Any illness in children for parents is a reason for panic. Of course, pharyngitis does not pose a threat to life, but nevertheless, you should not be negligent in treating it. The appearance of a sore throat is a common symptom of oropharyngeal diseases, which indicates inflammation of the mucous membrane. The symptoms of pharyngitis in children practically do not differ from the symptoms in adults, the difference lies only in the severity of clinical signs.
 The disease can be acute or chronic, which develops as a result of improper treatment of the disease. Before giving a child antibiotics or antiviral drugs, you need to understand what caused the pathology.
The disease can be acute or chronic, which develops as a result of improper treatment of the disease. Before giving a child antibiotics or antiviral drugs, you need to understand what caused the pathology.
Pharyngitis reasons
Most cases of pharyngitis are caused by viral infection of the body, as a result of which inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid structures develops. The disease can develop against the background of influenza, adenovirus infection, or measles.
As for the bacterial origin of the pathology, streptococcus is among the most common bacteria. In case of primary infection through the respiratory tract, microbes settle on the mucous membrane, provoking inflammation.
On the other hand, bacteria can be activated against the background of a weakened immune system (in case of allergies, exacerbation of chronic diseases). As a result, an intensive reproduction of conditionally pathogenic flora begins in the oropharynx, preparing the ground for the appearance of inflammation.
In addition, pharyngomycosis may develop in children with weakened immunity or after prolonged use of antibiotics. Its appearance is due to the activation of a fungal infection.
The difference between fungal pharyngitis is the absence of hyperthermia and the presence of a curd white coating on the mucous membrane of the throat.
Separately, it should be said about allergic pharyngitis, which often does not appear as the only symptom of allergy. After contact with an allergen, a child may be disturbed not only by a sore throat or sore throat, but also by a dry cough, nasal congestion and skin rashes.
Predisposing factors that increase the risk of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract include:
- severe hypothermia. The child may be exposed to rain with a cold wind or live in unfavorable conditions (with a low temperature in the room);
- weakened immunity with concomitant diseases, allergies, hypovitaminosis or severe infection;
- polluted air (dust, smog). This applies to the area near chemical plants and other industrial enterprises, as well as the cleanliness of the indoor air;
- overwork of the physical or mental plan;
- secondhand smoke, which is especially important for families with smoking parents;
- mechanical trauma to the throat (solid food or when choking with a foreign body during the game);
- eating very hot or cold food or drinks;
- Difficulty nasal breathing.
The first signs of the disease
 Depending on the spread of inflammation, pharyngitis in a child can proceed in the form of catarrhal inflammation, when only the mucous membrane of the throat is affected, as well as granulosa, in which lymphoid structures are involved in the pathological process.
Depending on the spread of inflammation, pharyngitis in a child can proceed in the form of catarrhal inflammation, when only the mucous membrane of the throat is affected, as well as granulosa, in which lymphoid structures are involved in the pathological process.
The limited form is manifested by hyperemia and edema of the lateral ridges, and with a widespread form, the posterior pharyngeal wall is affected. The first manifestation of pharyngitis is a sore throat. It can start gradually or quickly turn into soreness. It depends on the protective forces of the child's immunity and the aggressiveness of the microbes.
If pharyngitis is accompanied by severe intoxication, the child may be drowsy, moody and inattentive. Parents notice that he eats little and reluctantly or refuses to eat at all.
When pharyngitis develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, in addition to perspiration in grief, rhinorrhea and nasal congestion can be observed. In case of an allergic reaction, signs of conjunctivitis (redness, itching of the eyes, lacrimation) may appear.
Pharyngitis symptoms
If, at the stage of a sore throat, you do not start gargling with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory solutions, the pain intensifies and worries when swallowing. The fever gradually increases, but in most cases it does not exceed 38 degrees. In addition to pain, discomfort in the oropharynx and difficulty swallowing may be troubling.
You can learn about sore throat in young children by moodiness, refusal to breastfeed and increased anxiety.
To start treatment with the right drugs, you need to carry out a differential diagnosis between pharyngitis and sore throat.
| Sign | Pharyngitis | Angina |
|---|---|---|
| Sore throat | Moderate, appears on swallowing. | Pronounced, constantly worried |
| Temperature | Fever no higher than 37.5 degrees | Hyperthermia reaches 38 and above |
| Nervous system | Capriciousness. | Hysterics |
| Appetite | Reduced | Refusal to eat |
| Pharyngoscopy | Hyperemia, edema of the mucous membrane of the lateral ridges, as well as the posterior pharyngeal wall | Swelling, redness of the glands. The surface of the tonsils is tense, varnished. Festering follicles or pus in the lacunae are visible |
Complications of pharyngitis
Note that in children, inflammation from the throat quickly spreads to the nasopharynx, auditory tube and larynx. The child's weak immunity contributes to the progression of the disease. Parents should not be surprised if, with a viral infection, in addition to a sore throat, children develop a runny nose and cough.
