Inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa often occurs due to the development of other respiratory diseases. Therefore, the symptoms of laryngitis in adults at the initial stages of development practically do not differ from the manifestation of ARVI. Patients feel weakness in the body, sore throat, fever, malaise, etc. The disease can be diagnosed as early as 2-3 days after the defeat of the vocal cords and larynx.
 Spasmodic cough, hoarseness and shortness of breath are characteristic manifestations of laryngitis that are difficult to confuse with other diseases. Severe swelling of soft tissues is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen in the larynx, so patients complain of a lack of oxygen, stridor (noisy breathing) and dizziness. Is it possible to independently recognize laryngitis? The symptoms of the disease are quite specific, but it must be diagnosed as early as possible. Running inflammation in the respiratory organs can cause the development of false croup and loss of sonority, i.e. aphonia.
Spasmodic cough, hoarseness and shortness of breath are characteristic manifestations of laryngitis that are difficult to confuse with other diseases. Severe swelling of soft tissues is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen in the larynx, so patients complain of a lack of oxygen, stridor (noisy breathing) and dizziness. Is it possible to independently recognize laryngitis? The symptoms of the disease are quite specific, but it must be diagnosed as early as possible. Running inflammation in the respiratory organs can cause the development of false croup and loss of sonority, i.e. aphonia.
About the disease
Laryngitis is an infectious or allergic inflammation in the soft tissues of the larynx and vocal cords. As a rule, the disease occurs as a complication of ARVI, bronchitis, measles, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, sinusitis, flu and rhinosinusitis. Respiratory disease can be promoted by:
- overheating and hypothermia;
- tobacco smoking;
- overstrain of the vocal apparatus;
- trauma to the laryngopharyngeal mucosa;
- constant breathing through the mouth;
- dusty or gassed air;
- allergens (wool, household chemical vapors).
Depending on the characteristics of the course of inflammation in the larynx, the symptoms of laryngitis can vary significantly. In acute laryngitis, signs of airway damage appear suddenly. Sore throat and dry mucous membranes begin to disturb the patients. Sluggish laryngitis practically does not manifest itself in any way, which is why patients are in no hurry to see a pulmonologist or an ENT doctor. But it is the chronic form of laryngitis that is dangerous because it leads to a pathological change in the structure of tissues.
What's going on in the throat?
Inflammation of the larynx is triggered either by irritants or pathogens. Infection occurs, as a rule, against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses. The mucous membranes of the respiratory system become thinner, so they stop producing the required amount of proteolytic substances that destroy opportunistic fungi, viruses and microbes. All this creates optimal conditions for the development of pathogenic flora in the larynx, as a result of which inflammatory reactions occur.
Due to the penetration of viruses and bacteria into soft tissues, the blood vessels in the lesions expand. Due to this, protective cells (leukocytes, granulocytes) rush to the places of localization of the pathogenic flora with the blood flow. The subsequent release of histamine leads to severe tissue edema, as a result of which the disease begins to manifest itself.
Pathological processes in the ENT organs lead to thickening of the mucous membrane and vocal cords. For this reason, the glottis narrows somewhat, as a result of which the voice becomes hoarse. Inflammation of the larynx activates the so-called goblet cells, which begin to produce large amounts of phlegm. Due to irritation of the mucous membrane, patients have a spastic cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, etc.
Signs of laryngitis
What are the first signs of laryngitis in adults? 2-3 hours after the defeat of the larynx, patients feel unwell, a slight increase in temperature and drowsiness. Such manifestations indicate the intoxication of the body, which occurs as a result of the vital activity of bacteria or viruses in the respiratory tract.
Many sufferers think that the overwhelming fatigue is not due to a respiratory illness, so they do not try to stop the symptoms. The next day after waking up, the mouth is dry and there is a slight burning sensation in the throat. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms are accompanied by a feeling of a hard coma at the level of the Adam's apple. When a spastic cough appears, most people already suspect that they have a cold, SARS or other respiratory disease.
A low temperature, malaise, dry mucous membranes and a burning sensation in the throat are the very first signs of the development of laryngitis in adults.
Common Symptoms
The symptomatic picture of laryngitis is characterized by a moderate deterioration in well-being. Inflammation in the larynx is indicated by spastic cough, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and shortness of breath. How is laryngitis manifested in the late stages of development? The characteristic symptoms of the disease include:
- hoarseness of voice (up to aphonia);
- sore throat, aggravated by talking;
- a constant burning sensation in the throat;
- cough with little sputum production;
- shortness of breath (inspiratory dyspnea);
- moderate fever and chills.
