A person usually pays attention to the rhythm and quality of breathing in three situations: at the mention of this, during physical activity or with the development of pathological disorders.
A person usually pays attention to the rhythm and quality of breathing in three situations: at the mention of this, during physical activity or with the development of pathological disorders.
The feeling of shortness of breath and complaints of choking the throat are common in many diseases.
At the same time, it is important to find out what exactly causes such symptoms - in many cases, the patient needs urgent help.
Etiology
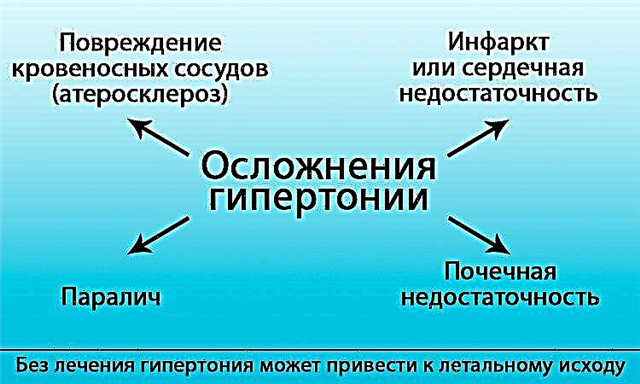
Breathing disorder is one of the most painful sensations for a person. Whatever the reason, lack of oxygen cannot go unnoticed. The feeling of suffocation appears suddenly or grows gradually, but in all cases it is accompanied by dizziness, increased respiratory movements - this is how the body tries to normalize the volume of air that enters the respiratory tract. Choking, a person experiences panic - and this is natural, since a decrease in the quality of blood oxygenation (oxygen content in it) threatens life.
Why is there a feeling of lack of air? If the leading symptom in the clinical picture is difficulty breathing, one can assume:
- Acute infectious laryngitis.
- Injury, foreign body of the larynx.
- Cicatricial stenosis of the larynx.
- Allergic reaction.
- Bronchial asthma (BA).
All of these pathologies have different causes. Some of them arise acutely, are characterized by the sudden onset and rapid development of symptoms of respiratory failure, others are characterized by a gradual deterioration, as a result of which the body temporarily adapts to a lack of oxygen.
The feeling of "insufficient" inhalation and lack of air is also observed in neuroses, depression, autonomic dysfunction syndrome.
Diagnostics is based on the identification of other symptoms characteristic of these pathologies. In addition, a person may complain of choking if they experience significant psycho-emotional stress.
Diseases leading to a feeling of suffocation are not always provoked by infectious agents - this causes the absence of signs of intoxication in the clinical picture (fever, nausea, weakness, dizziness). Sometimes the lack of air is combined with severe pain of various localization or proceeds without any pain. Thus, a single symptom, albeit as frightening as respiratory failure, cannot be immediately diagnosed. If it is difficult for the patient to breathe, then in order to understand what this may be, it is important to pay attention to all other manifestations.
Acute infectious laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammatory disease involving the laryngeal mucosa in the pathological process. Infectious laryngitis is provoked by a variety of microbial, viral and fungal pathogens. Since the larynx is part of the respiratory system, its patency is important for the unhindered flow of air into the underlying departments. If during an infectious-inflammatory process obstruction occurs (overlap of the lumen) as a result of edema, pressure of an inflammatory infiltrate or accumulation of pathological layers, the air flow stops, suffocation (asphyxia) occurs.
