The pharynx, as an organ of the digestive and respiratory system, performs many useful functions: it conducts air, saliva and food, resonates the sounds arising in the larynx, thereby taking part in voice formation. Pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the pharynx cannot go unnoticed: even mild symptoms of inflammation cause discomfort for the patient. The inflammatory process in the pharynx, or pharyngitis, is divided into different types, it can be acute or chronic. Among chronic forms, hypertrophic pharyngitis is of great importance - a disease characterized by a pathological increase in the lymphoid structures of the pharynx.
Etiology
 A disease such as pharyngitis is extremely common. The diagnosis can be made for both the child and the adult; in the structure of respiratory diseases, inflammation of the pharynx occupies one of the leading places. However, in this case, we are most often talking about an acute viral or bacterial inflammatory process; the hypertrophic type of changes is relatively rare.
A disease such as pharyngitis is extremely common. The diagnosis can be made for both the child and the adult; in the structure of respiratory diseases, inflammation of the pharynx occupies one of the leading places. However, in this case, we are most often talking about an acute viral or bacterial inflammatory process; the hypertrophic type of changes is relatively rare.
In the definition used by specialists, pharyngitis is identified as an inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx, proceeding in an acute or chronic form. It is not in vain that the emphasis is placed on which structures are involved in the pathological process: the lymphoid apparatus of the pharynx includes lymphoid granules on the posterior wall, lateral ridges; quite often the tonsils (palatine, tubal, etc.) are also referred to it. Hypertrophy, that is, an increase in size, affects not only the mucous membrane, but also lymphoid formations, which explains the changes that are visualized during an objective examination.
Pharyngitis, flowing in a hypertrophic form, is a chronic process. It is distinguished from acute inflammation by a special type of pathological changes, the absence of a tendency towards recovery and complete restoration of the affected anatomical region. The disease is observed throughout life, while with the help of adequate therapy it is possible to partially stop adverse manifestations and alleviate the patient's condition.
Why does hypertrophic pharyngitis develop? The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease are still being studied, but today experts associate its occurrence with such factors as:
- Infection, immunodeficiency.
As provocateurs of hypertrophy are considered mainly viruses of the herpes group and causative agents of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infections). In this case, the presence of immunodeficiencies of various etiologies, lymphoproliferative syndrome (an increase in the size of anatomical structures consisting of lymphoid tissue) is important.
- Compensatory and adaptive response.
Hypertrophy of lymphoid formations of the pharynx is observed after surgical removal of the adenoids, palatine tonsils, as well as in the case of their functional failure (chronic infectious and inflammatory processes - for example, chronic tonsillitis, developmental defects).
Thus, chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis develops due to insufficient functions of the lymphoid structures of the pharynx, susceptibility to infectious agents.
A decrease in the functional activity of lymphoid formations, in particular, tonsils, is closely associated with the existence of a focus of chronic infection, which becomes the reason for surgical intervention. The constant multiplication of infectious agents, the release of toxins by them and the destruction of the tissue of the tonsils is of great importance for the development of chronic inflammation of the pharynx - especially if there is no adequate treatment.
Manifestations
What happens to the mucous membrane and lymphoid formations of the pharynx in hypertrophic pharyngitis? In contrast to the rapidly increasing inflammation observed in the acute form, a sluggish chronic inflammatory process is characterized by:
- thickening and loosening of the mucous membrane;
- expansion of blood and lymphatic vessels;
- an increase in size, expansion of the excretory ducts and an increase in the functional activity of the mucous glands;
- an increase, expansion of lymphoid granules, which can merge with each other, while forming noticeable foci of hypertrophy.
Complaints of patients, both adults and children, are determined by the stage of the course of the disease. In the period of remission, that is, the manifestations subside, they can be reduced to a description of moderate discomfort, dryness, irritation of the mucous membrane. Patients indicate the sensation of a "lump in the throat" that bothers them periodically or constantly. The pain is also present, it is moderate, often insignificant, it can be both one-sided and two-sided. The pain syndrome is fickle, transient; at the same time, the mucous membrane of the pharynx is sensitive to irritant factors. Often there is a cough, dry cough.
During the period of exacerbation, hypertrophic pharyngitis, the symptoms of which intensify, proceeds against the background of subfebrile or febrile (in children) fever. At the same time, it is possible to maintain normal body temperature values. Patients are worried about:
- Severe or moderate sore throat, most pronounced when swallowing.