As a rule, a persistent cough is worse during sleep, when the patient takes a horizontal position. In this case, the patency of the airways decreases somewhat, which leads to even greater irritation of the mucous membrane and the occurrence of paroxysmal cough. Forced exhalation further injures the tissues of the larynx, therefore, when coughing up, blood impurities can be detected in the sputum.
Local manifestations
On examination, the laryngopharyngeal mucosa looks very reddened and swollen. In the area of the vocal cords, soft tissues swell greatly, therefore, patients show symptoms of respiratory failure. Due to inflammation, the blood vessels in the lesions expand greatly, and their walls become thinner. In this regard, crimson dots form on the walls of the larynx, which can bleed.
Diffuse inflammation of the larynx often causes damage to the trachea and bronchi, as a result of which tracheobronchitis and pneumonia develop.
With isolated laryngitis, local manifestations will have significant differences. Areas of redness often include the epiglottis and vocal cords. In the acute course of the disease, the upper trachea can be involved in inflammation. Laryngotracheitis is diagnosed in such patients. The associated disease is rather difficult. Laughter, loud conversation, or inhalation of frosty air can provoke attacks of a suffocating cough.
Types of acute laryngitis
As already mentioned, laryngitis often develops as a complication of influenza, tonsillitis, bronchitis and other respiratory diseases. In this regard, the clinical manifestations of the disease will have some differences. Depending on the characteristics of the course of inflammatory reactions and the causes of damage to the larynx, the following forms of acute laryngitis are distinguished:
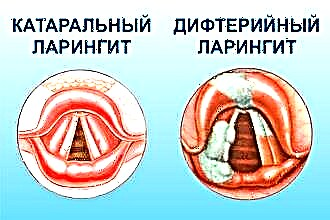 diphtheria - the walls of the larynx are covered with a white dense film, which, with a spastic cough, often separates from the mucous membrane and clogs the respiratory tract;
diphtheria - the walls of the larynx are covered with a white dense film, which, with a spastic cough, often separates from the mucous membrane and clogs the respiratory tract;- professional - the vocal cords in some places thicken and become covered with "singing nodules"; the disease is more common in people of speech professions (lecturers, teachers, TV presenters);
- hemorrhagic - small erosions form on the walls of the larynx, which can bleed and stain the sputum that is coughing up when coughing;
- syphilitic - the inner surface of the larynx is covered with mucous plaques, in the place of which scars form over time; due to tissue destruction, the vocal cords often lose elasticity, as a result of which patients develop persistent voice disorders;
- tuberculous - there is a deformation of the tissues of the epiglottis, vocal cords and laryngeal mucosa, on which nodular formations appear;
- catarrhal - the least dangerous form of the disease, which is characterized by slight swelling and redness of the mucous membranes, as well as "barking" cough.
Any of the above forms of acute laryngitis can provoke edema in the lining space of the larynx and, as a result, the development of false croup.
The most dangerous complication of laryngitis is a false croup, in which stenosing phenomena occur in the airways. A strong narrowing of the lumen in the laryngopharynx is fraught with the development of respiratory failure, asthma attacks, asphyxia and death.
Types of chronic laryngitis
Chronic (sluggish) laryngitis is a consequence of improper and delayed treatment of an acute form of respiratory disease. Sluggish inflammatory reactions in tissues occur due to non-observance of voice rest, smoking, work in hazardous enterprises, irrational intake of medicines, etc. In otolaryngology, it is customary to distinguish two main forms of chronic laryngitis, namely:
- atrophic - characterized by a strong thinning of the walls of the larynx, as a result of which it becomes crusted; patients suffer from constant dry throat, paroxysmal dry cough and a virtual absence of voice (aphonia);
- hyperplastic - accompanied by a strong thickening of the vocal cords and the mucous membrane of the larynx, as a result of which the voice becomes very coarse, and the airway patency decreases; patients develop persistent respiratory dysfunctions - shallow breathing, shortness of breath, involvement of the intercostal muscles in the breathing process (intercostal retractions).
Both forms of the disease pose a particular threat to the vocal cords. If the inflammation is not stopped in time, even after undergoing a course of treatment, the elasticity of the ligaments is not always restored. Subsequently, this can cause dysphonia or persistent loss of sonority of the voice.

 diphtheria - the walls of the larynx are covered with a white dense film, which, with a spastic cough, often separates from the mucous membrane and clogs the respiratory tract;
diphtheria - the walls of the larynx are covered with a white dense film, which, with a spastic cough, often separates from the mucous membrane and clogs the respiratory tract;