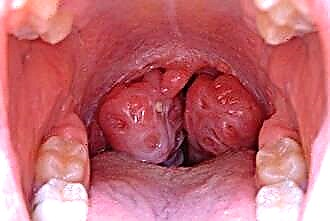
The most common pathology of the tonsils is tonsillitis, that is, an inflammatory tissue damage. However, do not forget about such formidable diseases as cancer, papillomas and a cyst of the palatine tonsil. This group of benign and malignant diseases poses a serious threat to life in the absence of timely treatment.
 First, we will analyze which neoplasms are related to a benign process. The difference between such cancers is the absence of metastasis and complete recovery after removal. Among benign tumors, we will dwell in more detail on angioma, fibroma, papilloma, cystic formations, teratoma, lipoma, as well as plasmacytoma.
First, we will analyze which neoplasms are related to a benign process. The difference between such cancers is the absence of metastasis and complete recovery after removal. Among benign tumors, we will dwell in more detail on angioma, fibroma, papilloma, cystic formations, teratoma, lipoma, as well as plasmacytoma.
In comparison with malignant foci, benign ones are diagnosed 10 times more often. According to otolaryngological statistics, men 25-40 years old often suffer from oncopathologies, but the risk of the appearance of pathological tissues in an infant is not excluded.
Predisposing factors include:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- prolonged inhalation of contaminated air (smog, occupational hazards);
- poor oral hygiene;
- chronic infectious and inflammatory processes of the mouth, nasopharynx;
- caries, stomatitis;
- removable dentures.
Symptomatically, the disease can be suspected based on the following clinical signs:
- sore throat;
- sensation of a foreign element in the oropharynx;
- difficulty swallowing;
- labored breathing;
- change in voice, the appearance of nasalism.
In some cases, there are manifestations of catarrhal inflammation in the form of pain in the oropharynx when swallowing or talking.
Let's take a closer look at some benign neoplasms:
- papilloma of the palatine tonsil appears as a result of the activation of the papilloma virus against the background of a decrease in immunity (colds, exacerbation of chronic pathology). In addition to papillomas, the development of warts or genital warts is possible. Visually, papillomas resemble nodules with papillae. The leg of the growth is narrow or wide, the nodes are located singly or in groups. Papillomas have a dense or loose structure, grayish color. The soft structure causes bleeding, germination into healthy tissues, self-removal, and re-formation. Hard papillomas do not recur and are incapable of bleeding. With multiple lesions of the tonsils and pharynx, it is worth talking about papillomatosis of the pharynx;
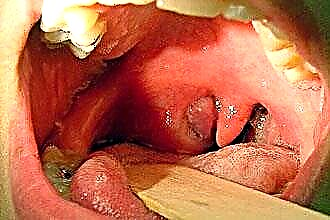
- fibroids - rounded, pinkish in color, with a wide stalk. The surface is smooth or bumpy and does not bleed when touched. The density of the formation can be cartilaginous, with the most dense area being the base. Microscopy reveals connective tissue and elastic fibers and blood vessels. Under the influence of negative factors, germination into healthy tissues and malignant transformation is possible. Reaching a large size, swallowing is significantly impaired and stenotic breathing appears. The risk of massive bleeding appears when germination into the vessels and the destruction of their walls. With the defeat of the Eustachian tube, hearing loss develops. Germination into bone structures leads to a change in the shape of the facial skeleton, and into the brain - the development of meningitis, impaired cerebral blood flow and nerve damage;
- teratomas are formed in the prenatal period due to violations of the laying and development of the organs of the embryo. Often, a hairy polyp is found that looks like a rounded outgrowth with vellus hair;
- angiomas develop from lymphoid structures or blood vessels. They can be localized on the tonsils, palate, pharyngeal wall and root of the tongue. The formations are characterized by a rapid increase with germination into unaffected tissues. Lymphangiomas are yellowish, multi-chambered and filled with lymph. As for the hemangioma, it is red and bleeds frequently;
- adenomas are gelatinous nodules on a wide base, surrounded by a capsule. The size reaches 20 mm. They are pink or grayish brown in color. Microscopy reveals atypical glands filled with mucus, purulent discharge and desquamated cells;
- cylindromes arise from the epithelium of the glands. Visually, the formation resembles a knot of more than 30 mm, of the correct shape with indistinct boundaries. Microscopic analysis reveals lobules and fibrous cords between them;
- neurogenic tumors type of neuroma, neurofibromas are rarely diagnosed. An oval neoplasm is located in a capsule with a flat surface. The neuroma is not prone to ulceration and bleeding;
- cystic formation can be of several types. Retention - cause clinical symptoms only at large sizes, which makes breathing difficult and increases the risk of asphyxia. They are usually round with a brittle wall. Dermoid formations refer to intrauterine defects;
- extramedullary plasmacytoma is a partially benign structure, since there have been cases of metastasis to the lymph nodes. One or more nodes are located on a wide base. The size reaches over 30 mm. Microscopy visualizes an infiltrate of polymorphic cells with a large number of plasma cells.
