It hurts in the throat and wants to cough for many diseases. Symptoms may indicate the initial stage of the pathology or indicate the progression of the disease. In most cases, an inflammatory process in the larynx is diagnosed, which provokes a desire to cough up.
 The most common causes that provoke a sore throat and dry cough include diseases of the respiratory system and digestive tract:
The most common causes that provoke a sore throat and dry cough include diseases of the respiratory system and digestive tract:
- pharyngitis, laryngitis, laryngotracheitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- allergic reaction.
The appearance of a cough can occur reflexively when the mucous membrane of the oropharynx dries up due to:
- dehydration (insufficient fluid intake - less than 500 ml per day, large losses with vomiting, diarrhea with dysentery, cholera, food toxicoinfection);
- a long course of taking antihistamines, diuretic, psychotropic, antihypertensive drugs with a diuretic effect, as well as the use of nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect;
- coughing can bother with oncopathology, when a neoplasm of benign or malignant origin spreads to the nerve endings;
- damage to the salivary glands due to the formation of calculi, inflammation, which leads to a decrease or complete cessation of saliva secretion;
- strong experience and stress.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis refers to an inflammatory pathology in which the pathological focus is located in the posterior pharyngeal wall. In 70% of cases, viral infection is diagnosed (parainfluenza, rhino, adenovirus). Among bacterial microorganisms, streptococcus is often detected as the cause of the development of the disease.
In addition, sore throat and coughing with pharyngitis can be caused by exposure to cold, polluted air, a foreign body, or smoking.
Symptomatically, the disease manifests itself as painful swallowing, talking, subfebrile hyperthermia, lymphadenitis, and mild malaise. There is a cough from a sore throat due to irritation of the laryngeal mucosa. In the chronic form, the throat is sore to a lesser extent, but with an exacerbation, the symptoms intensify significantly, and a cracking dry cough appears.
For diagnosis, pharyngeal swabs and pharyngoscopy are used:
- the catarrhal form is manifested by hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa and palatine tonsils, edema
 uvula, bloom of a mucopurulent character;
uvula, bloom of a mucopurulent character; - the atrophic chronic form leads to thinning, paleness and dryness of the mucous membrane, the surface of which becomes shiny with mucus and crusts;
- hypertrophic - characterized by the proliferation of lymphoid tissue in the pharyngeal area.
If untreated, the disease can be complicated by laryngitis, tracheitis, when a sharp sore throat and dry cough are worried, or the formation of a peritonsillar abscess.
With bacterial infection with hemolytic streptococcus, the risk of developing rheumatism (damage to the heart, kidneys, and joints) increases.
Laryngitis
Among the inflammatory diseases that contribute to the appearance of perspiration, it is worth highlighting laryngitis, which affects the larynx and vocal cords. Often, viral pathogens (ARVI, measles, scarlet fever, whooping cough) provoke laryngitis. Do not forget about the risk of disease due to the negative effects of cold air, overstrain of the ligaments, smoking or hypothermia.
From clinical symptoms, we draw attention to severe perspiration, sore throat, sudden intense cough and subfebrile hyperthermia. A lump is felt in the throat, the voice becomes rough, hoarse up to aphonia.
When a cough bothers you, your throat hurts, the temperature can remain at a normal level. If a wet cough occurs, a slight fever is possible. Throat can be torn with chronic laryngitis. The chronization of the process is influenced by many factors, for example, constant hypothermia, smoking or the presence of an infectious agent.
Untreated pathological process is complicated by acute stenosis of the larynx. From diagnostic techniques, a smear from the pharynx and laryngoscopy are prescribed:
- in an acute course, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the larynx, ligaments is visualized, mucus is noted, however, with flu, hemorrhages into the mucous membrane are possible;
- with chronic - there is congestive edema, hyperemia, some thickening of the mucous membrane, and thick mucus is visualized in the lumen of the larynx.
Tracheitis
The defeat of the trachea of an inflammatory nature develops in the form of laryngotracheitis or tracheobronchitis. The cause of the disease is infection with viral (influenza, parainfluenza, rubella, chickenpox), bacterial pathogens (streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus), allergic factors, hypothermia and smoking.
With tracheitis, there is a dry cough, perspiration, chest pain and febrile hyperthermia. Cough disturbs in the form of attacks, develops when screaming, after taking a deep breath of cold air or when laughing. At the end of the attack, a small amount of sputum is released.
With laryngotracheitis, in addition to coughing, dryness, tickling in the throat, lymphadenitis, headaches, impaired psychoemotional state and insomnia are noted.
Complications are presented by bronchitis and pneumonia. For diagnostics, sputum bacterial culture, examination of nasopharyngeal / oropharyngeal smears and laryngoscopy are used. The picture of laryngotracheoscopy is presented:
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of tissues;
- petechial hemorrhages;
- thickening of the mucous membrane (with a hypertrophic form);
- dryness, thinning of the mucous membrane, the presence of crusts (with an atrophic form).
