Cough is a fairly common and widespread phenomenon, especially during the off-season, when the body of a person with weakened immunity (and there are now, alas, most of them!) Do not have time to adapt to frequent changes in air temperature and weather conditions. By itself, it is not terrible, since it is a protective reaction of the body. But when a cough with wheezing appears, it is worth consulting a doctor as soon as possible - this may be a signal of the development of a serious disease.
Possible reasons
 Before considering possible causes, let's understand the terminology. Wheezing is a characteristic noise that is generated when an air stream passes through the respiratory tract, when there are any obstacles in them: neoplasms, mucus clots, foreign bodies. Hoarseness is a change in the timbre of the voice that occurs due to inflammation or damage to the vocal cords.
Before considering possible causes, let's understand the terminology. Wheezing is a characteristic noise that is generated when an air stream passes through the respiratory tract, when there are any obstacles in them: neoplasms, mucus clots, foreign bodies. Hoarseness is a change in the timbre of the voice that occurs due to inflammation or damage to the vocal cords.
A wheezing voice occurs with a very strong, dry, barking cough, which leads to constant irritation of the larynx and inflammation of the vocal cords from overexertion. The cause of such a cough can be a cold, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections or chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract: pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis. If they are not treated, the disease becomes chronic and complications develop.
A hoarse cough eventually appears in heavy smokers due to permanent burns of the laryngeal mucosa and chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract. Also at risk are people working in industries associated with chemicals, high air pollution and other irritants.
If they do not use personal protective equipment, then respiratory diseases, which are considered professional, gradually develop: asthma, allergies, bronchitis.
Coughing and wheezing in the chest are obvious signs of serious medical conditions such as:
 bronchial asthma - on exhalation or when coughing, a whistling sound is heard, which is formed due to a strong narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during spasm;
bronchial asthma - on exhalation or when coughing, a whistling sound is heard, which is formed due to a strong narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during spasm;- neoplasms on the bronchi - wheezing rales are constantly present when breathing;
- acute or chronic bronchitis - wheezing is caused by large accumulations of mucus that prevent air from passing freely;
- lung abscess - wheezing occurs when air passes through a cavity filled with pus, audible inside the chest;
- pneumonia - depending on the stage of the disease, wheezing is quiet or very sonorous, accompanied by a dry or wet cough;
- pulmonary edema - wheezing is barely audible, since the lungs do not function normally, and the person cannot take a full breath, a feeling of suffocation is created;
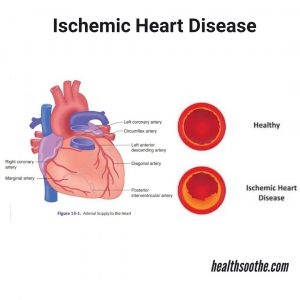
- heart failure - the brain senses it as oxygen starvation and tries to compensate with deep breathing, which is extremely difficult during an attack, a slight wheezing sound appears.
This is not a complete list of all possible reasons for coughing and obvious wheezing. In most cases, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, after a thorough examination and a comprehensive examination.
Alarming symptoms
 If you have a hoarse cough, do not delay the visit to the doctor. Especially if it is accompanied by one or more of the following symptoms:
If you have a hoarse cough, do not delay the visit to the doctor. Especially if it is accompanied by one or more of the following symptoms:
- severe or frequent shortness of breath;
- cold sweat with minimal physical exertion;
- feeling short of breath;
- signs of oxygen starvation;
- pain in the chest area (especially compressive or clearly localized);
- strong or constant, but slight increase in body temperature;
- wheezing when breathing or coughing is heard constantly.
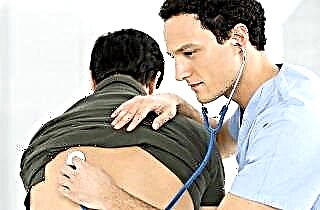
Diagnosis begins with a visit to a therapist, who listens to the patient's bronchi and lungs with a stethoscope. Wheezing is best heard when exhaling, so the doctor often asks the patient to take a deep breath or cough.
Diagnostic methods
The next mandatory stage of diagnosis is laboratory tests. As a rule, this is a general and biochemical blood test and a sputum microflora test. They make it possible to identify the presence of pathological microorganisms and active inflammatory processes in the body.
If the data turns out to be insufficient for medical prescriptions, then the following can be additionally recommended:
- chest x-ray - reveals pneumonia, tuberculosis, acute and chronic bronchitis, lung abscess;
- computed tomogram - allows for a detailed analysis of the state of any respiratory organ;
- spirometry - taking and analyzing vital indications of lung function;
- bronchoprovocation - done when bronchial asthma is suspected, it allows you to determine the sensitivity of the bronchi and a tendency to bronchospasm;
- bronchoscopy - an internal examination and a detailed study of the state of the mucous lining of the bronchi, allows you to measure the size of the lumen, detect neoplasms and take sputum for analysis;
- blood gases - another type of laboratory test that allows you to determine the level of oxygen in the blood;
 angiopulmonography - allows you to assess the state of the vessels in the lungs, the degree of their narrowing, the presence of blood clots;
angiopulmonography - allows you to assess the state of the vessels in the lungs, the degree of their narrowing, the presence of blood clots;- biopsy - a study of a tissue sample taken from the bronchi or lungs, which allows you to determine whether this neoplasm is benign or malignant.
If necessary, other specialists are involved in the examination: a pulmonologist, an allergist, an oncologist, etc. And only after receiving all the examination data, the doctor makes a final conclusion about the nature of the disease and the need to place the patient in a hospital.
