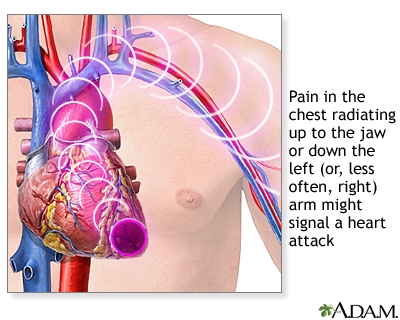
Cardiovascular pathology in European countries becomes the cause of death among the adult population in 50% of cases. On the territory of the CIS countries, diseases are found in 67% of deaths. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is the most readily available antithrombotic drug used for the prevention and secondary prevention of cardiac pathologies. "Aspecard" is distinguished by a huge number of positive reviews associated with an optimal price-quality ratio.
Instructions for use of the drug
 The active substance of "Aspekard" - ASA - belongs to the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with antithrombotic properties. The blood thinning effect is due to the effect on the adhesion ("sticking" to the vascular wall) and aggregation (sticking together) capabilities of platelets.
The active substance of "Aspekard" - ASA - belongs to the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with antithrombotic properties. The blood thinning effect is due to the effect on the adhesion ("sticking" to the vascular wall) and aggregation (sticking together) capabilities of platelets.
Features of the exchange of medication in the body:
- bioavailability (the amount of the drug that is delivered to sensitive structures) - 40-50%;
- plasma half-life - 20 minutes;
- the active substance begins to act a few minutes after absorption in the digestive tract;
- the maximum effect is determined in the portal system (vessels carrying blood from the intestinal wall to the liver).
"Aspeckard" causes irreversible dysfunction of the platelet (for the entire life of the "platelet").
Indications
"Aspeckard" is used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular "catastrophes" (stroke, myocardial infarction) in:
- acute coronary syndrome (ACS);
- rehabilitation of postinfarction patients;
- transient cerebral blood flow disorders (TIA) and stroke;
- angina pectoris: unstable, tension;
- type II diabetes mellitus;
- metabolic syndrome;
- obesity;
- hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- in elderly patients.
Indications for the use of "Aspekard" for prophylactic purposes:
- postoperative thromboembolism (with vascular interventions: transluminal angioplasty, endarterectomy, coronary artery bypass grafting);
- venous thrombosis and BODY (pulmonary embolism) in patients with forced prolonged immobilization (immobilization after trauma, abdominal surgery, paralysis);
- prevention of repeated occlusions (narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels.
Mechanism of action and composition
1 tablet of "Aspekard" contains 100 mg of ASA. There is no strip on the surface of the preparation, so it cannot be halved or chewed.
ASA by acetylation blocks the activity of cyclooxygenases (COX) in platelets. The pharmacological effects of the interaction are presented in the table.
| Effects | Clinical significance |
|---|---|
| Decreased synthesis of prostaglandin endoperoxides (PGH2, PGD2) | Blockade of the inflammatory cascade |
| Inhibition of the production of thromboxane A2 and arachidonic acid | Prevention of increased blood clot formation |
| Reduces the formation of prostacyclins | Expands the lumen of blood vessels, improves the rheological properties of blood |
| Stimulation of transcription in genetic material | Synthesis of anti-inflammatory mediators |
| Decreased ability to oxygenate lipoprotein complexes | Prevention of atherosclerosis |
| Increases the synthesis of ferritin | Increased blood oxygen capacity, improved iron metabolism |
| Induction of production and release of adenosine, P-selectin, endothelial growth factor | Anti-inflammatory effect |
Disaggregation action of "Aspekard" is based on inhibition of COX-1 of platelet membranes and thromboxane activation mechanism.
Additional cardioprotective effects are due to the ability of ASA to stimulate the formation of pro-resolution mediators - substances that:
- eliminate signs of aseptic inflammation;
- promote tissue regeneration (restoration);
- affect the exchange of NO-synthetase of the vascular endothelium with the subsequent release of nitric oxide - a molecule that expands the lumen of the arteries.
Acetylation of COX-2 changes the structure of the molecule, converting it into lipoxygenase. After enzymatic transformation, "aspirin-induced" lipoxin is formed, which has anti-inflammatory properties and enhances the reverse transport of cholesterol.
Increasing the dose of "Aspekard" does not affect the antiplatelet properties, but increases the risk of adverse reactions.
Method of administration and dosage
The concentration of the active substance in "Aspekard" is calculated for a single dose.
Recommendations for use:
- the pill is drunk 30 minutes - an hour before meals;
- drink plenty of fluids (to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects);
- use the drug in the evening.
The latter is explained by the circadian rhythms of platelet aggregation (the peak of activity falls at 22 hours).
The standard dose for the prevention of cardiovascular accidents is 100-200 mg / day for 1 month with a further revision of the dosage of the drug and the presence of indications for continuing therapy with ASA. Alternative scheme: 300 mg "Aspecard" once every 48 hours.
American Heart Association guidelines for ACS and unstable angina:
- start ASA therapy at a dose of 150-325 mg as early as possible;
- transition to maintenance treatment at 75-150 mg / day.
Such a system reduces cardiovascular mortality by 23% from repeated myocardial infarction and by 50-70% from fatal rhythm disturbances in the acute phase.