For additional diagnostics, rhinoscopy, pharyngoscopy, chest x-ray and paranasal sinuses are prescribed.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Digestive dysfunction occurs due to reflux, in which a lump of food is thrown into the upper respiratory tract. Among the reasons it is worth highlighting:
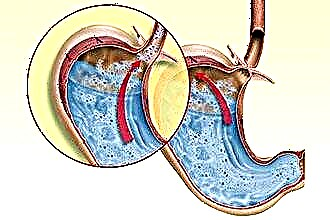 a decrease in the tone of the esophageal sphincter due to the abuse of coffee, carbonated, alcoholic beverages, prolonged use of certain medications, smoking or pregnancy;
a decrease in the tone of the esophageal sphincter due to the abuse of coffee, carbonated, alcoholic beverages, prolonged use of certain medications, smoking or pregnancy;- increased intra-abdominal pressure due to ascites, flatulence, obesity;
- diaphragmatic hernia, in which there is a decrease in pressure on the lower esophageal region;
- rapid consumption of food in large volumes, swallowing of air, which, in combination, leads to an increase in intragastric pressure;
- abuse of fatty foods, hot seasonings and fried foods.
Of the symptoms, a person is worried about tickling and coughing, which occurs reflexively when acidic contents enter the larynx and trachea. Irritation of the esophageal mucosa develops esophagitis, manifested by:
- heartburn (retrosternal burning sensation radiating to the neck);
- sour eructation (sour tastes are felt in the mouth, aggravated in the supine position, when bending);
- odonophagy (pain syndrome when swallowing, as the esophagus moves);
- hiccups;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
GERD is the basis for the development of strictures and oncological neoplasms of the esophagus.
To diagnose the disease, the following is used:
- test with a drug that reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid. If after 2 weeks of taking medication the symptoms of the disease decrease, the diagnosis is confirmed;
- pH monitoring during the day when the pH level is measured with reflux;
- endoscopic methods, thanks to which it is possible to establish esophagitis, precancerous conditions and malignant pathologies;
- biopsy of the neoplasm;
- ECG, Holter monitoring, which allows diagnosing cardiac pathology;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray diagnostics makes it possible to visualize narrowings, ulcerative defects and hernias;
- a test for Helicobacter pylori, according to the results of which a special therapy is prescribed.
With the progression of the disease, complications develop in the form of erosions, ulcerative lesions, obstructive bronchitis, bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, cicatricial changes and precancerous processes.
Allergic reaction
 A sore throat and dry cough are observed with an allergic reaction. Symptomatically, allergy also manifests itself as coughing fits with the development of choking, respiratory failure, conjunctivitis, keratitis, rhinitis, or skin manifestations (itching, rash, redness).
A sore throat and dry cough are observed with an allergic reaction. Symptomatically, allergy also manifests itself as coughing fits with the development of choking, respiratory failure, conjunctivitis, keratitis, rhinitis, or skin manifestations (itching, rash, redness).
With a secondary infection, a purulent discharge appears when coughing, which indicates an infectious-allergic process. Allergies often begin with rhinorrhea, which occurs when plants bloom, poplar fluff spreads, or after contact with animals.
In the diagnosis, laboratory tests and the study of a genetic history are used.
Therapeutic tactics
After confirming the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease, specific treatment is prescribed:
- adherence to a diet;
- proton pump inhibitors (pantoprazole);
- prokinetics (motilium);
- blockers of histamine receptors;
- ursodeoxycholic acid (ursofalk);
- phospholugel - for relieving heartburn.
In addition, it is recommended to give up smoking, wear a belt, which increases intra-abdominal pressure, control body weight, eat small amounts of food up to 5 times a day. After eating, do not run, lie or bend forward. To prevent an exacerbation of the disease, a preventive examination and a therapeutic course in the autumn-spring period are recommended.
If an allergic reaction develops, antihistamines should be taken, and the effects of the allergen should be eliminated. To treat inflammatory and infectious pathology and reduce sore throat, rinses with antiseptic solutions are prescribed.
When a dry cough occurs, drugs are used that suppress the cough reflex, for example, Sinekod, Bronholitin. If a person is worried about a wet cough, the use of Prospan, Gedelix and Lazolvan is recommended.
Rinsing can be carried out with Miramistin, Furacilin, herbal decoctions, soda, salt and other natural remedies. Inhalation with Dekasan, Rotokan and alkaline mineral water (still) is also effective.
Complex treatment allows to provide a powerful anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, analgesic and antimicrobial effect. Reducing the viscosity of the phlegm facilitates its excretion. Do not forget about proper nutrition, good rest, humidifying the air in the room, frequent ventilation, wet cleaning and vitamin therapy.

 uvula, bloom of a mucopurulent character;
uvula, bloom of a mucopurulent character; a decrease in the tone of the esophageal sphincter due to the abuse of coffee, carbonated, alcoholic beverages, prolonged use of certain medications, smoking or pregnancy;
a decrease in the tone of the esophageal sphincter due to the abuse of coffee, carbonated, alcoholic beverages, prolonged use of certain medications, smoking or pregnancy;