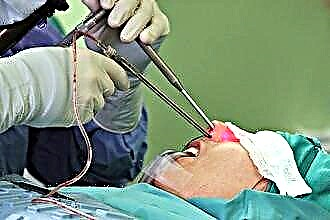
Drug treatment of adenoiditis in children allows you to eliminate inflammatory reactions in the pharyngeal tonsil and prevent further tissue hyperplasia. Removal of the adenoids (adenotomy) is carried out in extreme cases, as this negatively affects the body's resistance to infections.
Drug treatment of adenoiditis in children allows you to eliminate inflammatory reactions in the pharyngeal tonsil and prevent further tissue hyperplasia. Removal of the adenoids (adenotomy) is carried out in extreme cases, as this negatively affects the body's resistance to infections.
The pharyngeal tonsil is an immune organ, its excision leads to a decrease in local immunity, which entails frequent relapses of respiratory diseases. Drug and physiotherapy treatment allows you to stop catarrhal processes in the tissues and restore the normal physiological dimensions of the organ.
Adenoids 1, 2 and 3 degrees
How to treat adenoiditis in a child? The methods of therapy are determined by the degree of proliferation of lymphadenoid tissues and the stage of development of inflammatory processes in the pharyngeal tonsil. A critical increase in the size of the organ requires radical intervention, up to the removal of adenoid vegetations. ENT disease not only negatively affects the quality of life of patients, but also leads to serious complications.
In otolaryngology, there are 3 stages of development of adenoid vegetations:
- Grade 1 - overgrown lymphoid tissues cover only the third part of the vomer (bone that is part of the nasal septum) and choanas;
- 2 degree - hyperplastic nasopharyngeal tonsil overlaps ½ part of the choans and vomer;
- Grade 3 - an enlarged amygdala almost completely blocks the airways, as a result of which nasal breathing is impaired.
Important! Adenoiditis is most common in children aged 3 to 7 years.
Grade 1 adenoiditis is difficult to diagnose, since the amygdala is slightly enlarged. Difficulty breathing occurs exclusively when the child takes a horizontal position. Disease of 2 and 3 degrees of development requires medication, and in some cases, surgical treatment. Untimely elimination of pathology can cause the development of catarrhal otitis media or salpingootitis (eustachitis).
When to see a pediatrician?
How to diagnose and treat grade 2 and 3 adenoiditis in children? Treatment of ENT disease can only be prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient. Inflammation of adenoid vegetations can be provoked by pathogens of a bacterial, fungal or viral nature, the reproduction of which can be prevented by various medications.
Typical manifestations of inflammation of the hypertrophied pharyngeal tonsil are:
- headache;
- hearing loss;
- constantly open mouth;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- Difficulty nasal breathing;
- nasal voice and unintelligible speech;
- frequent relapses of infectious diseases.
Constant breathing through the mouth leads to the formation of the so-called "adenoid face".
If you find the above symptoms, you should seek help from a pediatrician. After rhinoscopy and endoscopy, the specialist will be able to determine the degree of proliferation of lymphoid tissues and, accordingly, the optimal treatment regimen for pathology.
Features of therapy
Can adenoiditis in children be cured? When diagnosing adenoiditis, they try to eliminate inflammatory processes in the pharyngeal tonsil using conservative methods. Timely prescription of drugs of symptomatic and pathogenetic action allows not only to stop inflammation, but also to reduce the volume of overgrown lymphadenoid tissues.
The scheme of conservative therapy for ENT pathology includes:
- etiotropic treatment with antibiotics and antiviral agents;
- instilling anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drops into the nose;
- irrigation of the nasal cavity with phytopreparations and saline solutions;
 inhalation with a nebulizer using anti-edematous and antiphlogistic drugs;
inhalation with a nebulizer using anti-edematous and antiphlogistic drugs;- taking drugs of immunostimulating and immunomodulating action.
In the absence of positive dynamics and a critical increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, children are prescribed surgical treatment. Removal of the immune organ leads to a decrease in the body's reactivity, but prevents the development of severe local and systemic complications.
