Congestion and noise in the ear is an alarming symptom, signaling the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the auditory analyzer. Extraneous noise and hearing impairment can be a consequence of the development of systemic and infectious diseases, barotrauma and neurological disorders. Untimely identification and elimination of pathology is fraught with the development of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
 In the absence of pathologies, the ear membrane does not experience stretching, which is due to the equal pressure in the outer and middle ear.
In the absence of pathologies, the ear membrane does not experience stretching, which is due to the equal pressure in the outer and middle ear.
Pressure drops inevitably lead to deformation of the membrane, as a result of which it bulges into the external auditory canal or pulls into the tympanic cavity.
This leads to uncomfortable sensations associated with congestion, hearing impairment and the appearance of extraneous noise.
Development mechanism
Why is the ear blocked and makes a noise? Discomfort in most cases is caused by the pressure difference in the external auditory canal and the tympanic cavity. Since the ear membrane is not airtight, excess air pressure causes it to stretch. In this state, she practically does not experience fluctuations during the passage of a sound signal, as a result of which a feeling of congestion arises.
Noise is a separate symptom, the occurrence of which may be associated with inflammatory processes in the main parts of the sound-receiving or sound-conducting system. Pathological changes are often caused by inflammatory processes of a septic and aseptic nature, barotrauma and damage to the auditory nerve.
If the ear is blocked and makes a noise, what to do? The presence of two symptoms at once indicates dysfunction of the auditory analyzer, which can be caused by serious pathologies. If discomfort is found, you should seek the help of an otolaryngologist, who will be able to determine for sure the cause of the symptoms and the optimal principle of treatment.
Ear diseases
The main reason for the appearance of discomfort in the organ of hearing is ear pathologies. Impaired conduction and perception of sound signals often leads to the occurrence of audiological disorders. If noise and congestion in the ears suddenly appear, the causes of the phenomenon may lie in the development of such diseases:
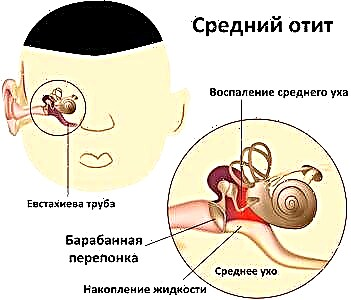 otitis media - inflammatory processes in the tympanic cavity, ossicles and auditory tube. The development of pathogenic flora in soft tissues leads to the appearance of edema, which creates barriers to the passage of sound waves, as a result of which uncomfortable sensations appear;
otitis media - inflammatory processes in the tympanic cavity, ossicles and auditory tube. The development of pathogenic flora in soft tissues leads to the appearance of edema, which creates barriers to the passage of sound waves, as a result of which uncomfortable sensations appear;- otosclerosis - abnormal growth of bone tissue in the ear, which leads to hearing impairment and the development of deafness. At the initial stages of the development of the disease, the appearance of extraneous noise, autophony and congestion is noted;
- myringitis is an acute inflammation in the ear membrane, which occurs as a result of the development of external (diffuse) or middle (purulent, serous, diffuse) otitis media. Destruction of the membrane leads to distortion of sound signals and the appearance of extraneous noise;
- eustachitis - catarrhal inflammation in the mucous membrane of the auditory tube, which leads to impaired ventilation of the middle ear. As a result, negative pressure builds up in the tympanic cavity, which causes the ear membrane to retract into the ear;
- Meniere's disease is an ear pathology characterized by the accumulation of endolymph in the inner ear. Excessive fluid pressure on the hair cells leads to the occurrence of audiological disorders and impaired coordination of movements.
Untimely elimination of ear pathologies leads to irreversible morphological changes in soft tissues, which is fraught with the development of chronic hearing loss.
Infectious diseases
According to otolaryngologists, noise and congestion in the ears can be a consequence of the development of inflammation in the mucous membranes of the airways. Since the nasopharynx is connected to the middle ear cavity by the Eustachian tube, the appearance of a cold can cause the pathogenic flora to enter the middle ear by the tubular route.
- frontal;
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- flu;
- rhinitis;
- tonsillitis.
Important! Untimely relief of infectious diseases can cause generalization of inflammatory reactions, which is fraught with brain abscess.
Nasal congestion and tinnitus are phenomena with an obvious connection. The onset of rhinitis is caused by inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, which lead to the separation of excess mucus. In turn, with swelling of the nasopharynx, the mouth of the Eustachian tube closes, as a result of which the air pressure in the middle ear cavity decreases. As a result, atmospheric pressure "forces" the eardrum to be drawn into the ear, which becomes the cause of the development of autophony.
