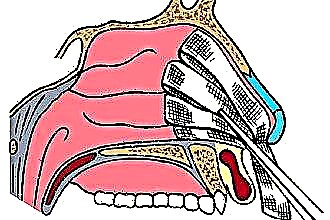
Frontitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the inner surface of the frontal sinuses. Recently, the disease is getting younger and more common. At an early stage, it responds well enough to treatment, but neglected frontal sinusitis is fraught with serious complications. There is no single scheme for treating frontal sinusitis - the choice of method depends on the stage, form, characteristics of the course of the disease and the general state of health of the patient.
Types of frontal sinusitis
 Like any inflammatory disease, frontal sinusitis has an acute and chronic form. The acute form is most often provoked by contact with the mucous membranes of pathogens, and in the absence of proper treatment, it gradually turns into a chronic one, in which the disease either fades away or worsens again.
Like any inflammatory disease, frontal sinusitis has an acute and chronic form. The acute form is most often provoked by contact with the mucous membranes of pathogens, and in the absence of proper treatment, it gradually turns into a chronic one, in which the disease either fades away or worsens again.
Since the frontal sinuses are a paired formation, right-sided, left-sided and bilateral frontal sinusitis are divided according to localization. For reasons of occurrence, frontal sinusitis is conventionally divided into: allergic, polyposis, infectious, edematous. The division is conditional, since most often the disease develops under the simultaneous influence of several negative factors at once:
- a sharp and / or significant decrease in immunity, which can be caused by severe hypothermia, stress, vitamin deficiency, recent diseases;
- strong or prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane (physical or chemical): polluted air, strong odors, chemical fumes, bad habits;
- chronic respiratory diseases, especially rhinitis or other types of sinusitis: sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- significant curvature of the nasal septum, leading to a violation of air circulation in the sinuses;
- frequent allergic reactions, accompanied by severe edema and profuse mucus production;
- overgrowth of polyps formed in the nose or frontal sinuses, which block the exit of mucus into the nasal cavity;
- activity of pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria) that provoke inflammatory processes.
The treatment depends primarily on how quickly and correctly the frontal sinusitis is diagnosed, since it should be aimed mainly at eliminating the external and internal factors provoking it.
If the root cause of the disease is not completely eliminated, it will continue in a sluggish form and become chronic, and eventually spread to adjacent sinuses or lead to the development of complications.
Symptoms
For the acute form of frontal sinusitis, rather pronounced symptoms are characteristic, based on which a preliminary diagnosis can be made:
 a headache clearly localized in the middle part of the forehead, which is aggravated by palpation, tapping and tilting the head down;
a headache clearly localized in the middle part of the forehead, which is aggravated by palpation, tapping and tilting the head down;- orbital symptoms: redness of the inner corner of the eyes, tearing, photophobia, swelling of the upper eyelid;
- change in the color and temperature of the skin in the projection zone of the lesion;
- an increase in body temperature, the range of which can be from subfebrile values to 38-39 degrees;
- difficulty breathing through one nostril, persistent nasal congestion;
- copious mucous discharge: transparent or yellow-green with a characteristic purulent odor;
- a noticeable decrease in the acuity of the sense of smell or its complete loss;
- signs of general intoxication (especially with a purulent form): nausea, vomiting, intestinal disorders.
In the chronic form, the same symptoms are present, but they give a blurred picture: the head hurts periodically, nasal discharge is usually only in the morning, there is no temperature, the sense of smell is partially restored.
It is important to remember here that there is no residual rhinitis, and if any of the symptoms persist for more than 3-4 weeks, you should consult a doctor again.
According to the patient's complaints and the existing symptoms, one can only assume the presence of the disease. But it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis by visual examination - this requires hardware examination and laboratory tests. So the doctor will be able to get a complete picture of how the disease is progressing, what is its main cause and whether there are complications.
Conservative methods
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults, even with a severe degree of the disease, is initially carried out conservatively. Based on the test results, the doctor selects the drugs that are most effective in this case and describes in detail the regimen. Usually, the course of treatment simultaneously covers several areas:
- Reduced puffiness. Achieved by the use of antihistamines or vasoconstrictor drugs. After the edema subsides, a channel opens, connecting the frontal sinuses with the nasal cavity, and mucus begins to actively move out. At the same time, these drugs reduce the amount of mucus produced so that it does not accumulate as quickly.
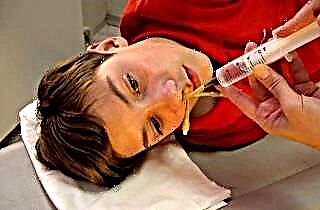 Relief of inflammation. It all depends on the root cause. If there is an infection in the sinuses, antibiotics or antifungal agents should be used. If the inflammation is caused by a chronic allergy, antihistamines are sufficient. With a polyposis form, these measures will only have a temporary effect. Most modern anti-inflammatories simultaneously relieve pain and lower body temperature.
