Kadik is the protruding part of the larynx formed by the thyroid cartilage. This anatomical structure is present in people of both sexes, but in men, the Adam's apple is often prominent on the front of the neck and becomes clearly visible when swallowing. On the neck of women, it is usually much more difficult to see it. When describing the symptoms of sore throat, patients often indicate the specific localization of the sensations that bother them - this is very important for the diagnosis of various diseases. Why does the throat in the Adam's apple region hurt and how to act in order to help the patient?
Causes
 A seemingly simple complaint of a sore throat in a practical sense means many diseases that differ in both etiological and pathogenetic principles. Of course, most often such symptoms are detected in infections caused by respiratory viruses - then the pain is combined with coughing, sneezing, nasal congestion and fever. However, at the same time, it can be associated with dozens of other pathologies - which is why the localization of sensations is so important when a doctor interviews a patient.
A seemingly simple complaint of a sore throat in a practical sense means many diseases that differ in both etiological and pathogenetic principles. Of course, most often such symptoms are detected in infections caused by respiratory viruses - then the pain is combined with coughing, sneezing, nasal congestion and fever. However, at the same time, it can be associated with dozens of other pathologies - which is why the localization of sensations is so important when a doctor interviews a patient.
The pain in the Adam's apple is often of varying intensity. The probable causes of its occurrence can be divided into main groups:
- Pathology of the oropharynx and larynx.
- Thyroid pathology.
- Digestive system pathologies.
- Neoplasms.
Sore throat and Adam's apple may also be associated with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS).
There are many theories explaining the development of CFS, and complaints of discomfort in the throat remain classic when interviewing patients. They are often localized precisely in the Adam's apple. In this case, it is necessary to be critical of the symptom: to confirm the presence of CFS, the exclusion of other pathologies is required.
A wide variety of diseases in which patients are worried about sore throat, necessitates a thorough and often multi-stage diagnosis. The most simple pathologies in this sense are infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx and tonsils. The diagnosis is established on the basis of objective clinical data and is confirmed, if necessary, using laboratory and instrumental tests available in most medical institutions. Also, with these diseases, it is easier to get a response to therapy, this does not require a long wait.
As for neoplasms, they can remain asymptomatic for a long time. Most complaints of pain below the Adam's apple or directly in the area of this anatomical structure are most often caused by the occurrence of an inflammatory process as a result of the presence of a tumor.
Pathology of the oropharynx and larynx
Patients can complain of pain concentrated in the area of the Adam's apple when:
- pharyngitis;
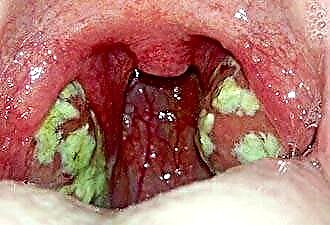
- tonsillitis;
- laryngitis.
With pharyngitis, the mucous membrane of the pharynx is affected, tonsillitis implies inflammation of the tonsils, and laryngitis - the mucous membrane of the larynx. Usually we are talking about an acute infectious process provoked by respiratory viruses (adenoviruses, respiratory syncytial virus, etc.) or bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci). If inflammatory changes are localized in several areas at once, the patient describes the symptoms of damage to all parts at the same time. Most often, not only painful sensations are present, but also dryness and perspiration. It should be noted that the pain is felt "inside the throat", and there are no external changes in the neck surface.
The Adam's apple area is painful with chondroperichondritis of the thyroid cartilage.
This is an inflammatory lesion of cartilage tissue caused by the penetration of pyogenic bacterial flora. It develops as a result of trauma - acute, dull (including those received during surgery). On examination, a slight bulging is found in the area where the thyroid cartilage is located. If its outer surface is involved in the pathological process, a swelling in the neck is determined by palpation. The patient may notice that the throat is sore to the left of the Adam's apple - or on the right side. Inflammation of the inner part of the cartilage is also likely, in which case the mucous membrane is edematous, hyperemic, but changes are visible only during laryngoscopy (examination of the larynx with a special device).
Chondroperichondritis of the thyroid cartilage lasts for a long time - for several months, in rare cases - for several years. If untreated, an abscess forms, and fragments of cartilaginous tissue may be released through a purulent fistula.
Thyroid pathology
When pain appears in the area of the thyroid cartilage, it is imperative to exclude (or confirm) the presence of an infectious and inflammatory pathology on the part of the thyroid gland:
- acute thyroiditis;
- sharp strumite;
- subacute thyroiditis.
Acute thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland as a result of penetration of pathogens of a bacterial nature into its tissue (streptococci, staphylococci). A patient who has recently suffered from bacterial sinusitis, otitis media can get sick; characterized by an acute onset and sudden onset of symptoms - one of the leading is pain in the anterior surface of the neck within the boundaries of the Adam's apple. There is also swelling of the affected area, fever.
The etiology and clinical picture of acute strumitis coincides with the signs of acute thyroiditis - the difference is that thyroiditis develops as an inflammatory process in the unchanged thyroid gland, and strumite occurs against the background of goiter (enlargement of the gland as a result of colloid accumulation or cell hyperplasia).
Subacute thyroiditis is thought to have a viral etiology. It develops a few weeks after the acute form of a viral infection:
- Mumps (inflammation of the parotid salivary gland).
- ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection).
- Infectious mononucleosis.
At the heart of subacute thyroiditis is an inflammatory and destructive process.