Other reasons
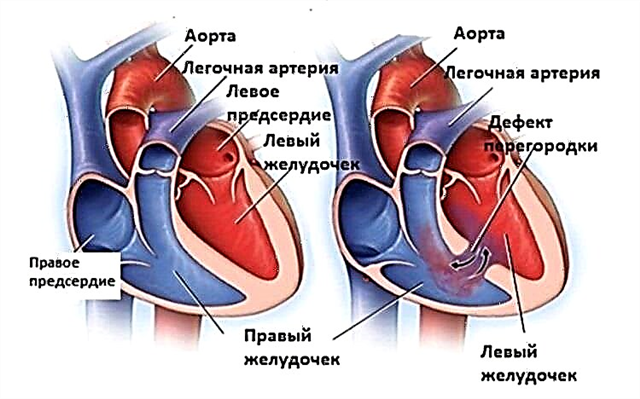
If the ear is blocked and makes noise, it can signal the development of cardiovascular and neurological disorders. Untimely treatment of diseases entails the emergence of serious complications that threaten the patient's life. If for a long time the discomfort in the organ of hearing does not go away, this may indicate the occurrence of such pathologies as:
- arterial hypertension - an increase in blood pressure leads to an intensive blood supply to the brain, as a result of which vasospasm occurs. Narrowing of the inner diameter of the capillaries contributes to the appearance of pulsating tinnitus;
- mechanical causes - trauma to the auditory analyzer, osteoma, stenosis of the external auditory canal and sulfur plugs inevitably lead to the occurrence of audiological disorders, characterized by the appearance of a feeling of congestion and noise;
- tumor diseases - the proliferation of cholesteatomas, meningiomas and epidermal tumors interferes with the passage of the sound wave, as a result of which the threshold of auditory sensitivity decreases and noise in the head occurs;
 kidney dysfunction is a disease in the development of which the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine is disrupted. As a result, blood pressure indicators increase, which leads to spasm of blood vessels in the brain and the appearance of pulsating noises.
kidney dysfunction is a disease in the development of which the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine is disrupted. As a result, blood pressure indicators increase, which leads to spasm of blood vessels in the brain and the appearance of pulsating noises.
In most cases, audiological disorders are subjective, due to pathological irritation of the auditory nerves.
Ototoxic effect of drugs
Discomfort in the organ of hearing often occurs as a result of the abuse of medications that have an ototoxic effect. Their use leads to the appearance of pathological changes in the soft tissues of the auditory analyzer, which contributes to the occurrence of audiological disorders and auditory dysfunction. Drugs with a pronounced ototoxic effect include:
- "Metronidazole" and "Methyl alcohol";
- Tolmetin and Furosemide;
- Tetracycline and Naproxen; "
- Vibramycin "and" Zamepirac ";
- Clindamycin and Prednisolone; "
- Mefevamic acid "and" B-blockers ".
Important! Ototoxic drugs have a destructive effect on neurons, which, even with timely treatment, can hardly be restored.
If the ear is blocked and the noise in the ear has arisen due to the abuse of medications, you need to stop using them.If persistent hearing loss occurs, it is necessary to undergo an audiometric examination by an otolaryngologist. Site - directory of individuals: prostitutes Yekaterinburg Intimate rest for men
Pharmacotherapy
Medication should be prescribed only by a specialist after examining the patient and passing the necessary tests. To stop ringing in the ears and congestion, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and psychotropic drugs are used. Effective drugs include:
 nootropics ("Cortexin", "Omaron") - have a beneficial effect on corticosubcortical connections, help to reduce neurological deficits;
nootropics ("Cortexin", "Omaron") - have a beneficial effect on corticosubcortical connections, help to reduce neurological deficits;- anticonvulsants ("Finlepsin", "Enkorat") - are prescribed to relax smooth muscles and eliminate spasms in the vessels;
- antihypoxants (Preductal, Rimecor) - increase the brain's resistance to oxygen deficiency;
- blood thinners ("Cavinton", "Telektol") - normalize blood circulation in the brain, prevent the formation of blood clots;
- antihistamines ("Diprazin", "Atarax") - eliminate inflammation and swelling in the affected tissues, which helps to restore the aeration function of the Eustachian tube.
Important! Patients suffering from renal failure and diabetes mellitus should not take medications without the recommendation of a specialist.
If the ears and tinnitus are blocked, physiotherapy may be used to treat patients. In the event of inflammatory processes in the organ of hearing, pneumomassage of the ear membrane, laser therapy and electrophoresis are most often prescribed.

 otitis media - inflammatory processes in the tympanic cavity, ossicles and auditory tube. The development of pathogenic flora in soft tissues leads to the appearance of edema, which creates barriers to the passage of sound waves, as a result of which uncomfortable sensations appear;
otitis media - inflammatory processes in the tympanic cavity, ossicles and auditory tube. The development of pathogenic flora in soft tissues leads to the appearance of edema, which creates barriers to the passage of sound waves, as a result of which uncomfortable sensations appear; kidney dysfunction is a disease in the development of which the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine is disrupted. As a result, blood pressure indicators increase, which leads to spasm of blood vessels in the brain and the appearance of pulsating noises.
kidney dysfunction is a disease in the development of which the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine is disrupted. As a result, blood pressure indicators increase, which leads to spasm of blood vessels in the brain and the appearance of pulsating noises. nootropics ("Cortexin", "Omaron") - have a beneficial effect on corticosubcortical connections, help to reduce neurological deficits;
nootropics ("Cortexin", "Omaron") - have a beneficial effect on corticosubcortical connections, help to reduce neurological deficits;