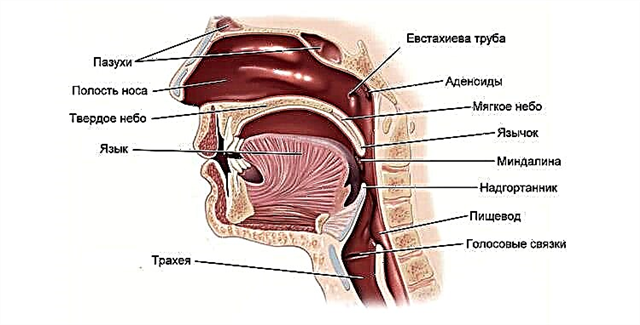
The term "tonsillopharyngitis" is used mainly by foreign otolaryngologists. This is a combination of symptoms of two diseases at once - tonsillitis (the well-known sore throat) and pharyngitis. With this disease, not only the mucous membrane itself lining the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed, but also the lymphoid ring of the pharynx. We call this ailment easier - angina.
Inflammations of the tonsils and pharynx of various origins are the most numerous pathologies among those that affect the upper respiratory tract. Problems with swallowing, sore throat and headache, as well as fever and enlarged cervical lymph nodes - this set of symptoms makes you want to see your doctor. Acute tonsillopharyngitis is confidently leading in the number of patients seeking help from a family doctor, therapist, otolaryngologist and pediatrician.
Reasons for development
 From 70 to 90% of all cases of acute tonsillopharyngitis are of viral origin. Most often it is provoked by "cold" viruses (adeno-, rino- and coronavirus, as well as influenza viruses). Sometimes the disease can appear due to rubella and measles viruses, herpes simplex and Epstein-Barr. In all other cases, harmful bacteria are to blame. Basically, the disease is caused by hemolytic streptococci of group A. Less often - Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococcus, mycoplasmas and chlamydia. Very rarely - the causative agents of diseases such as diphtheria, whooping cough, gonorrhea and syphilis.
From 70 to 90% of all cases of acute tonsillopharyngitis are of viral origin. Most often it is provoked by "cold" viruses (adeno-, rino- and coronavirus, as well as influenza viruses). Sometimes the disease can appear due to rubella and measles viruses, herpes simplex and Epstein-Barr. In all other cases, harmful bacteria are to blame. Basically, the disease is caused by hemolytic streptococci of group A. Less often - Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococcus, mycoplasmas and chlamydia. Very rarely - the causative agents of diseases such as diphtheria, whooping cough, gonorrhea and syphilis.
In addition to all of the above, fungal microorganisms (usually Candida) may be to blame for the occurrence of tonsillopharyngitis. Also, the disease can be of mixed origin - fungal-bacterial.
If the child is under 3 years old, this ailment will almost always be viral. But from the age of 5, on the contrary, the bacterial form is diagnosed much more often.
It is much easier for pathogenic microorganisms to penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and provoke an inflammatory process there when:
- immunodeficiency (often this condition appears due to frequent problems with the digestive system);
- malfunctions in the work of internal organs (developing renal, pulmonary and heart failure);
- problems in the endocrine sphere (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism or menopause);
- lack of vitamins A and C, improper metabolism of minerals;
- complex somatic ailments;
- unsatisfactory environmental situation;
- ignoring hygiene standards;
- the presence of addictions (with tobacco smoking and alcohol abuse).
Symptoms
For the acute form of tonsillopharyngitis, a sharp onset is characteristic. You can get sick against a background of stress (immunity decreases) or as a result of hypothermia. One of the most striking signs is a sharp rise in temperature. Depending on individual characteristics, it ranges from subfebrile to high. Chills, aching bones, myalgia complement the general clinical picture of the disease. If the temperature exceeds 39 ° C, it is possible convulsions. In children, the severity of signs of intoxication is higher than in adults. Symptoms appear:
 general weakness;
general weakness;- a significant decrease in activity;
- headache and dizziness;
- dyspepsia (diarrhea, vomiting, regurgitation in infants);
- insomnia.
To the high temperature with tonsillopharyngitis, pain is added during the swallowing process, often radiating to the ears. Such pain makes babies who have not yet learned to speak to refuse food. An unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, and inside it - a rash, the voice becomes nasal. If you examine the tonsils, you can see that they are swollen and reddened. In most cases, they are covered with a bloom of pus. You should also pay attention to the cervical lymph nodes. With this disease, they are enlarged and painful when touched.