- Intensification of the sensation of discomfort, foreign body in the throat, dryness, irritation.
- Irradiation (recoil) of pain in the ears, which is especially noticeable at the time of swallowing movement.
- Frequent coughing without expectoration or with scanty pathological discharge.
Severe irradiation of pain in the ears with pharyngitis of a hypertrophic form may indicate pathological changes in the lymphoid tissue of the lateral ridges.
The general condition is most often relatively satisfactory. Severe weakness, pain in muscles and joints without a specific localization, headache may appear. Adult patients describe impaired well-being in different ways, the presence of chronic tonsillitis and other foci of chronic infection is important. Children suffer exacerbations of pharyngitis more difficult than adults; treatment must necessarily include bed rest during the period of increased body temperature.
Pharyngoscopic picture
Pharyngitis, flowing in a hypertrophic form, cannot always be distinguished from inflammation of the pharynx of another type, based only on the patient's complaints. The manifestations of the inflammatory process, especially during the period of exacerbation, are similar - fever, weakness, sore throat. For differential diagnosis, a visual examination of the pharyngeal mucosa is required. With hypertrophic inflammation, you can identify:
- redness, thickening and induration of the mucous membrane;
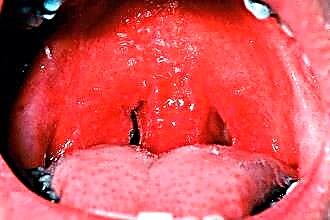
- swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- the presence of red, "granular" follicles of a round or oblong shape;
- the presence of branching veins, copious amounts of mucus;
- swelling of the uvula and soft palate.
Since the production of mucus is increased, when coughing, an admixture of mucous secretions appears in the saliva. Redness and swelling are noticeable even without exacerbation, enlarged lymphadenoid follicles rise above the surface of the mucous membrane.
Principles of therapy
Treatment of the hypertrophic form of inflammation of the pharynx in adults and children is built according to the scheme:
- Diet.
- Elimination of the influence of irritants.
- Remediation of foci of chronic infection.
- Hygiene of the oral cavity and pharynx.
- Systemic and local drug therapy.
Diet and elimination of the influence of irritants are important measures, without which it is difficult to achieve the effectiveness of drugs.Patients are advised to eliminate:
- thermal irritants (inhalation of cold or hot air, eating too cold or, conversely, overheated food);
- mechanical irritants (hard, crumbling food, as well as food with a lot of bones).
It is also worth giving up hot spices, alcohol, smoking, normalizing the microclimate in the room - correcting humidity and air temperature. Children should not be near smoking adults. You should swallow food carefully; if it contains bones, it is better to select them in advance, leaving only the soft part.
Elimination of foci of chronic infection is a prerequisite for the treatment of chronic hypertrophic inflammation of the pharynx.
 Rehabilitation of foci of chronic infection involves treatment by a dentist (carious teeth, gingivitis), an ENT doctor (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis). Also of importance is the timely treatment of diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems, which can indirectly affect the condition of the pharynx.
Rehabilitation of foci of chronic infection involves treatment by a dentist (carious teeth, gingivitis), an ENT doctor (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis). Also of importance is the timely treatment of diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems, which can indirectly affect the condition of the pharynx.
Hygiene of the oral cavity and pharynx consists in regular rinsing after meals, after sleeping. This helps to remove the accumulation of mucus (especially if the patient also has post-anasal syndrome, that is, drainage of the contents of the nasal cavity into the pharynx), moisturize the mucous membrane, and eliminate the feeling of discomfort. You can use solutions:
- sodium bicarbonate at a concentration of 0.5-2%;
- sodium chloride at a concentration of 1%.
These funds are used not only for rinsing, but also for irrigation with a spray bottle and for inhalation.
Systemic therapy, including antibacterial drugs, is rarely used to treat hypertrophic pharyngitis. The main one is local impact:
- lubrication of the mucous membrane with a solution of tannin, lapis;
- rinsing with infusion, broth of sage, chamomile;
- hygienic rinsing.
With a significant degree of hypertrophy of lymphoid granules, treatment implies their removal, which is carried out using a laser or by means of cryotherapy. Physiotherapy methods selected by the attending physician can also alleviate the patient's condition.