Squelching in the ear is a symptom that in most cases signals the occurrence of pathological changes in the ENT organs. Ignoring discomfort can cause the development of ear diseases, accompanied by degenerative changes in the soft and bone tissues of the hearing organ.
The sudden appearance of clicks can be associated with the ingress of water into the auditory canal, inflammation of the mucous membranes in the middle and inner ear, disruptions in the conduction of sound signals by the auditory ossicles, vascular disease, etc. Timely diagnosis and treatment prevents the development of complications and persistent hearing loss. In the event of audiological disorders, you need to be examined by an otolaryngologist who will be able to determine for sure the cause of their occurrence and the best way to solve the problem.
Causes of noise

What should you do if your ear gurgles, but does not hurt? The absence of pain does not always signal the presence of minor malfunctions in the auditory analyzer, which can go away by themselves. According to experts, you should not worry only in those situations if the noise is probably caused by the ingress of water into the outer ear. In all other cases, it is advisable to be examined by an ENT doctor who can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the key cause of the onset of audiological disorders.
Why does my ear gurgle? Usually, discomfort occurs due to pathological changes in the middle and inner ear. But sometimes the reason for the appearance of extraneous sounds lies in dysfunction of the musculoskeletal, cardiovascular and nervous systems. The main reasons for the appearance of acoustic anomalies include:
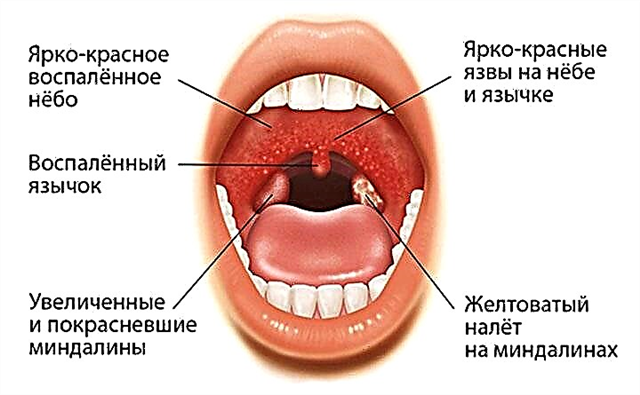
- serous otitis media;
- labyrinthitis;
- purulent otitis media;
- salpingotitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- arthritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- facial paresis;
- spasms of the pharynx;
- chronic rhinitis;
- mental disorders;
- sulfur plugs;
- abnormal ear structure;
- ingress of moisture into the ear canal.
Important! Most often, audiological disorders occur due to the development of serous (exudative) otitis media. Untimely treatment of pathology leads to the chronicization of inflammatory processes in the middle ear.
Impedance measurement
If it squishes in the ear, what to do? When acoustic abnormalities occur, otolaryngologists conduct a diagnostic examination, during which they determine the cause of the pathological symptom. Impedance measurement is one of the most effective diagnostic procedures that can be used to assess the condition of the auditory analyzer and the main parts of the sound-conducting system responsible for the transmission and subsequent processing of sound signals.
Periodic gurgling in the ear may indicate inflammation of the ear membrane, limited mobility of the auditory ossicles, accumulation of serous effusions in the middle ear, and damage to the ear labyrinth. Comprehensive audiological diagnostics, consisting in the study of auditory reflexes, makes it possible to determine the degree of hearing impairment, pathology of the middle ear, patency of the auditory canals, etc.
Important! You can not conduct an examination with a severe cold. Due to edema of the nasopharyngeal mucosa and Eustachian tube, the pressure in the tympanic cavity can change, which will lead to a distortion of the results of audiometry.
Using a special device and a rubber probe inserted into the external auditory canal, the audiologist changes the pressure on the ear membrane. During the acoustic test, a specialist evaluates the patient's condition. Tonal, computer and speech audiometry allows you to determine the presence of catarrhal processes, hemorrhages, adhesions on the ear membrane and mobility of the auditory ossicles.
Symptom elimination methods
Ways to eliminate acoustic anomalies are determined by the reasons that provoked their occurrence. If it gurgles in the ear, what to do? In most cases, the occurrence of unpleasant sensations in one ear is associated with the development of ear diseases. After accurate confirmation of the diagnosis, the otolaryngologist prescribes appropriate physiotherapy and medication, which includes:
- electrophoresis;
- blowing through Politzer;
- pneumomassage of the ear membrane;
- UHF therapy;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- instillation of vasoconstrictor drops;
- taking antihistamines and antimicrobial drugs.