A plaque on the tonsils, a rash in the mouth, fever and enlarged lymph nodes all indicate that tonsillopharyngitis is most likely provoked by hemolytic group A streptococci.
However, it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis based on symptoms alone. After all, the signs of an ailment of a viral nature are not much different.
Sometimes the disease affects the cardiovascular system. This may be evidenced by altered sonority of tones, disturbances in the heart rhythm and the occurrence of functional noises. All this is accompanied by the corresponding changes displayed on the ECG.
The viral nature of the disease is characterized by respiratory manifestations: cough, hoarseness, runny nose, conjunctivitis. In some cases, diarrhea is possible.
How is the disease diagnosed?
In principle, it is not difficult to diagnose tonsillopharyngitis. To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient and performs a pharyngoscopy procedure. The presence of the disease is indicated by:
- swollen back wall of the pharynx, bright red with a granular surface;
- hypertrophy of the follicles located on the pharynx.
 You can find out the origin of the disease (viral or bacterial) using an ordinary general blood test. An increase in the number of lymphocytes indicates the presence of a virus in the body. And an increased level of ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is a marker of microbial nature.
You can find out the origin of the disease (viral or bacterial) using an ordinary general blood test. An increase in the number of lymphocytes indicates the presence of a virus in the body. And an increased level of ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is a marker of microbial nature.
At the same time, it is rather difficult to determine the specific causative agent of the disease. After all, the symptoms of tonsillopharyngitis are not specific. Its symptoms overlap with almost any respiratory illness. Therefore, to find out the exact cause of the disease, it is necessary to do laboratory diagnostics. This is necessary so that the doctor can prescribe the most effective medications (in particular, antibiotics). The accuracy of the diagnosis is directly influenced by the quality of the collected biomaterials. If the technique of their collection is observed at a high level, then the degree of sensitivity of this method is 90%.
If you suspect a streptococcal nature of tonsillopharyngitis, it is advisable to perform microbiological laboratory diagnostics. This type of disease is characterized by:
- a bloom of pus covering the tonsils;
- prolonged fever;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- lack of cough.
Treatment of tonsillopharyngitis in adults
Treatment of tonsillopharyngitis should be comprehensive. However, before you start taking even the most harmless drugs, you should definitely find out the origin of the disease. Knowing which pathogen provoked the disease, you can choose the most effective drugs.
For example, if the bacterial nature of the disease is found, it is necessary to treat with antibiotics. By inhibiting the growth and reproduction of harmful microorganisms, they also eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
 In accordance with the indicators of the performed antibioticogram (determination of the sensitivity of a specific pathogen to the drug), you can choose the following antibiotics:
In accordance with the indicators of the performed antibioticogram (determination of the sensitivity of a specific pathogen to the drug), you can choose the following antibiotics:
- Penicillins (the safest group - they can be taken even by pregnant women and young children) - "Ampicillin", "Oxacillin", "Ampiox".
- Macrolides - "Azithromycin", "Clarithromycin", "Erythromycin".
- Cephalosporins (very effective against streptococci, meningococci and Haemophilus influenzae) - Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime.
Treatment with antibacterial drugs allows:
- quickly slow down the inflammatory process;
- to accelerate the restoration of the previous quality of life and working capacity;
- prevent the development of possible complications in the cardiovascular, musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
If tonsillopharyngitis was provoked by a virus, it should be treated, respectively, with antiviral drugs - Lavomax, Arbidol, Groprinazin.
When the body temperature has reached 38 ° C and rises above, you can use antipyretic medications - "Nurofen", "Ibuprofen" or "Paracetamol". The drug must be selected in accordance with age and strictly adhere to the dosage.
If the throat is very sore, it is not recommended to use analgesics. They are practically useless in this case. Local preparations are much more effective.
 To stop the development of the inflammatory process, eliminate puffiness and relieve pain, it is necessary to treat the mucous membrane with antiseptics. They are produced in a variety of forms - dragees, lozenges, lozenges, aerosols, rinses. Among aerosols, it is better to prefer "Yoks", "Proposol", "Orasept", "Ingalipt", "Tantum Verde" and "Hexoral". And for rinsing, it is advisable to use decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants, a solution of soda, sea salt and iodine, as well as the well-known preparations "Miramistin" and "Furacilin". Dragees ("Neo-angin", "Falimint"), tablets ("Strepsils", "Faringosept") and lozenges ("Coldrex Larry +", "Septolete") have proven themselves well.
