthermia usually accompanies the formation of abscesses on the tonsils. This symptom is a sure sign that the body has begun to fight infectious agents.
However, over the course of several years, experts have increasingly noted that the disease can proceed without hyperthermia. The decisive factor in making a diagnosis is the examination of the throat. Normal temperature with a purulent inflammatory process may indicate:
- decreased immunity and depletion of the body;
- autoimmune disease;
- the transition of the disease to the chronic stage;
- alcohol intoxication;
- heart failure;
- menses.
General principles of therapy
 Effective drug treatment is impossible without strict adherence to the following prescriptions:
Effective drug treatment is impossible without strict adherence to the following prescriptions:
- Bed rest, refusal to stay on the street for 5-6 days in order to avoid a sharp deterioration.
- Plentiful warm drink, especially still mineral water, milk with soda, herbal preparations with rose hips, chamomile and sage. In order not to injure the inflamed mucosa, the temperature of the liquid should not be too high.
- The diet should consist of homogeneous foods without spices, such as cereals, broths, purees and soups.
Solid food increases pain when swallowing and can lead to mechanical damage to the inflamed areas of the mouth and pharynx.
- The room where the patient is located must be cleaned and ventilated daily.
- Regular rinsing of the throat, 7-10 times a day, which will clear the throat of purulent secretions that remain after the maturation and opening of the follicle.
The patient can recover within 5 days, but it is not recommended to immediately go to work and visit public places. Immunity needs time to recover from an illness. Doctors recommend protecting the body from contact with the external environment for 10 days. Healthy sleep, good rest, balanced diet, vegetables and fruits will help improve your health.
Antibacterial therapy
Follicular tonsillitis is fraught with complications, the most severe of which is rheumatism, which is characterized by severe heart valve defects and leads to disability. To suppress the bacterial flora, antibiotics are the main drug treatment.
In the absence of allergic reactions, the doctor prescribes antibiotics from two groups:
- Penicillins, which have a broad spectrum of action and are effective against streptococci and staphylococci. The most famous representative is Amoxicillin. The course of treatment is 10 days. If the pathogen has resistance, Augmentin (Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid) is prescribed.
- Macrolides that gradually accumulate in the blood: Azithromycin (Sumamed), josamycin, clarithromycin. The course of administration is up to 5 days, which gives an effective effect on bacteria within the same 10 days.
The effective selected antibiotic is assessed by the doctor after 72 hours, as evidenced by a decrease in temperature and general well-being of the patient. If the drug does not work, it is changed to a drug from another group.
With antibiotic therapy, it is important to strictly adhere to the regimen and period of taking the medication prescribed by the doctor.
Stopping the antibiotic early will lead to the development of bacterial resistance to this drug: in the event of a relapse or complication, it will be ineffective.
Surgery
 For recurrent tonsillitis, your doctor may order a tonsillectomy (excision of the tonsils). The main indications for this procedure are:
For recurrent tonsillitis, your doctor may order a tonsillectomy (excision of the tonsils). The main indications for this procedure are:
- ineffectiveness of antibacterial treatment;
- enlarged tonsils, making it difficult to swallow and breathe;
- the spread of the purulent process to closely spaced tissues.
There are various instruments for removing tonsils, such as an infrared scalpel, an electric scalpel, an ultrasonic scalpel, and a carbon laser to reduce them.
Alternative medicine
Some traditional medicine recipes during the main therapeutic treatment will help speed up the healing process. To prepare an antibacterial solution for gargling you will need:
- 1 beet
- 1 tbsp. l. 6% apple cider vinegar.
Beets are grated on a fine grater and mixed with vinegar. Leave the mixture for 4 hours in a dark place, then strain the juice through a thick cloth. Gargle with the resulting solution every 3 hours.
Honey and bee products can help relieve inflammation. A piece of propolis after meals 3 times a day for 2-3 days will help relieve the symptoms of follicular sore throat. Good quality propolis leaves a tingling or burning sensation in the mouth after chewing.
Berries and ripe fruits will help restore a weakened immune system. In cold weather, they can be replaced by raspberry jam, cranberry juice. Add blackberries, raspberries and rose hips to a variety of herbal teas such as linden blossom or thyme.
It should be remembered that folk prescriptions do not replace drug treatment, and a doctor's consultation is needed before using them.

 group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus,
group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus,