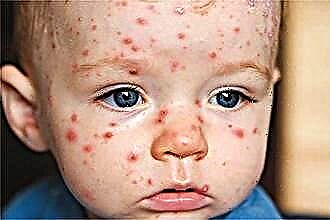
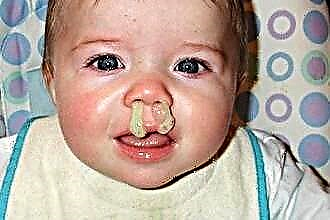
Hypertrophy of the tonsils is not an independent diagnosis, but a symptom indicating the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. What to do if the child's tonsils are enlarged?
 The principles of therapy depend on the etiological factors provoking pathological changes in the lymphadenoid tissues.
The principles of therapy depend on the etiological factors provoking pathological changes in the lymphadenoid tissues.
According to pediatrician E.O. Komarovsky, loosening and enlargement of the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils in children is most often associated with the development of infectious diseases. Reducing the reactivity of the child's body stimulates the reproduction of pathogenic viruses and bacteria. As a result, the components of the lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring, which perform a protective function, become inflamed, which leads to an increase in the size of the glands and the pharyngeal tonsil.
Tonsils - what is it?
Tonsils are small oval-shaped formations that are located in the oral cavity and nasopharynx. They consist of lymphadenoid tissues involved in the synthesis of blood and immunocompetent cells. The pharyngeal, lingual, tubal and palatine tonsils are the main components of the pharyngeal ring, which protect the respiratory system from the penetration of pathogens.
In the absence of functional disorders in the work of the tonsils, medical and surgical intervention is not required.
Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissues most often occurs in childhood and affects mainly the pharyngeal tonsil and tonsils (tonsils). In the case of organ inflammation, treatment begins with the use of a conservative therapy. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention may be required, involving partial (tonsillotomy) or complete (tonsillectomy) removal of lymphoid accumulations.
Inflammation causes
Why does tonsil hypertrophy occur? An increase in lymphoid tissues in some cases is associated with an intensification of the synthesis of immunocompetent cells. Therapeutic treatment is prescribed only in the case of catarrhal or purulent inflammation of the organs. The defense mechanisms of the child's body are not fully regulated, therefore, preschool children are more susceptible to infectious diseases than adults.
The causative agents of pathological processes in the tonsils can be:
 adenoviruses;
adenoviruses;- rhinoviruses;
- herpes viruses;
- influenza virus;
- coronaviruses;
- staphylococci;
- meningococci;
- streptococci;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- mycoplasma;
- fungi;
- spirochetes.
Septic inflammation of lymphoid accumulations leads to edema, hyperemia and tissue melting. The critical increase in the size of the tonsils makes breathing difficult, which can cause acute hypoxia in a child.
When to see a doctor?
E.O. Komarovsky argues that the untimely passage of drug therapy can lead to the chronicization of pathological processes. Therefore, if the first signs of sore throat are found, you should seek the help of a specialist. Diseases such as adenoiditis, purulent tonsillitis, diphtheria and chronic tonsillitis pose a particular threat to children.
Direct indications for contacting a pediatrician are the following signs of the disease:
- red throat;
- hypertrophy of the tonsils;
- difficulty swallowing;
- heat;
- white bloom and dots on the tonsils;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Adenoiditis in children under the age of 3 years causes hypoxia, which negatively affects the physical and mental development of the child.
In the case of the development of a bacterial infection, there is a strong intoxication of the body with metabolites of pathogens. Symptoms of body poisoning by toxic substances of pathogenic bacteria are myalgia, headaches, fever, weakness and lack of appetite.
Recommendations of E. O Komarovsky
What should be the treatment for tonsil hypertrophy in children? Inflammation of lymphadenoid tissues requires immediate medical therapy, which includes a whole range of therapeutic measures. The scheme and principles of treatment can only be determined by a specialist after examining the child and identifying the causative agent of the infection.
To prevent the development of systemic and local complications allows the implementation of several important recommendations:
- adherence to bed rest;
- prevention of hypothermia of the child;
- regular ventilation of the room;
- drinking enough warm drinks;
- exclusion from the diet of solid foods that injure the throat.
 Physical overstrain accelerates blood circulation in the tissues, which only contributes to the progression of infection and the spread of lesions.
Physical overstrain accelerates blood circulation in the tissues, which only contributes to the progression of infection and the spread of lesions.
That is why during the period of acute inflammation of the throat and glands, it is advisable to strictly observe bed rest.
In turn, drinking a lot of drinks stimulates the process of removing toxic substances from the body, which helps to eliminate the general symptoms of intoxication.
Treatment principles
Hypertrophy of the tonsils in children causes a number of disorders in the body. A constant lack of oxygen (hypoxia), due to the overlap of the airways by hypertrophied tonsils, leads to a lag in children in physical development. Approximately 25% of patients with enlarged glands develop enuresis and associated mental disorders.
How to treat enlarged tonsils in a child? Komarovsky claims that it is possible to eliminate the hypertrophy of lymphadenoid tissues without surgical intervention only in the case of complex therapy. As a rule, the treatment plan for ENT diseases in children is as follows:
- cleansing the lacunae and follicles of the tonsils from pathological mucus and infectious pathogens with solution antiseptics;
- elimination of allergic manifestations and puffiness with the help of antihistamines;
- increasing general and local immunity with vitamin and mineral complexes and immunostimulants;
- destruction of pathogens with drugs of etiotropic action - antibiotics, antifungal and antiviral agents;
- acceleration of tissue healing processes using physiotherapy procedures.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used only at the stage of resolving inflammatory processes in lymphadenoid tissues.
Etiotropic therapy
 What are the means to treat inflammation of the tonsils? As a rule, hypertrophy of lymphadenoid accumulations is caused by the development of a bacterial, less often a viral infection. To eliminate causative agents of ENT diseases, drugs of etiotropic action are used. Systemic antibiotics and antiviral drugs inhibit the development of pathogenic flora, which contributes to the regression of inflammation and epithelialization of the affected tissues.
What are the means to treat inflammation of the tonsils? As a rule, hypertrophy of lymphadenoid accumulations is caused by the development of a bacterial, less often a viral infection. To eliminate causative agents of ENT diseases, drugs of etiotropic action are used. Systemic antibiotics and antiviral drugs inhibit the development of pathogenic flora, which contributes to the regression of inflammation and epithelialization of the affected tissues.
It is possible to eliminate the manifestations of bacterial inflammation with the help of broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents. Some of the most effective drugs include:
- Panklav is a semi-synthetic antibiotic of the penicillin series that destroys most of the gram-positive microbes that synthesize beta-lactamase; used in the treatment of follicular and lacunar tonsillitis, pharyngitis, phlegmon, sinusitis, etc.;
- "Augmentin" is a bacteriolytic drug that prevents the development of most strains of aerobic bacteria; used to eliminate purulent-infectious processes in the respiratory system;
- "Zi-factor" is a macrolide antibiotic of bacteriostatic and anti-inflammatory action, which is used to eliminate purulent processes in the ENT organs of any localization;
- "Clarithromycin" is a drug from the macrolide group that inhibits the reproductive activity of microbes; used in the treatment of infectious inflammation in the lower and upper airways.
If there is no white plaque and purulent plugs on the tonsils, the inflammation is most likely caused by viral pathogens. In this case, the treatment is carried out using drugs with antiviral and immunostimulating action. The following medications allow to stop catarrhal inflammation in lymphoid tissues:
- "Orvirem" is an antiviral agent that interferes with the replication of RNA of pathogens, which leads to the elimination of pathogenic flora in the lesions;
- "Relenza" is a selective drug that inhibits the biosynthesis of neuraminidase of pathogenic viruses, which accelerates the regression of inflammation;
- "Viferon" is an interferon inhibitor with antiproliferative and immunostimulating effects; increases the activity of immunocompetent cells, which accelerates the process of destroying pathogens;
- "Kagocel" is a combined action medication with antimicrobial, fungistatic and antiviral effects.

You can not use interferon inducers for the treatment of children under the age of 6-7 years.
The destruction of the pathogenic flora prevents the progression of pathological processes. A gradual increase in local immunity contributes to the regeneration of damaged tissues, the resorption of infiltrates in the mucous membranes and the elimination of glandular hypertrophy.
Symptomatic therapy
Symptomatic treatment allows you to alleviate the course of the disease, eliminate discomfort in the throat, myalgia, headaches, etc. The regimen of pediatric therapy usually includes lozenges, solutions for rinsing the oropharynx, sprays for extinguishing the throat, and vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system.
It is possible to eliminate signs of lymphoid tissue hypertrophy and general symptoms of intoxication with the help of the following medications:
- "Loratadin" is an antiallergic drug that helps to eliminate swelling and tissue hyperemia;
- "Cameton" - spray for irrigation of the oropharynx, which has an antiseptic, wound healing and local anesthetic effect;
- "Stopangin" - tablets for resorption, inhibiting the development of pathogenic flora in the affected tonsils;
 "Chlorophyllipt" - a solution for rinsing, disinfecting, decongestant and wound-healing action;
"Chlorophyllipt" - a solution for rinsing, disinfecting, decongestant and wound-healing action;- "Imunorix" - an immunostimulant that promotes the synthesis of interferon in the body, which is involved in the destruction of viruses;
- "Centrum" is a vitamin and mineral complex that normalizes cellular metabolism and regeneration processes in tissues;
- "Ibuprofen" is an antipyretic with anti-inflammatory action that interferes with the synthesis of inflammatory mediators.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and further enlargement of the tonsils, surgical treatment is prescribed, involving partial or complete removal of lymphoid formations.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment is aimed at restoring the functions of hypertrophied tonsils. Exposure of tissues to ultraviolet light, magnetic fields, alternating current and ultrasound stimulates blood circulation in tissues. The elimination of stagnant processes helps to restore the drainage function of the glands and, as a result, reduce their size.
For the treatment of acute tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis and other ENT diseases in children, the following physiotherapy methods can be used:
- ultraviolet irradiation - destroys pathogenic bacteria, relieves swelling and inflammation from lymphadenoid formations;
- UHF therapy - normalizes blood microcirculation in tissues, which contributes to the regeneration of tonsils affected by inflammation;
- ultrasound therapy - cleans lacunae and follicles from purulent contents, as a result of which the drainage function of organs is restored;
- laser therapy - destroys pathogens and cleans lymphoid tissues from pathological exudate.
To eliminate chronic inflammation and hypertrophy of the tonsils, it is necessary to undergo at least 7-10 courses of physiotherapy.
During treatment, it is undesirable to refuse taking medications with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial action.

 adenoviruses;
adenoviruses; "Chlorophyllipt" - a solution for rinsing, disinfecting, decongestant and wound-healing action;
"Chlorophyllipt" - a solution for rinsing, disinfecting, decongestant and wound-healing action;