Pharyngitis is often diagnosed with:
 laryngitis. It develops as a result of the spread of infection and inflammation to the vocal cords, making them swollen and less mobile. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as a dry cough, similar to the barking of a dog, which further irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and increases the pain. In childhood, especially at 2-5 years of age, there is an increased risk of developing croup, which is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of a child. The fact is that against the background of pronounced inflammation, the lumen of the larynx becomes much narrower, making it difficult for air to pass. Parents may notice noisy, rapid breathing and shortness of breath when playing. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the lungs, internal organs suffer from hypoxia. The brain is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation, which is clinically manifested by drowsiness, yawning and moodiness;
laryngitis. It develops as a result of the spread of infection and inflammation to the vocal cords, making them swollen and less mobile. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as a dry cough, similar to the barking of a dog, which further irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and increases the pain. In childhood, especially at 2-5 years of age, there is an increased risk of developing croup, which is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of a child. The fact is that against the background of pronounced inflammation, the lumen of the larynx becomes much narrower, making it difficult for air to pass. Parents may notice noisy, rapid breathing and shortness of breath when playing. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the lungs, internal organs suffer from hypoxia. The brain is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation, which is clinically manifested by drowsiness, yawning and moodiness;- runny nose and sinusitis. Inflammation, spreading to the nasopharynx, leads to the appearance of edema of the mucous membrane and intense secretion of mucous discharge. Clinically, sinusitis is manifested by congestion, lack of nasal breathing, headache and mucous discharge. If a child has chronic sinusitis, purulent mucus from the nose may appear. In this case, the fever can exceed 38 degrees;
- eustachitis and otitis media. When inflammation engulfs the Eustachian tube, the mucous membrane becomes edematous, thereby narrowing the lumen. The consequence of this is the obstructed passage of air, which is why the ears are often "stuffed up". Violation of the ventilation work of the pipe leads to the activation of conditionally pathogenic flora in the middle ear section and the development of inflammation. In addition, the infection can pass from the oropharynx, provoking otitis media. Symptomatically, the disease manifests itself as soreness in the ear or sore throat when swallowing, which radiates into the ear. Hearing gradually decreases, the child complains of ear congestion, tries to lie on the sore side, and the temperature can reach 38.5 degrees. If the treatment of otitis media is not started on time, the risk of accumulation of pus in the inner ear and rupture of the membrane increases.With the appearance of suppuration, the tactics of treatment change, because with perforation of the membrane, alcohol-containing ear drops are prohibited.
In children, the incidence of complications of pharyngitis in the form of otitis media is much higher, due to anatomical features (narrower diameter of the Eustachian tube and frequent adenoiditis).
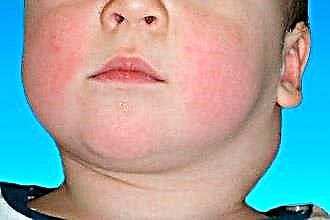 lymphadenitis. With the progression of the inflammatory process, local lymphadenitis is observed. When probing closely located lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular), their soreness is noted. They become edematous and slightly increase in size.
lymphadenitis. With the progression of the inflammatory process, local lymphadenitis is observed. When probing closely located lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular), their soreness is noted. They become edematous and slightly increase in size.
Prophylaxis
Signs of pharyngitis may bother much less often if you follow some recommendations. They will help not only protect the child from sore throat, but also reduce the risk of developing other diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis):
- the child needs good rest. This applies to night and day sleep, limitation of physical labor, control over mental stress and getting rid of stress;
- nutrition in childhood is one of the main components of strong immunity, in connection with which parents are required to enrich the diet with useful products (dairy products, cereals, soups, fruits, vegetables, herbs). At the same time, the abuse of flour, sweets, crackers, canned food, fatty, fried foods and carbonated drinks leads to indigestion and weakening of the immune system;
- regular visits to the ENT doctor and dentist for a preventive examination. This is especially true for children with caries, chronic diseases of the ENT organs and diathesis;
- limiting the child's contact with people who are sick with an infection, especially during an epidemic;
- if a child is sick, it is not worth sending him to kindergarten in order to give him an opportunity to “lie down” and restore the internal forces of the body. In addition, you will save other children from illness;
- spa treatment is useful for every person. For children, there is nothing better than the sun and sea water, but you need to remember about the permissible time spent in the sun in the summer (in the morning before 10:00 and in the afternoon from 16:00).
Believe me, a child's immunity depends not only on the genetic material, but also on the efforts of the parents to raise him strong and healthy.

 laryngitis. It develops as a result of the spread of infection and inflammation to the vocal cords, making them swollen and less mobile. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as a dry cough, similar to the barking of a dog, which further irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and increases the pain. In childhood, especially at 2-5 years of age, there is an increased risk of developing croup, which is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of a child. The fact is that against the background of pronounced inflammation, the lumen of the larynx becomes much narrower, making it difficult for air to pass. Parents may notice noisy, rapid breathing and shortness of breath when playing. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the lungs, internal organs suffer from hypoxia. The brain is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation, which is clinically manifested by drowsiness, yawning and moodiness;
laryngitis. It develops as a result of the spread of infection and inflammation to the vocal cords, making them swollen and less mobile. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as a dry cough, similar to the barking of a dog, which further irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and increases the pain. In childhood, especially at 2-5 years of age, there is an increased risk of developing croup, which is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of a child. The fact is that against the background of pronounced inflammation, the lumen of the larynx becomes much narrower, making it difficult for air to pass. Parents may notice noisy, rapid breathing and shortness of breath when playing. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the lungs, internal organs suffer from hypoxia. The brain is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation, which is clinically manifested by drowsiness, yawning and moodiness; lymphadenitis. With the progression of the inflammatory process, local lymphadenitis is observed. When probing closely located lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular), their soreness is noted. They become edematous and slightly increase in size.
lymphadenitis. With the progression of the inflammatory process, local lymphadenitis is observed. When probing closely located lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular), their soreness is noted. They become edematous and slightly increase in size.