In some cases, hypertrophic rhinitis develops as a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process, which is localized in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavities. It is quite difficult to distinguish the disease symptomatically from other forms of the common cold, therefore, the diagnosis should be carried out exclusively by the otolaryngologist.
 The development of pathology is based on hypertrophic processes, as a result of which a thickening of the nasopharyngeal mucosa is observed and nasal breathing becomes difficult. In some cases, the growth of the bone structures of the nose is revealed. There are many factors that predispose to the onset of the disease. Among them, it is worth highlighting:
The development of pathology is based on hypertrophic processes, as a result of which a thickening of the nasopharyngeal mucosa is observed and nasal breathing becomes difficult. In some cases, the growth of the bone structures of the nose is revealed. There are many factors that predispose to the onset of the disease. Among them, it is worth highlighting:
- long-term influence of an allergic factor (wool, dust, household chemicals, cosmetic products). As a result, the nasal mucosa is constantly attacked by allergens, which supports the allergic reaction. Separately, it should be said about hay fever, when seasonal allergies are observed during the flowering period of plants. The lack of therapeutic measures leads to the progression of inflammation and tissue hypertrophy;
- chronic infectious foci in the ENT organs, for example, otitis media, tonsillitis. Even a slight hypothermia can cause the activation of pathogenic microorganisms and the development of inflammation. Without adequate treatment, the infection, the inflammatory process spreads to the surrounding tissues, which is accompanied by tissue hypertrophy;
- frequent colds and infections. Against the background of reduced immunity, microbes, when they enter the nasal cavity, settle on the mucous membrane and damage it. Intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms leads to an increase in intoxication and persistence of inflammation for a long period of time;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions, as well as occupational hazards, lead to the fact that polluted air reduces the protective functions of the nasal mucosa. The result of this may be the activation of conditionally pathogenic flora in the nasopharynx, which also leads to the onset of an inflammatory process;
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous system, when microcirculation and regulation of the tone of blood vessels are disturbed;
- congenital malformations of the nasopharynx (narrow nasal passages), deformation of the septum of traumatic origin;
- improper treatment of acute rhinitis, when the inflammation is not completely cured, predisposing to tissue hypertrophy;
- adenoids, polyposis formations make it difficult for air to pass through the nasal passages, increasing the risk of pathological proliferation of the mucous membrane;
- long experience of smoking;
- immunodeficiency due to severe infection or systemic disease.
Overgrowing tissue gradually squeezes blood vessels, disrupting blood supply, oxygen and nutrient delivery to healthy tissues. Due to a lack of oxygen, the body suffers from hypoxia, and the work of internal organs is disrupted.
Breathing through the mouth causes cold, untreated air to enter the lower respiratory tract, which is why tracheitis or bronchitis is often diagnosed.
It is necessary to start the prevention of hypertrophic rhinitis when frequent episodes of nasal congestion and rhinorrhea appear.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
It is not always possible to notice the first signs of the disease in a timely manner. Not everyone pays attention to periodically stuffy nose, a small amount of mucous secretions or swelling of the mucous membrane. Only with the appearance of narrowing of the nasal passages, hypertrophic rhinitis begins to manifest itself with symptoms typical of the common cold.
Among the frequent clinical signs, it is worth highlighting:
- Difficulty nasal breathing due to tissue growth, as well as narrowing of the nasal lumens. The complete absence of breathing through the nose is observed with extensive hypertrophy, which is not so common;
- nasal discharge of a mucous consistency with an admixture of pus, a yellow-green hue. The volume of discharge is small, but increases with exacerbation. Frequent rubbing of the wings of the nose leads to flaking and redness of the skin;
- nasal congestion;
- feeling of a foreign element in the nose;
- nasal voice, which is caused by impaired air permeability in the nasal cavities;
- poor sleep, snoring;
- headache;
- irritability;
- decreased sense of smell - due to tissue growth in the upper zone of the nasal passages, where the olfactory bulbs are localized;
- fast fatiguability.
With exacerbation, hypertrophic rhinitis manifests itself with more pronounced symptoms.