If a serious malfunction occurs in the auditory analyzer, surgery may be required. If the patient has gurgling in his ears, this may signal the development of serous or purulent otitis media. To prevent the development of conductive hearing loss and autophony, specialists perform sanitizing operations and tympanoplasty to eliminate perforations in the ear cavity. With mineralization of the auditory ossicles, hearing aids may be required, which involves replacing the immobilized elements of the sound-conducting system with autocartilages.
Eliminate water in the ear
As a rule, audiological disorders result from the penetration of water into the ear canal. If the patient has chomping in the ear, this may indicate irritation of the nerve receptors in the membrane by the liquid that has entered the ear canal. To prevent the multiplication of opportunistic microorganisms leading to the development of myringitis, water from the ear must be eliminated.
To remove fluid from the ear canal, do the following:
- take a deep breath, pressing the wings of the nose against the cartilaginous septum;
- close your mouth and try to blow air out through your nasal passages;
- tilt your head so that the sore ear is on the bottom;
- make 2-3 swallowing movements.
Sharp exhalation of air with a closed mouth and nose can cause barotrauma.
The procedure increases the internal pressure on the ear membrane, as a result of which it protrudes slightly towards the outer ear. As a result, water flows over the isthmus in the ear canal, from where it can be easily removed with a gauze turunda.
Treatment of tubo-otitis
Often in patients seeking help from an otolaryngologist, gurgles in the ear due to the development of eustachitis (tubo-otitis). The disease is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane in the auditory canal, which connects the nasopharynx with the middle ear cavity. As a result of blockage of the Eustachian tube in the ear cavity, negative pressure arises, which entails the accumulation of serous effusions. Their occurrence is a key cause of the appearance of audiological disorders.
To eliminate puffiness in the auditory canals, the following groups of medications are used:
 mucolytics ("Ambroxol", "Carbocisteine") - help to reduce the viscosity of the secretion in the nasopharynx and the Eustachian tube, which leads to an increase in its internal diameter;
mucolytics ("Ambroxol", "Carbocisteine") - help to reduce the viscosity of the secretion in the nasopharynx and the Eustachian tube, which leads to an increase in its internal diameter;- antibiotics ("Vilprafen", "Rovamycin") - inhibit the synthesis of DNA of pathogenic bacteria, as a result of which their reproductive function is impaired;
- immunomodulators ("Levamisole", "Cardyceps") - increase the reactivity of the body, as a result of which local immunity is strengthened;
- vasoconstrictor drops (Nazol, Otrivin) - reduce swelling in the mucous membranes of the ENT organs, thereby normalizing the ventilation function of the ear canals;
- glucocorticosteroids ("Fliksonase", "Nasonex") - eliminate inflammatory processes in the lesions, as a result of which the swelling in the mucous membranes decreases.
To restore the aeration of the tympanic cavity, physiotherapeutic procedures such as pneumomassage of the ear membrane, phototherapy, microwave therapy, etc. can be used. They help to improve the trophism of the affected tissues, which affects the rate of regression of catarrhal processes and epithelialization of the mucous membrane of the auditory organ.
What not to do
If liquid seems to squelch in your ear, you need to seek the help of a qualified professional. Self-medication in most cases leads to disastrous consequences and complications. When detecting acoustic anomalies, otolaryngologists do not recommend:
- try to dry your ears with cotton swabs;
- instill alcohol solutions into the ear canals;
- abuse hygroscopic turundas;
- dry ears with hot air;
- use topical preparations without a doctor's prescription.
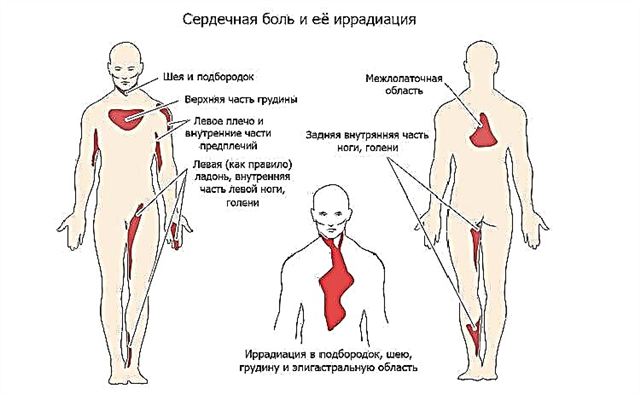
The emergence of discomfort in the organ of hearing can signal the defeat of the trigeminal nerve, pinching of the nerve roots in the cervical spine, the development of osteochondrosis, etc. For an accurate diagnosis and treatment, you need to seek help from a therapist or otolaryngologist.


 mucolytics ("Ambroxol", "Carbocisteine") - help to reduce the viscosity of the secretion in the nasopharynx and the Eustachian tube, which leads to an increase in its internal diameter;
mucolytics ("Ambroxol", "Carbocisteine") - help to reduce the viscosity of the secretion in the nasopharynx and the Eustachian tube, which leads to an increase in its internal diameter;