Diagnosis begins with pharyngoscopy, in which a neoplasm is detected. At the same time, the gland can enlarge, change its shape, color and become painful. To assess the prevalence of the pathological process, rino-, laryngo-, otoscopy, radiography and tomography are prescribed.
If not only the palatine tonsils are affected, but also neighboring organs, consultation with an ophthalmologist, neurologist and neurosurgeon is indicated. To confirm the benign nature, a biopsy is performed, however, histological analysis is often performed after the removal of the formation.
In differential diagnosis, one should distinguish lymphogranulomatosis, scleroma and benign neoplasms.
Treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination.
In most cases, surgical intervention is prescribed, since it is impractical to treat the tumor with conservative methods.
Taking into account the size of the focus and the presence of germination, the most convenient access and removal method are selected.
So, the operation may include transection of the leg, exfoliation of the tumor from the capsule, followed by its removal, cryotherapy, sclerosing or diathermocoagulation.
Malignant neoplasms
Palatine tonsil cancer is characterized by rapid growth, infiltration into adjacent healthy tissues, local and distant metastasis. In most cases, malignant diseases in otolaryngology affect people after 40 years. More than half of the diagnoses are represented by the defeat of the tonsils, and 26% are diagnosed with cancer of the pharynx and palate.
 The neoplasms have the structure of lymphoepithelioma, carcinoma, cytoblastoma or reticulocytoma. The difficulties in detecting cancer at an early stage are the asymptomatic course at the beginning of the disease. At 3, 4 stages, pathology is detected in more than 40% of patients, and in 45% of cases, metastases are found.
The neoplasms have the structure of lymphoepithelioma, carcinoma, cytoblastoma or reticulocytoma. The difficulties in detecting cancer at an early stage are the asymptomatic course at the beginning of the disease. At 3, 4 stages, pathology is detected in more than 40% of patients, and in 45% of cases, metastases are found.
Lymphoepithelioma refers to a type of squamous cell malignant tumor. The disease develops from lymphoid tissues, looks like a knot with a bumpy surface, grayish tint and with indistinct boundaries.
Of the clinical symptoms, it should be noted:
- earlier metastasis with dysfunction of internal organs;
- damage to the lymph nodes;
- labored breathing;
- difficulty swallowing;
- nasal voice;
- soreness in the oropharynx;
- a lump in the throat.
As it grows, the oncological process involves the nasal cavity, sinuses and the orbit. The defeat of the cranial nerves is observed when they grow into the brain. With pharyngoscopy - the palatine tonsil is enlarged on one side, the mucous membrane is tense, hyperemic, and the lacunae are practically not visualized.
When germinating into the posterior pharyngeal wall and tongue, bleeding from ulcerative defects is observed. Clinically, this is manifested by profuse salivation, difficulty chewing, shortness of breath, putrid odor, and weight loss.
In 25% of cases, the detection of regional lymph nodes is the first symptom of the disease. Other malignant tumors of this localization practically do not differ in symptoms. Their difference is established in the diagnostic process. For this, pharyngoscopy, laryngoscopy, radiography, tomography and biopsy are prescribed.
Treatment is based on the type of malignant neoplasm, its aggressiveness and sensitivity to chemotherapy. In addition to chemotherapy, radiation and surgery can be used. A positive effect can be achieved with an integrated approach. If the tumor is inoperable, when large vessels or vital organs are involved in the oncological process, palliative treatment is indicated.
Medical care is considered the most effective in detecting a tumor at the initial stage. The issue of tube feeding, gastrostomy and tracheostomy is also considered.
The prognosis of diseases depends on many factors. Preventive examinations help to identify oncopathology at the beginning of development, which makes it possible to improve the prognosis and prolong life.