Differential diagnosis of diseases is perhaps one of the most difficult tasks that are performed in the course of a diagnostic search. It is necessary to correctly compare the objective signs, complaints and anamnestic data, that is, information about the events preceding the disease. When it comes to tonsillitis, the symptoms of inflammation of the glands and other tonsils included in the Pirogov-Waldeyer lymphadenoid ring help differentiate the disease from pharyngitis or ARVI. But at the same time, it is necessary to distinguish between numerous types of tonsillitis, which makes it necessary to know what signs are characteristic of different types of inflammation of the tonsils.
Inflammation as a typical process
 The tonsils are anatomical structures made up of lymphoid tissue. There are only six of them: two palatine (also often referred to as "tonsils"), two trumpets, one pharyngeal and one lingual. Inflammation can affect any of the tonsils, but an independent examination of the pharyngeal cavity (pharyngoscopy) without special devices will allow you to see only the tonsils. The inflammatory process involving the tonsils is denoted by the term "tonsillitis".
The tonsils are anatomical structures made up of lymphoid tissue. There are only six of them: two palatine (also often referred to as "tonsils"), two trumpets, one pharyngeal and one lingual. Inflammation can affect any of the tonsils, but an independent examination of the pharyngeal cavity (pharyngoscopy) without special devices will allow you to see only the tonsils. The inflammatory process involving the tonsils is denoted by the term "tonsillitis".
Specialists in the field of pathological anatomy, pathological physiology and other medical disciplines classify inflammation of the tonsils in different ways - depending on the reactivity of the body, the prevalence of any disturbances in pathogenesis. However, for the diagnosis of tonsillitis, it is important, first of all, to distinguish between such types of the inflammatory process as:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Acute inflammation is characterized by active development, an intensive course - while it resolves after a short time, it does not last longer than several weeks. Tissue damage can be quite extensive, but the likelihood of complete recovery is higher - especially if only the surface layers are affected. With timely relief of the acute process, the damaged tissue does not undergo irreversible changes. Plaques, even if they have covered the entire tonsil, disappear without leaving scars.
In chronic inflammation, the situation is different. An example is chronic tonsillitis, in which plugs form in the palatine tonsils, and damage due to the multiplication of bacteria and the release of toxins by them continues constantly. The possibility of developing hypertrophy (increase in size), the existence of foci of necrosis, and the deposition of calcium salts cannot be ruled out. Although the course of the chronic inflammatory process is sluggish, it is characterized by exacerbations (relapses), which lead to the aggravation of existing disorders.
You need to know that inflammation is considered a typical pathological process. This means that the cascade of reactions that initiate changes in the area of inflamed tissues will be the same regardless of the localization of the focus and the type of etiological factor. Inflammation is the result of damage, violation of adaptive capabilities, it always develops consistently and naturally, over a period of time. The symptoms of tonsil inflammation can be classified as:
- Local.
- General.
Local features include:
- redness (hyperemia);
- swelling (swelling);
- local hyperthermia (local heat);
- pain.
Also, we must not forget that local disturbances can be accompanied by a change in the appearance of the tonsils due to the appearance of various plaques on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Inflammation of the tonsils should be distinguished from inflammation of the pharynx (pharyngitis) - these are different diseases; a simultaneous combination of symptoms is called tonsillopharyngitis.
With pharyngitis, the back wall of the pharynx is affected, and the tonsils can only partially redden, along the edges. Since sore throat as a symptom combines both diseases, it is important to conduct an objective examination for the correct choice of therapy.
Among the common signs of tonsillitis, first of all, fever should be called - it can reach various values, but one way or another accompanies the inflammatory process, since it is a protective reaction on the part of the immune system. The severity of fever, like the severity of local changes, reflects the degree of reactivity of the organism.
The most complete picture of the pathological process will be in the acute type of inflammatory reactions, since chronic inflammation of the glands, as mentioned earlier, has a less vivid course and in a state of remission (between exacerbations) its signs are erased. In addition, most of the general and local symptoms (such as a violation of the general condition, an increase in the general and local temperature, noticeable edema and redness, severe soreness) are not typical for chronic tonsillitis, if we are not talking about a relapse.
Acute banal tonsillitis
Acute banal tonsillitis, or angina, is understood as an acute inflammation of the glands with a bacterial etiology (beta-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus). At the same time, it is important to remember that disorders in acute inflammation appear suddenly, "acutely", and grow rapidly.
Catarrhal sore throat
All local signs of an inflammatory response are present. The glands swell, turn red, there is a sore throat, especially pronounced when swallowing, but there are no plaques. Palatine arches can also become inflamed.
Follicular tonsillitis
Inflammation of the glands is characterized by widespread swelling and redness. In this case, the follicles in which pus has accumulated are visible through the mucous membrane, look like whitish and yellowish dots (round, 1 to 3 mm in size) on the surface of the tonsils.