Treatment features
As you can see, the reasons why wheezing and coughing may appear are so varied that there is no universal recipe for their treatment in principle. That is why a professionally performed diagnosis is so important. It is necessary to treat not wheezing, but the underlying disease. And since most of them are serious, it is better not to self-medicate.
 Folk remedies in this case can only be auxiliary. In the presence of chronic diseases, infections, purulent discharge, only correctly selected drug therapy will be effective. It includes drugs of several groups, which, interacting, enhance the properties of each other and prevent the appearance of side effects:
Folk remedies in this case can only be auxiliary. In the presence of chronic diseases, infections, purulent discharge, only correctly selected drug therapy will be effective. It includes drugs of several groups, which, interacting, enhance the properties of each other and prevent the appearance of side effects:
- antibiotics - you cannot do without them for bronchitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, triggered by ARVI;
- antihistamines - they help well with allergic cough and relieve attacks of bronchial asthma, prevent an allergic reaction to antibiotics;
- bronchodilator drugs - are prescribed for bronchospasm, narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, to facilitate coughing up with large accumulations of mucus;
- mucolytic agents - liquefy phlegm and make it easier to cough up, turn dry barking cough into productive cough, effective for bronchitis, pneumonia, tracheitis;
- antipyretic drugs - are prescribed symptomatically when the body temperature exceeds 38.5OC, as soon as it steadily decreases, this type of drug is canceled.
Antiviral agents for wheezing are not prescribed. They are effective only in the first 72 hours after the onset of the disease, and during this time the disease does not have time to develop to such an extent that a person begins to wheeze. Therefore, it makes sense to start taking them on your own, as a prevention of the development of serious respiratory diseases.
An integral part of the treatment is regular gargling, for which you can use a saline solution, decoctions of medicinal plants or ready-made pharmaceutical preparations. Gargle at least 4-5 times a day. It soothes irritated laryngeal lining, moisturizes and relieves inflammation.
It is especially important to rinse your mouth frequently when sputum is actively coughing up. It avoids the spread of infection in the oral cavity and the return of mucus to the bronchi. For the same purpose, you can treat the throat with antiseptic solutions: chlorophyllipt, furacilin, etc.
Inhalation and warming up
 Inhalation always relieves coughing. If the wheezing is superficial, then steam inhalations help well. With deep wheezing, when it is necessary to heal the lower bronchi and lungs, the best effect will be after using a nebulizer. This device converts a diluted drug mixture into a finely dispersed solution, the microminized particles of which are able to penetrate very deeply and linger on the mucous membrane and in the alveoli.
Inhalation always relieves coughing. If the wheezing is superficial, then steam inhalations help well. With deep wheezing, when it is necessary to heal the lower bronchi and lungs, the best effect will be after using a nebulizer. This device converts a diluted drug mixture into a finely dispersed solution, the microminized particles of which are able to penetrate very deeply and linger on the mucous membrane and in the alveoli.
Warming up should be treated with caution. In some diseases, it is categorically contraindicated: edema and abscess of the lung, tuberculosis, etc. Therefore, at least one cannot prescribe thermal procedures for oneself until the final diagnosis is made. For the period of diagnosis, it is advisable to limit ourselves to inhalations alone.
But if there are no medical contraindications, then the lungs and bronchi can be warmed up by various home methods: mustard plasters, wraps, compresses, paraffin.
If there is an opportunity to visit the clinic, then electrophoresis, UHF, laser heating are used as directed by a doctor. The course of treatment is from 5 to 10 procedures, after which a noticeable improvement usually occurs.
Prevention of wheezing
A wheezing cough is much more difficult to cure than a regular dry or wet cough. Therefore, it is advisable to do everything possible to prevent its occurrence. Sometimes standard preventive measures are sufficient:
 quitting smoking and other bad habits;
quitting smoking and other bad habits;- when working in "harmful" industries, use personal protective equipment;
- start cough treatment with folk remedies in the very first days after its appearance;
- be sure to consult a doctor if the cause of your cough is not clear to you;
- seek professional help in time if after 3-4 days of home treatment the condition does not improve and the cough does not get weaker;
- keep cleanliness in the working and living quarters, monitor the temperature and humidity of the air;
- regularly do antifungal prophylaxis and cleaning the air conditioner;
- prevent the appearance and even more the accumulation of mold in the house;
- inspect the room at least once every 2-3 months for the presence of possible allergens and irritants;
- do not smoke yourself and do not allow guests to do so in the apartment and work premises.
It is equally important to eat right and regularly strengthen the immune system. The diet should contain fresh fruits and vegetables, citrus fruits, seafood. They provide the body with essential vitamins and minerals.
Try to spend at least an hour a day in the fresh air, preferably on the move (walking, jogging, sports games). And the main thing is not to start the disease and not to self-medicate, as this often leads to serious complications and unpredictable consequences.

 bronchial asthma - on exhalation or when coughing, a whistling sound is heard, which is formed due to a strong narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during spasm;
bronchial asthma - on exhalation or when coughing, a whistling sound is heard, which is formed due to a strong narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during spasm; angiopulmonography - allows you to assess the state of the vessels in the lungs, the degree of their narrowing, the presence of blood clots;
angiopulmonography - allows you to assess the state of the vessels in the lungs, the degree of their narrowing, the presence of blood clots; quitting smoking and other bad habits;
quitting smoking and other bad habits;