Relief of inflammation. It all depends on the root cause. If there is an infection in the sinuses, antibiotics or antifungal agents should be used. If the inflammation is caused by a chronic allergy, antihistamines are sufficient. With a polyposis form, these measures will only have a temporary effect. Most modern anti-inflammatories simultaneously relieve pain and lower body temperature.- Cleansing the sinuses. The most effective way to do this is to rinse your nose. To do this, you can use antiseptic solutions or carefully strained decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus). In a hospital setting, catheter irrigation can be done, after which the mucous membranes are irrigated with drugs. This procedure is not very pleasant, but it significantly speeds up recovery.
- Thinning mucus. Viscous mucus is difficult to escape through a narrow channel, so it is advisable to change its consistency. This can be easily done with heating or steam inhalation. But the decision to use these procedures can only be made by a doctor: with a purulent form and some types of infection, they are contraindicated.
- Diet and regime. The patient must be prescribed a sparing daily regimen; in bad weather and in the cold season, he will have to temporarily refrain from walking. Food during illness should be light and of high quality, rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants. In this case, you will have to give up products that irritate the mucous membrane: carbonated water, hot seasonings and spices, too hot, salty and acidic foods.
Usually, conservative treatment of frontal sinusitis in an adult takes place at home. Hospitalization can be offered only with an advanced purulent form with a threat or already begun complications, when there is a possibility that surgery may be required.
Surgical intervention
With the accumulation of a large amount of pus, which does not find a way out, the risk of developing serious complications rapidly increases:
 inflammation of the meninges;
inflammation of the meninges;- multiple abscesses of the brain;
- general blood poisoning (sepsis);
- osteomyelitis of the bones of the nose and skull.
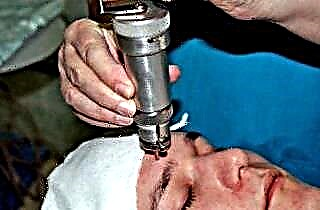
To quickly cure frontal sinusitis, in this case, you have to resort to surgical intervention - puncture of the frontal sinus. A puncture at the front allows you to pump out purulent contents in one procedure, thoroughly rinse the sinus and treat the mucous membranes with powerful drugs.
The operation is not difficult, but it requires the skill of the surgeon and careful observance of the conditions of sterility. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 15 minutes.
Puncture of the frontal sinus can be performed directly on the forehead or by inserting a needle through the nasal passage and the lower wall.With a large amount of pus, after all the manipulations have been performed, drainage is placed in the sinus to facilitate the passage of fluid. After 3-5 days, it is removed, and the puncture site quickly overgrows.
If, without a puncture, treatment in adults with a severe form can last up to 2-3 weeks, then after a puncture the condition improves significantly already by 2-3 days, and after 7-10 days the patient is discharged. But the decision on the need for such a procedure is made only by the attending physician, since it is associated, like any operation, with some risks.
To prevent an increase in inflammation after a puncture, a course of antibiotic treatment must be prescribed.
Ethnoscience
Acute purulent frontal sinusitis cannot be cured only with folk remedies! Such attempts, especially with the use of thermal procedures, will only lead to an accelerated development of the disease and an increase in the amount of pus with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, in the presence of characteristic yellow-green discharge and high body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor and follow his recommendations.
 If you have just begun frontal sinusitis, treatment with folk remedies is permissible, but only with constant monitoring of the general condition of the patient and changes in the symptoms of the disease. Traditional methods are not as effective as pharmaceutical drugs, so visible improvements should occur approximately 4-5 days from the start of treatment. If this did not happen, then your actions are wrong and you need medical help.
If you have just begun frontal sinusitis, treatment with folk remedies is permissible, but only with constant monitoring of the general condition of the patient and changes in the symptoms of the disease. Traditional methods are not as effective as pharmaceutical drugs, so visible improvements should occur approximately 4-5 days from the start of treatment. If this did not happen, then your actions are wrong and you need medical help.
From the home arsenal for the treatment of frontal sinusitis, you can use:
- Steam inhalation. For them, a soda solution (1 tsp per glass of water) or decoctions of medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects are suitable: St. John's wort, chamomile, sage, coltsfoot, eucalyptus, calendula. A good effect is obtained by adding essential oils of mint, menthol, cedar, pine, thuja, and juniper to the water. They also have antibacterial properties. The duration of inhalation at the front is 7-10 minutes, you can repeat it up to 2 times a day. After the procedure, active mucus discharge usually begins, so you need to clean your nose well.