Etiotropic treatment
Etiotropic therapy - treatment with medications, which is aimed at eliminating the causes of the development of adenoiditis. As a rule, inflammation in adenoid vegetations occurs against the background of the development of viral and bacterial pathologies - angina, pharyngitis, sinusitis, laryngotracheitis, rhinopharyngitis, measles, etc. It is possible to destroy pathogens with the help of systemic antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
In pediatric therapy, to eliminate inflammation in the hypertrophied nasopharyngeal tonsil, use:
- antibiotics:
- "Klacid";
- Augmentin;
- "Ampicillin";
- Ospin.
- antiviral agents:
- Orvirem;
- "Kagocel";
- Isoprinosine;
- Groprinosin;
- "Rimantadin".
Antibacterial and antiviral drugs eliminate inflammation, but do not help to reduce hyperplastic lymphoid tissue.
Local therapy
To eliminate the symptoms of adenoiditis of the second degree, local drugs, which have anti-inflammatory and decongestant properties, allow. Nasal drops make nasal breathing easier by reducing tissue swelling. Regular use of medications can eliminate congestion, rhinitis, headaches and difficulty breathing through the nose.
For the treatment of inflammation in adenoid vegetations, the following can be used:
- "Tizine";
- Sanorin;
- Aqua Maris;
- Aqualor Baby;
- "Vibrocil".
Important! You can not use vasoconstrictor nasal drugs for more than 5 days in a row, as this will lead to addiction, as well as dehydration and irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
It is possible to eliminate nasal congestion with the help of cotton turundas soaked in medicinal solutions. Protargol, Avamis and Bioparox have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect.
Irrigation of the nasopharynx
Irrigation (washing) of the nasal cavity is an effective therapeutic procedure that allows you to eliminate pathological mucus from the nasal passages and flush out more than 70% of pathogenic agents. Sanitizing procedures with the use of solutions of antibacterial, decongestant and wound healing action can eliminate adenoiditis in children aged 4-5 years.
Regular cleansing of the nasal passages from allergens and pathogens helps to increase the tone of capillaries, restore the functions of the ciliated epithelium and eliminate inflammation in adenoid vegetations. Preparations based on sea salt not only accelerate the regression of catarrhal processes, but also reduce the volume of hyperplastic lymphoid tissues. For the treatment of ENT pathology in children, it is advisable to use:
- Furacilin;
 Elekasol;
Elekasol;- Physimer;
- Miramistin;
- Marimer.
Self-rinsing of the nasopharynx without following the recommendations of a specialist can lead to the penetration of fluid into the Eustachian tube, which is fraught with the development of tubo-otitis. For sanitizing procedures, it is advisable to use special irrigators for the nose.Easy-to-use devices are equipped with special tubes through which the nasopharyngeal mucosa is irrigated.
Surgery
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and strong proliferation of lymphoid tissue, patients are prescribed surgical treatment. As a rule, it is not possible to eliminate the symptoms of grade 3 adenoiditis with medicines and physiotherapy procedures. Full or partial excision of hypertrophied tissues allows to restore normal nasal breathing. The absolute indications for surgery are:
- hearing loss;
- frequent relapses of ENT diseases;
- adenoiditis 2 and 3 degrees;
- deformation of the facial skull;
- persistent rhinitis.
Operations for children are performed under local or general anesthesia in one of the following ways:
- classical adenotomy - excision of the enlarged pharyngeal tonsil with a scalpel under the control of the laryngeal speculum;
- cold plasma adenotomy - evaporation of hyperplastic tissues with an electrosurgical cold plasma coblator;
- radio wave adenotomy - removal of adenoid vegetations with radio wave adenotomas, coagulating injured tissues.
The least traumatic methods of removing the pharyngeal tonsil are cold plasma and radio wave adenotomy. After the procedure, patients undergo antibacterial and immunostimulating therapy, which prevents septic inflammation of the tissues in the operated area.

 inhalation with a nebulizer using anti-edematous and antiphlogistic drugs;
inhalation with a nebulizer using anti-edematous and antiphlogistic drugs; Elekasol;
Elekasol;