Lacunar angina
Swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane is combined with the appearance of insular plaques. At the beginning of the disease, they are small, located separately, but then merge and form films of a white-yellow hue. This plaque can cover the entire amygdala and lasts for several days.
Plaque with a lacunar form of inflammation is removed with a spatula without damaging the mucous membrane, does not go beyond the tonsils.
This is an important feature in distinguishing lacunar tonsillitis from diphtheria. When examining, one should also not forget about mixed sore throat - it does not occur so often, it combines signs of different forms. Inflammation of the tonsils on the one hand can be catarrhal, and on the other - follicular, lacunar.
For banal tonsillitis, similar general manifestations are characteristic - weakness, headache, febrile fever (38-38.9 ° C). Regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. At the same time, the phenomena of intoxication can be striking in any form, especially if the patient is a small child. But usually the lacunar angina is the most difficult, and the catarrhal is the most easy.
Other types
In addition to banal tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils can be provoked by bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi. Angina, in fact, is tonsil diphtheria, scarlet fever; symptoms of tonsillitis are observed with measles, herpes infection, may be present with leukemia, typhoid fever, tularemia. It is impossible to describe a single picture that would accurately illustrate all the changes observed in all variants of tonsillitis. Therefore, it is advisable to pay attention to the features of the most common pathologies:
- diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- herpetic sore throat.
Diphtheria is one of the most dangerous forms of damage to the tonsils. This is due not only to a special type of inflammation (fibrinous), but also to the active production of a toxin by the causative agent, corynebacterium. Local signs of diphtheria:
- enlargement of the glands due to edema;
- mild redness, sometimes with a cyanotic shade;
- the presence of dirty gray, whitish patches with a smooth, sometimes wavy surface;
- moderate pain when swallowing.
Inflammation of the glands in diphtheria is characterized by the spread of dense plaque beyond their anatomical boundaries; when trying to remove his mucous membrane bleeds.
With scarlet fever, not only inflammation of the tonsils is observed, but also inflammation of the back of the pharynx, severe sore throat. Changes in the tongue are also characteristic - a dense white coating at the onset of the disease and the acquisition of a bright pink hue after a few days. Symptoms of a sore throat are combined with a rash on the skin, the changes correspond to the picture of a banal sore throat; with a necrotic form, areas of necrosis in the form of ulcers on the surface of the amygdala are visible.
Signs of inflammation of the glands in herpes sore throat include:
- Redness, swelling.
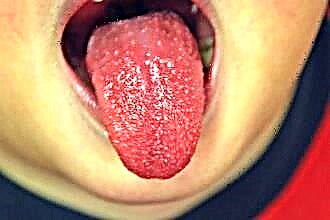
- Sore throat.
- The presence of a blistering rash on the tonsils.
The rash can be located not only on the tonsils, often spreads to the palatine arches, uvula, pharynx. Vesicles appear with the formation of defects in the mucous membrane, usually not prone to fusion.
Common signs depend on the form of the flow and a number of other factors. However, diphtheria is more often characterized by a moderate febrile reaction, while scarlet fever and herpetic sore throat are characterized by febrile and pyretic (38-39.9 ° C) indicators. The patient's well-being is due to the degree of intoxication - usually there is a headache, lethargy, pain in muscles and joints without a specific localization.
Chronic tonsillitis
What are the symptoms that distinguish acute from chronic tonsillitis? Both local and general signs are important. At the same time, during an objective examination, pus, both of a liquid consistency and in the form of plugs, filling the gaps is always visualized. The formation of traffic jams is one of the manifestations that indicate the long-term existence of a pathological process. In addition, the tonsils can be enlarged in size, adhered to the arches, adhesions often form between them.
Also for chronic tonsillitis symptoms are characteristic:
- Zak (swelling of the edges of the upper palatine arches);
- Giese (redness of the edges of the arches);
- Preobrazhensky (soaking with pus and redness of the edges of the palatine-lingual arches);
- bad breath, not caused by caries, diseases of the digestive system;
- a feeling of discomfort in the throat, mild pain when swallowing.
Palpation of regional lymph nodes is painful, their increase in size is determined. Some patients are worried about ear pain, intermittent coughing, unproductive cough.
Inflammation of the tonsils in the chronic form of tonsillitis has been observed for many months and even years, does not regress on its own.
How else do inflamed glands manifest themselves - do the symptoms of a general nature have features? In chronic tonsillitis, patients are worried about persistent weakness, fatigue, decreased ability to work, and weight loss. Periodically there are pains in the joints, in the region of the heart, episodes of subfebrile (37.1-37.9 ° C) fever. Frequent sore throats are noted, while episodes of exacerbation have manifestations similar to the banal purulent form of tonsillitis.