The disease develops slowly (up to 2 months), in stages, characterized by a moderate inflammatory reaction, against which the destruction of the thyroid follicles occurs. Subsequently, pseudogranulomas are formed, fibrosis of the damaged areas occurs (replacement by connective tissue). Soreness in the Adam's apple is characteristic of the initial stage of subacute thyroiditis, combined with symptoms of hyperthyroidism (palpitations, increased excitability, increased body temperature to subfebrile values, etc.).
Digestive system pathologies
 Some symptoms of diseases of the digestive system can simulate the picture of ENT pathology for a long time - gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is of the greatest importance. Experts distinguish the so-called extraesophageal syndrome, which includes the phenomenon of laryngopharyngeal reflux - the throwing of aggressive gastric contents into the larynx with insufficient contraction force of the lower esophageal sphincter, dysfunction of the upper esophageal sphincter and impaired motor function of the digestive tract as a whole.
Some symptoms of diseases of the digestive system can simulate the picture of ENT pathology for a long time - gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is of the greatest importance. Experts distinguish the so-called extraesophageal syndrome, which includes the phenomenon of laryngopharyngeal reflux - the throwing of aggressive gastric contents into the larynx with insufficient contraction force of the lower esophageal sphincter, dysfunction of the upper esophageal sphincter and impaired motor function of the digestive tract as a whole.
Sore throat in the area of the thyroid cartilage with GERD occurs:
- in case of violation of the diet;
- with alcohol abuse;
- in the presence of volumetric formations of the abdominal cavity
- during pregnancy, etc.
The contents of the stomach (hydrochloric acid, activated pepsin) can enter the esophagus in small amounts even in healthy people, but in this case it is inactivated by a special enzyme called carbanhydrase. Dysfunction of the esophageal sphincters and low tone of the pharyngeal muscles contribute to the fact that an aggressive substance is thrown into the upper respiratory tract, damaging the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx. Reflux laryngitis develops, manifested by pain in the Adam's apple, combined with a feeling of a lump in the throat, constant coughing, increased salivation, and hoarseness. A sore throat (often of moderate intensity) is accompanied by a sensation of irritation of the mucous membrane.
Treatment
To eliminate the pain at the bottom of the Adam's apple, you need to understand what pathological process it has become. There is no one-size-fits-all recipe for any disease; in addition, treating pain alone is pointless, since this is only one of the many signs.
Diseases of the oropharynx and larynx
 With pharyngitis, tonsillitis and laryngitis, the patient needs:
With pharyngitis, tonsillitis and laryngitis, the patient needs:
- Plentiful warm drink.
- Exclusion from the diet of spicy, salty, crumbling dishes.
- Quitting smoking, alcohol.
- Gargling with medicinal solutions (saline, chamomile infusion, etc.).
- The use of local anti-inflammatory drugs (Islam-moos, Falimint).
If pain occurs against the background of hoarseness of the voice (laryngitis), you need a mode of silence (voice rest) for several days, inhalation of drugs. In case of severe pain, you can use local anesthetics and analgesics in the form of sprays, lozenges (Tantum Verde, Strepsils Intensive). With ARVI, these measures are usually sufficient, but with bacterial (in particular streptococcal) tonsillitis, antibacterial drugs are also required.
Chondroperichondritis of the thyroid cartilage
Treatment of chondroperichondritis of the thyroid cartilage consists in massive antibiotic therapy (Amoxiclav, Cefepim). Physiotherapy is also used (phonoelectrophoresis with Augmentin, ionogalvanization with calcium chloride, etc.). Additionally, in order to increase immune resistance, biostimulants (Aloe, Gumisol), vitamin therapy are shown.
The food that the patient eats should be mushy - this makes it easier to swallow.
Feeding through a gastric tube is undesirable, since it puts pressure on the tissues of the larynx and thereby provokes their irritation. The formation of an abscess and fistula is an indication for surgical treatment.
Acute thyroiditis (strumite)
The disease cannot be treated at home, and even more so independently - the patient is hospitalized in  specialized department of a surgical hospital. In the initial period (during the first or second week after the onset of symptoms), conservative management is usually possible - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, detoxification and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
specialized department of a surgical hospital. In the initial period (during the first or second week after the onset of symptoms), conservative management is usually possible - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, detoxification and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
If an abscess has formed, it must be surgically opened and drained to drain the pus. Otherwise, spontaneous opening into the lumen of the trachea, esophagus, and also into the mediastinum, where the inflammatory process develops - mediastinitis, is likely.
Subacute thyroiditis
The therapy regimen depends on the stage of the disease. In the first, hyperthyroid period, apply:
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Metamizole sodium);
- beta-blockers (Anaprilin), etc.
If the patient has already developed hypothyroidism, substitution therapy (L-Thyroxine) is considered.
Laryngopharyngeal reflux, reflux laryngitis
Complex treatment of the primary disease, GERD, is required. Compliance with a diet, elimination of factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure is recommended. Prescribed proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Esomeprazole), antacids (Gaviscon). With pronounced changes in the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed, which are selected by a doctor. If conservative treatment of GERD is ineffective, surgical correction of esophageal sphincter insufficiency (fundoplication) is performed.
The appearance of pain in the Adam's apple is a reason for contacting a specialist. It is easier to cure any of the described diseases in the initial stage. The patient can be helped by a general practitioner or an ENT doctor. If necessary, the patient is referred to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, surgeon.