- Nasal drops. Properly prepared and used, they often have an even more pronounced effect than pharmaceutical preparations. Juice of beetroot, cyclamen root, celandine, Kalanchoe helps well against all types of sinusitis. Use Kalanchoe juice with caution - it stimulates sneezing and, due to this, actively cleanses the sinuses. But if the outlet is blocked by pus, then sneezing can cause severe pain. An excellent remedy for edema is fresh potato juice. But all these drops should be done only immediately before use - upon contact with air, they quickly lose their useful properties.
- Warming up. Can be used at the initial stage of the disease or at the stage of recovery. They improve blood circulation, thin mucus and accelerate its passage, stimulate the regeneration of damaged mucous membranes. Any dry heat should be used for warming up: a blue lamp, solux, a bag of rice or salt, warm stones, etc. The duration of the procedure is no more than 15 minutes, the temperature is pleasant so that there is no skin burn. It is advisable to do it at night, so that later you do not go outside. During the course of treatment, avoid drafts and stay away from the operating air conditioner.
 Oil solutions. An excellent remedy for the restoration and moisturizing of mucous membranes. Can be applied in the form of drops or applications. For application in oil, moisten a gauze turunda and insert into the nasal passage for 10-15 minutes. Before the procedure, it is advisable to rinse the nose with saline. It is better to use an oil solution of chlorophyllipt, sea buckthorn or camphor oil diluted in half with sunflower oil. Essential oils (the same as for inhalation) can be diluted in a base (olive, sunflower, etc.) in a ratio of 1:10 - they help well with bacterial or viral frontitis.
Oil solutions. An excellent remedy for the restoration and moisturizing of mucous membranes. Can be applied in the form of drops or applications. For application in oil, moisten a gauze turunda and insert into the nasal passage for 10-15 minutes. Before the procedure, it is advisable to rinse the nose with saline. It is better to use an oil solution of chlorophyllipt, sea buckthorn or camphor oil diluted in half with sunflower oil. Essential oils (the same as for inhalation) can be diluted in a base (olive, sunflower, etc.) in a ratio of 1:10 - they help well with bacterial or viral frontitis.- Herbal teas. Drinking a lot for any respiratory disease. It warms up the respiratory tract, helps to thin mucus, neutralizes and removes toxins and decay products of drugs from the body, strengthens the immune system and restores the vitamin balance. It is useful to brew raspberry branches and fruits, currant leaves, elderberry and linden flowers, you can add a little chamomile, horsetail, thyme, sage, thyme. Tea is drunk warm up to 1.5 liters per day, with the addition of honey and lemon.
By agreement with the doctor, folk remedies can also be used as part of complex therapy with drug treatment. But at the same time, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of their interaction with traditional drugs. So even with home treatment, a consultation with a doctor doesn't hurt.

 a headache clearly localized in the middle part of the forehead, which is aggravated by palpation, tapping and tilting the head down;
a headache clearly localized in the middle part of the forehead, which is aggravated by palpation, tapping and tilting the head down; Relief of inflammation. It all depends on the root cause. If there is an infection in the sinuses, antibiotics or antifungal agents should be used. If the inflammation is caused by a chronic allergy, antihistamines are sufficient. With a polyposis form, these measures will only have a temporary effect. Most modern anti-inflammatories simultaneously relieve pain and lower body temperature.
Relief of inflammation. It all depends on the root cause. If there is an infection in the sinuses, antibiotics or antifungal agents should be used. If the inflammation is caused by a chronic allergy, antihistamines are sufficient. With a polyposis form, these measures will only have a temporary effect. Most modern anti-inflammatories simultaneously relieve pain and lower body temperature. inflammation of the meninges;
inflammation of the meninges; Oil solutions. An excellent remedy for the restoration and moisturizing of mucous membranes. Can be applied in the form of drops or applications. For application in oil, moisten a gauze turunda and insert into the nasal passage for 10-15 minutes. Before the procedure, it is advisable to rinse the nose with saline. It is better to use an oil solution of chlorophyllipt, sea buckthorn or camphor oil diluted in half with sunflower oil. Essential oils (the same as for inhalation) can be diluted in a base (olive, sunflower, etc.) in a ratio of 1:10 - they help well with bacterial or viral frontitis.
Oil solutions. An excellent remedy for the restoration and moisturizing of mucous membranes. Can be applied in the form of drops or applications. For application in oil, moisten a gauze turunda and insert into the nasal passage for 10-15 minutes. Before the procedure, it is advisable to rinse the nose with saline. It is better to use an oil solution of chlorophyllipt, sea buckthorn or camphor oil diluted in half with sunflower oil. Essential oils (the same as for inhalation) can be diluted in a base (olive, sunflower, etc.) in a ratio of 1:10 - they help well with bacterial or viral frontitis.