For the prevention of recurrent strokes, it is recommended to start treatment with "Aspekard" 24-48 hours after the onset of symptoms. If the patient is planned to undergo thrombolytic therapy, the use of ASA should be postponed for 24 hours.
Contraindications and symptoms of overdose
The appointment of "Aspeckard" is contraindicated in case of:
- hypersensitivity to ASA and other salicylates;
- aspirin bronchial asthma;
- patients with asthma attacks after using other NSAIDs in history;
- acute ulcers of the digestive tract (including Crohn's disease, colitis);
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- end-stage renal failure;
- severe hepatic dysfunction;
- high degree of circulatory failure;
- co-administration with "Methotrexate" at a dosage of more than 15 mg / week (the combination increases hematological toxicity);
It is not recommended to take "Aspecard" in the I and III trimesters of pregnancy. Up to 12 weeks, the use of high doses of ASA (more than 100 mg / day) increases the likelihood of arbitrary abortion and the birth of a child with developmental abnormalities:
- gastroschisis - incomplete bowel rotation in the embryonic period with non-closure of the anterior abdominal wall;
- The "cleft palate" —the cleft of the hard palate;
- spina bifida;
- heart defects;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- hypospadias in boys.
In the third trimester, Acetylsalicylic acid provokes premature closure of the ductus arteriosus with the development of cardiopulmonary failure, kidney damage in the fetus, weakness of labor, postpartum hemorrhage, the formation of cephalohematoma in the newborn. The use of low doses of ASA should be discontinued 4 weeks before delivery.
Long-term use of high doses of ASA is accompanied by the risk of chronic salicylate intoxication. Symptoms of a drug overdose:
- vertigo (dizziness);
- noise, ringing, buzzing in the ears;
- dyspepsia (indigestion);
- migraine;
- increased sweating;
- violation of consciousness;
- acid-base imbalance (shift towards the acidic side);
- hyperventilation, pulmonary edema;
- increased bleeding;
- renal dysfunction.
Salicilism therapy includes gastric lavage, sorbents, forced diuresis and correction of the acid-base state.
Treatment of hemorrhagic complications from the gastrointestinal tract is carried out in a surgical hospital.
Special instructions
Aspecard is prescribed with caution to patients with:
- allergies to painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antirheumatic drugs;
- history of ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- with simultaneous treatment with direct anticoagulants ("Heparin", "Fraxiparin");
- circulatory disorders: pathology of renal vessels, congestive heart failure, massive surgical interventions, blood loss;
- lack of enzymes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (high probability of hemolysis);
- liver failure.
The combined use of ASA with Ibuprofen enhances the antithrombotic effect.
In patients with gout, Aspecard causes an exacerbation of the process due to a delay in the excretion of uric acid.
The use of ASA during fever in children with acute respiratory viral infections provokes the development of Ray's syndrome (severe liver damage).
Long-term use of drugs containing ASA increases the risk of gastropathy. Therefore, the recommended parallel intake of H2-blockers or PPIs ("Ranitidine", "Omeprazole"). Recent studies have shown that the combined use of ASA and nitrates reduces the risk of damage to the gastric mucosa in the same way as H2 blockers.
The enteric membrane protects against the ulcerogenic effect of ASA, which prevents the acid from acting on the stomach. In such forms, the onset of drug release is delayed by 2 hours, which is not suitable for providing assistance in emergency situations.
Analogues and substitutes
The original "Aspecard" is temporarily absent on the Russian market. The drug is produced at the request of Stirolbiopharm Baltikum LLC at factories located in different countries.
There are imported analogues of the medication on the market - drugs with an identical composition and indications for admission:
- Akard (Poland);
- Anopyrin (Slovakia);
- Aspirin Cardio (Germany, Switzerland);
- Godasal (Germany);
- Reokard (USA);
- Trombopol (Poland);
- Ecorin (India).
The cheapest substitute for Aspecard is Acetylsalicylic acid. For the prevention of cardiovascular complications, enteric forms of tablet coating have been developed. The main goal is to minimize the adverse effect of ASA on the inner lining of the stomach. "Acetylsalicylic acid" - a product without the necessary protective "capsule".
In the absence of effect, intolerance - in the pharmacy you can buy substitutes for the drug "Aspecard" (drugs with a different composition, but a similar effect):
- "Cardiomagnil" (Austria). Magnesium hydroxide in the composition provides additional protection to the gastric mucosa.
- Clopidogrel, Agrel, Clodia, Lopirel, Plavix. The active substance blocks platelet ADP receptors, providing an effect similar to Aspecard.
- Dipyridamole, Curantil. The drugs block platelet phosphodiesterase.
There are combinations of ASA with indirect anticoagulants: Clopidogrel (Aspigrel, Coplavix) or Dipyridamole (Agrenox). These drugs are expensive and are indicated for use in the acute period of TIA or after ischemic stroke.
Conclusions
In international cardiology recommendations, low doses of ASA are the main method for preventing complications. Aspecard is a weak inhibitor of platelet aggregation that produces a lasting therapeutic result.
Numerous clinical studies confirm the high efficiency of acetylsalicylic acid in standard regimens for the prevention and treatment of atherothrombotic events. Instructions for use "Aspecard" 100 mg contains comprehensive information required by the patient.