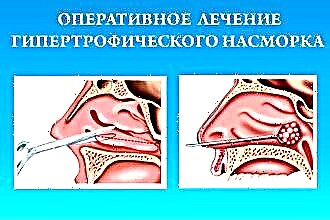
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis is a disease that affects the nasal mucosa. A feature of the disease is the uncontrolled division of cells of the epithelium of the mucous membrane, as well as the proliferation of cartilage and the nasal skeleton, i.e. their hypertrophy.
 This disease develops slowly and does not attract the patient's attention in the early stages. The hospital is usually treated already with a severe form of hypertrophic rhinitis. In the later stages of the development of the disease, the normal morphological structure of the nose is significantly impaired, and therefore the only effective method of treatment is usually surgery. Nevertheless, there are some conservative methods of treatment for this disease that avoid surgery. Their effectiveness depends both on the stage of hypertrophic rhinitis and on the characteristics of the patient's body - the state of his immune and endocrine systems, the metabolic rate and the ability to quickly regenerate.
This disease develops slowly and does not attract the patient's attention in the early stages. The hospital is usually treated already with a severe form of hypertrophic rhinitis. In the later stages of the development of the disease, the normal morphological structure of the nose is significantly impaired, and therefore the only effective method of treatment is usually surgery. Nevertheless, there are some conservative methods of treatment for this disease that avoid surgery. Their effectiveness depends both on the stage of hypertrophic rhinitis and on the characteristics of the patient's body - the state of his immune and endocrine systems, the metabolic rate and the ability to quickly regenerate.
Read more about the features of hypertrophic rhinitis and the existing methods of its treatment in our article.
Symptoms
Hypertrophic processes in the tissues of the nose can develop over the years, and the patient will think that he is simply prone to frequent rhinitis. Indeed, the manifestations of hypertrophic rhinitis are in many ways similar to the symptoms of a catarrhal rhinitis, which occurs, for example, with a cold.
So, with chronic hypertrophic rhinitis, the patient is worried about the following symptoms:
- Nasal congestion, which is weakly responsive to vasoconstrictor nasal drops (their effect lasts no more than an hour).
- Deterioration of smell.
- Constantly labored breathing through the nose. Often, the patient unconsciously begins to breathe through the mouth, especially during physical exertion.
In the early stages of the disease, nasal breathing is intermittently disturbed, and in the later stages, the ability to breathe through the nose may completely disappear.
- Snoring during sleep, poor sleep.
- Persistent nasal discharge (sticky mucus or pus) that is hard to blow out.
- Weak resistance to colds, persistent rhinitis. Almost every cold spills over into inflammation of the paranasal sinuses - sinusitis or frontal sinusitis.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the nasopharynx.
- Dry mouth and oropharynx.
- In some cases, ear congestion, hearing impairment (associated with hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate and impaired ventilation of the auditory tube).
- Vileness of the voice.
- Rapid physical and mental fatigue, memory impairment, recurrent headaches.
The above symptoms can be found in other diseases of the nasopharynx, such as polyps of the nasal cavity, syphilis or tuberculosis of the nose, neoplasms, curvature of the nasal septum, etc. That is why, when the described disorders appear, it is necessary to consult an ENT doctor.
General principles of treatment
All methods of treatment of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis can be divided into surgical and conservative (medication).
Conservative treatment includes the use of nasal drops (vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory), the use of general anti-inflammatory drugs (in the form of tablets or injections), etc. Also used are glucocorticosteroids - hormonal drugs with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. If the nasal mucosa is affected by a bacterial infection, treatment is supplemented with antibiotics.
These measures can help stop the underlying chronic inflammation of the disease. However, medications are not able to reduce the volume of hypertrophied tissues and restore the normal structure of the nasal tissues.
It should be noted that in the presence of structural rearrangements of the tissues of the nose, conservative treatment is ineffective, since medications can only temporarily improve the patient's well-being.
Surgical treatment consists in mechanical or thermal action on the hypertrophied tissues of the turbinates, which makes it possible to restore the patency of the nasal passages and achieve a long-term improvement in nasal breathing. Unfortunately, the operation does not always end in full recovery - in some patients, some time after the intervention, the hypertrophic processes in the nasal cavity are restored. This is rare, and only in patients predisposed to tissue hypertrophy. This is usually due to hormonal imbalances and requires additional treatment.
Types of operations
The type of operation is selected strictly individually, depending on the patient's age, the stage of development of the hypertrophic process and other data obtained during the examination and laboratory tests.