To stop the development of the inflammatory process, eliminate puffiness and relieve pain, it is necessary to treat the mucous membrane with antiseptics. They are produced in a variety of forms - dragees, lozenges, lozenges, aerosols, rinses. Among aerosols, it is better to prefer "Yoks", "Proposol", "Orasept", "Ingalipt", "Tantum Verde" and "Hexoral". And for rinsing, it is advisable to use decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants, a solution of soda, sea salt and iodine, as well as the well-known preparations "Miramistin" and "Furacilin". Dragees ("Neo-angin", "Falimint"), tablets ("Strepsils", "Faringosept") and lozenges ("Coldrex Larry +", "Septolete") have proven themselves well.
It is advisable to supplement complex therapy with inhalation procedures. If the temperature remains high, it is permissible to inhale with a nebulizer. This device converts the liquid poured into it into an aerosol. However, it does not heat up. You can pour various expectorant drugs, antiseptic solutions and ordinary saline into the device.
To strengthen the immune system, the doctor recommends drinking a course of immunomodulators and vitamins.
Features of the treatment of children
If a child is sick with tonsillopharyngitis, self-medication is absolutely unacceptable. The necessary drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor. What they will be depends on the origin of the disease. Attempts to treat a child on their own can lead to the transition of an acute form of the disease to a chronic one, as well as to the development of a number of complications - for example, glomerulonephritis or acute fever.
The only thing that parents can and should do is to ensure that the child adheres to bed rest, regularly give him warm liquid and give him an antipyretic agent if necessary.
It is difficult even for an experienced doctor to determine the nature of the disease based on only one symptomatology. Therefore, children need to pass a number of tests: blood, urine, as well as a smear from the pharynx - to find out the pathogen. Inflamed tonsils, enlarged lymph nodes and fever may indicate a bacterial origin. There should be no cough. With such a picture, the doctor usually prescribes antibacterial drugs and explains in what dosage and when they should be taken. Most often, children are prescribed "Amoxicillin", "Penicillin V" and "Benzylpenicillin" (single intramuscular injection).
 In addition, the treatment of children is carried out:
In addition, the treatment of children is carried out:
- "Phenoxymethylpenicillin" (therapeutic course is 10 days);
- "Amoxicillin" (should be taken from 8 to 10 days);
- "Cephalexin" (cephalosporin, which is prescribed if a child has a penicillin intolerance);
- "Lincomycin" (prescribed for intolerance to beta-lactams and macrolides).
Treatment of tonsillopharyngitis of a viral nature involves a complete rejection of food, which irritates the throat, inhalation, and rinsing with warm alkaline solutions. As for medicines, antiviral, antipyretic and expectorant drugs are used. Children are best suited "Ibuprofen". It eliminates pain, brings down the temperature and fights the virus.
If the child is already 2 years old, you can use a local drug - Fusafungin aerosol, non-steroidal drug Benzydamine or local antiseptic agents with imudon, hexetidine or ambazon.
Adaptogens - conventional herbal remedies - will be an excellent addition to complex therapy. They can include flowers of chamomile, yarrow and dandelion, oak bark, marshmallow root, walnut and a number of other components.
Post factum
In order for recovery to occur as quickly as possible, you must first find out the origin of tonsillopharyngitis, and only then start treatment. When bacteria are present in the throat swab, antibiotics will have to be treated. If a virus is detected, antiviral medications will need to be taken. The fungus found in the biomaterial requires specific antifungal therapy.
 General recommendations for dealing with tonsillopharyngitis of any nature are diet, antiseptic rinsing and taking vitamins. Inhalation procedures will help restore a shrunken voice.
General recommendations for dealing with tonsillopharyngitis of any nature are diet, antiseptic rinsing and taking vitamins. Inhalation procedures will help restore a shrunken voice.
The acute form of tonsillopharyngitis is especially dangerous. After all, if treated incorrectly, it can become chronic. A permanent focus of infection located in the tonsils can subsequently cause such serious diseases as otitis media, glomerulonephritis and rheumatism.
Timely and competent treatment makes it possible to return to work in a short time and prevents the development of complications.

 general weakness;
general weakness;