Long-term preservation of the inflammatory process and tissue hypertrophy lead to the development of complications that are associated with the spread of infection and edema to the surrounding healthy tissues. Hypertrophic rhinitis can lead to such serious consequences:
 eustachitis - observed as a result of obstruction of the lumen of the auditory tube by growths at the posterior ends of the turbinates. The accumulation of secretions leads to inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane. Symptomatically, the condition is manifested by soreness in the ear area and hearing loss;
eustachitis - observed as a result of obstruction of the lumen of the auditory tube by growths at the posterior ends of the turbinates. The accumulation of secretions leads to inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane. Symptomatically, the condition is manifested by soreness in the ear area and hearing loss;- otitis media - occurs as a consequence of eustachitis, when the inflammatory process covers the middle ear section. Ventilation is disturbed in it and conditionally pathogenic flora is activated. Clinically, otitis media is manifested by pain, noise in the ear, hearing loss and hyperthermia;
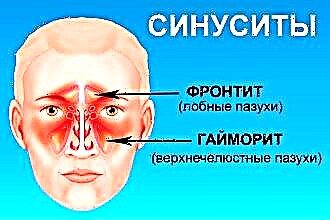
- sinusitis - develop when the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses is covered. Swelling of the mucous membrane and impaired outflow from the sinuses leads to the accumulation of secretions, the appearance of purulent masses and the development of chronic frontal sinusitis, sinusitis. Among the clinical signs should be highlighted pain in the area of the paranasal sinuses, hyperthermia and purulent discharge from the nose;
- frequent conjunctivitis - are the result of a sharp thickening of the anterior zone of the inferior nasal concha and inflammation of the lacrimal ducts. A person is worried about lacrimation, cramps in the eyes, redness of the conjunctiva and decreased visual function;
- pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis - develop as a result of inhalation of unpurified cold air through the mouth;
- anosmia (complete inability to smell).
Traditional treatment
The medical tactics are determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination.
Hypertrophic rhinitis is treated conservatively only at the initial stage.
Appropriate therapy can lead to regression of symptoms. Physiotherapy procedures and medications are used with success:
- ultraviolet irradiation of the turbinates;
- UHF therapy;
- hydrocortisone injections;
- nasal spray with a hormonal component (Nasonex);
- Protargol (remedy with silver).
Also effective is the massage of the nasal mucosa with special ointments, which slow down hypertrophic tissue changes.
Conservative methods can slow down the hypertrophic process and relieve a person from the symptoms of a cold. However, in the case of continued exposure to the provoking factor, the disease will progress, manifesting itself as a more pronounced symptom complex.
If the growths increase and hypertrophic rhinitis cannot be treated conservatively, treatment should include surgical methods. When the deep parts of the nose are involved in the pathological process, surgical treatment is indicated.
Minimally invasive techniques are used with an average degree of growth. They are represented by cauterization with chemicals, ultrasonic action on the inferior nasal concha and destruction by a laser beam.Not so often you can find galvanic caustics and moxibustion due to the low efficiency of the techniques.
Treatment of severe hypertrophic rhinitis requires more extensive surgical interventions, for example, partial removal of the turbinates, their bone margins, or excision of the mucous membranes.
For anesthesia, local anesthesia is used, sometimes general anesthesia (depending on the volume of surgery and the patient's condition). The duration of the operation is about 20 minutes, provided that endoscopic instruments are used.
Traditional therapy
 There are many recipes that traditional medicine recommends. Note that they are used only as a complementary therapy.
There are many recipes that traditional medicine recommends. Note that they are used only as a complementary therapy.
It is impossible to cure this form of rhinitis using unconventional methods, however, in combination with medications, a satisfactory result can be obtained.
Here are some recipes:
- 15 g of St. John's wort (sage or chamomile) should be poured with 230 ml boiling water, left for half an hour and filtered. The infusion should be used to rinse the nose three times a day;
- 5 g of sea or table salt should be dissolved in warm water with a volume of 270 ml and a couple of drops of iodine should be added. Use the solution to rinse the nose twice a day;
- 50 g of chopped mint must be poured with boiling water in a volume of 260 ml, add a drop of lemon oil. After slightly cooling the remedy, you need to inhale the vapors for 5-6 minutes;
- inhalation can also be done with lavender oil, orange, tea tree. Take two drops of each and add to 600 ml hot water. Inhale vapors for about 6 minutes.
Preventive Tips
It is necessary to engage in the prevention of hypertrophic rhinitis, having noticed the frequent appearance of rhinorrhea. The main task of prevention is to strengthen the immune system, which will allow you to cope not only with a cold, but many other diseases.
To avoid the appearance of growths in the nose, you should stop smoking, eliminate the provoking factor (change your profession or even your place of residence). It is necessary to go in for sports, hardening, often walk in the fresh air and do not forget about ventilation and wet cleaning in the room.

 eustachitis - observed as a result of obstruction of the lumen of the auditory tube by growths at the posterior ends of the turbinates. The accumulation of secretions leads to inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane. Symptomatically, the condition is manifested by soreness in the ear area and hearing loss;
eustachitis - observed as a result of obstruction of the lumen of the auditory tube by growths at the posterior ends of the turbinates. The accumulation of secretions leads to inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane. Symptomatically, the condition is manifested by soreness in the ear area and hearing loss;