For example, in the early stages of hypertrophic rhinitis, cauterization of the mucous membrane with chemicals (30-50% trichloroacetic or chromic acid) is usually recommended. When noticeable signs of hypertrophy appear, galvanic caustics, laser, ultrasonic or cryodestruction are indicated.
In the later stages of this type of rhinitis, a significant effect can be achieved only by mechanical disintegration of hypertrophied tissues.
Let's talk in more detail about the existing methods of surgical treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
- Galvanocaustics is an operation in which hypertrophied tissues are cauterized using metal tips, through which an electric current passes. This technique is also known as electrocaustics. The operation takes place quickly, with local anesthesia with novocaine, trimecaine or dicanne. Bleeding during the procedure is usually not observed, since blood quickly coagulates upon contact with a hot instrument.
 Cryosurgical destruction consists in the destruction of hypertrophied tissue by deep freezing. The instrument for the operation - a cryoapplicator - is cooled in liquid nitrogen (t = -195.8 ° C). When exposed to ultra-low temperatures, tissues die off and are subsequently rejected. This method has proven itself in the treatment of polyposis hypertrophy.
Cryosurgical destruction consists in the destruction of hypertrophied tissue by deep freezing. The instrument for the operation - a cryoapplicator - is cooled in liquid nitrogen (t = -195.8 ° C). When exposed to ultra-low temperatures, tissues die off and are subsequently rejected. This method has proven itself in the treatment of polyposis hypertrophy.- Laser treatment - laser excision of altered tissues. The operation is performed using local anesthetics. No bleeding occurs when exposed to the laser.
- Ultrasound destruction (ultrasonic destruction of hypertrophied areas). Also performed under local anesthesia. During the operation, a surgical instrument generating ultrasonic waves is inserted into the thickness of the hypertrophied mucous membrane. Thanks to ultrasound, cells die off and stop dividing.
- Intracranial mechanical disintegration (resection) is a classic variant of surgery for hypertrophic rhinitis. The operation involves an incision of soft tissues with damage to the parenchyma of the hypertrophied area and removal of part of the altered tissues. This causes the formation of a kind of scar, which prevents further proliferation of the mucous membrane. Thanks to this, the lumen of the airway expands, and the person can again breathe freely through the nose. If the cartilage and bones of the nose have also undergone changes, their size and shape are corrected during the operation. Depending on the degree of hypertrophy (and, accordingly, on the complexity of the operation), the doctor selects the appropriate type of anesthesia - local anesthesia or general anesthesia. After the operation, cotton-gauze tampons are inserted into the nasal passages to prevent bleeding. After 1-2 days, the tamponade is removed.
It should be noted that at present, the efficiency and safety of intranasal surgeries have significantly increased due to the introduction of modern endoscopic equipment into medicine, which allows the doctor to clearly see and control each stage of the operation.
Ethnoscience
Can traditional medicine fight hypertrophic rhinitis? To answer this question, it is enough to look at the methods proposed for the treatment of this disease by traditional medicine. So, some argue that you will be helped to achieve recovery:
- steam inhalation with herbal infusions (chamomile, sage, peppermint);
- instillation of the nasal passages with an oil infusion of propolis;
- dry and steam inhalations using essential oils of tea tree, eucalyptus;
- rinsing the nose with water with the addition of aloe juice (in a 3: 1 ratio);
- lubrication of the nasal passages with honey.
As you can see, the above recipes are no different from those for catarrhal (cold) rhinitis. What effect should be expected from them? Most of these methods have an antiseptic and mild anti-inflammatory effect. Indeed, some of them (for example, nasal rinsing and inhalation) can provide short-term relief. Unfortunately, the restoration of the normal morphology of the nasal tissues does not occur.
Traditional medicine methods can temporarily relieve the symptoms of hypertrophic rhinitis, but complete cure requires a full-fledged complex treatment.

 Cryosurgical destruction consists in the destruction of hypertrophied tissue by deep freezing. The instrument for the operation - a cryoapplicator - is cooled in liquid nitrogen (t = -195.8 ° C). When exposed to ultra-low temperatures, tissues die off and are subsequently rejected. This method has proven itself in the treatment of polyposis hypertrophy.
Cryosurgical destruction consists in the destruction of hypertrophied tissue by deep freezing. The instrument for the operation - a cryoapplicator - is cooled in liquid nitrogen (t = -195.8 ° C). When exposed to ultra-low temperatures, tissues die off and are subsequently rejected. This method has proven itself in the treatment of polyposis hypertrophy.