There are many types of infectious laryngitis, but they are not always accompanied by respiratory disorders. In this case, age-related anatomical characteristics are important - for example, in children, the lumen of the larynx is narrow, and the likelihood of its partial or complete overlap is very high. There are several variants of laryngeal inflammation that are most important in the diagnosis of breathing disorders:
| Pathology | Etiology | Characteristics of respiratory disorders | Asphyxiation probability | Features of the flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laryngeal diphtheria | Corynebacterium diphtheria (diphtheria bacillus, Leffler's bacillus). | First, there is hoarseness of the voice (dysphonia), a barking cough, which after 1-2 days are supplemented by noisy (stridor) breathing. Asthma attacks are often repeated, the voice disappears (aphonia). When breathing, the intercostal spaces are drawn in, as well as the pits above and below the collarbones. | Very high, can occur when the films overlap the lumen of the larynx or toxic damage to the vasomotor and respiratory centers in the terminal stage of the disease. | Diphtheria croup, that is, inflammation of the larynx, complicated by stenosis (narrowing of the lumen), can develop as a symptom of a toxic or isolated form of diphtheria. Most often occurs in children under 5 years of age, but sometimes it occurs in adults. At the same time, the onset of the disease before the appearance of diphtheria films resembles a classic cold, which complicates timely diagnosis. |
| Influenza laryngitis | Flu virus | Dysphonia is observed, which increases with increasing edema and airway obstruction. The patient develops shortness of breath, is agitated, sometimes takes a forced position to facilitate inhalation. | High, associated with edema obstructing the airway. | The attack begins more often in the evening or at night - as a rule, in young children or with a severe course of influenza infection. |
| Laryngeal sore throat | Streptococci, staphylococci | A dry or unproductive cough is combined with dysphonia, retraction of the intercostal spaces, tachypnea (increased respiratory rate). | Depends on the degree of stenosis, the severity of the edema. | Usually accompanies infectious and inflammatory pathologies of adjacent areas; stenosis is a rare but possible complication of the course. |
| Epiglottitis (inflammation of the epiglottis) | Streptococci, staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, respiratory viruses | The pathologically altered epiglottis blocks the entrance to the larynx, which provokes shortness of breath, hoarseness and hoarseness of the voice. | Very high, especially in children. | Epiglottitis is a form of phlegmonous laryngitis, accompanied by severe, sometimes almost unbearable sore throat, a rapid increase in stenosis. |
| Thrush of the larynx | Candida albicans - yeast-like fungus | The patient feels difficulty swallowing, notes hoarseness and a foreign body in the larynx - these symptoms can progress and turn into a feeling of choking in the throat. | Depends on the severity of the course, high in severe form. | On the mucous membrane, white, white-gray or yellowish deposits are present, which are tightly adhered to the underlying surface. The disease is characterized by a slow development and an increase in symptoms, a recurrent course. |
There is also the concept of stenosing laryngotracheitis, in which not only the larynx is affected, but also the trachea.
In this case, there are phenomena of stenosis and respiratory failure of varying severity. Most often, the disease develops in childhood, the greatest risk of stenosis is associated with influenza and streptococcal infections. When the bronchi are involved in the pathological process, which is likely in a small child, the disease is called stenosing laryngotracheobronchitis. This pathology is a frequent companion of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infections) in children.
Trauma, foreign body, cicatricial stenosis
There is a volumetric classification of traumatic injuries of the larynx - the symptoms depend on the type and severity of the injury. With mechanical compression, violation of the integrity of the anatomical structures of the larynx, obstruction of the airways, suffocation occurs. With severe trauma, shock develops.
A foreign body can cause asphyxiation:
- when closing the lumen of the larynx (cotton swab, cork);
- when provoking a reflex spasm of the larynx (crumbs, beads).
 There is a choking in the throat - symptoms develop very quickly. The patient is agitated, convulsively tries to inhale, rushes about, grabs his throat, his complexion changes. The voice is hoarse or disappears altogether, so the person is not able to call for help. In case of incomplete obstruction, the protective mechanisms of the larynx are activated, a cough arises up to vomiting, in full force, designed to push out the foreign body that blocks the air flow. It is far from always effective, and emergency care should be provided to the patient within the first three minutes from the moment the characteristic signs appear.
There is a choking in the throat - symptoms develop very quickly. The patient is agitated, convulsively tries to inhale, rushes about, grabs his throat, his complexion changes. The voice is hoarse or disappears altogether, so the person is not able to call for help. In case of incomplete obstruction, the protective mechanisms of the larynx are activated, a cough arises up to vomiting, in full force, designed to push out the foreign body that blocks the air flow. It is far from always effective, and emergency care should be provided to the patient within the first three minutes from the moment the characteristic signs appear.
Cicatricial stenosis of the larynx occurs:
- After injury.
- After operation.
- After the inflammatory process.
The patient can get sick as a result of tracheostomy, damage to the cartilage of the larynx. The signs of respiratory distress progress slowly. At first, the patient complains of shortness of breath - usually only with physical exertion, occasionally at rest. With the gradual development of narrowing, adaptation to oxygen deficiency occurs, and compensated chronic stenosis is observed.
Compensated stenosis can threaten asphyxiation in an acute inflammatory process - laryngitis.
Inflammatory edema blocks the already narrowed lumen of the larynx. The patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating - the throat hurts, it is difficult to breathe. The swelling is rapidly increasing, so treatment should be started as soon as symptoms are detected.
Allergy, BA
An allergic reaction, expressed in the form of angioedema of the larynx (Quincke's edema) is provoked by:
- food allergens;
- respiratory allergens;
- insect bites.
Characterized by a sudden onset, rapid development of edema of the lips and tongue. There is usually no pain - this symptom replaces the feeling of swelling of the swollen tissues. The signs of suffocation are explained by the cessation of air flow through the narrowed edematous larynx. Clinical objective signs coincide with other options for airway obstruction:
- hoarseness of the voice occurs;
- it becomes difficult for the patient to breathe;
- the voice disappears, the inhalation becomes ineffective.
With edema of the larynx, the patient may die as a result of asphyxia; the pathological process often involves not only the mucous membrane of the larynx, but also the trachea and bronchi. Urgent care required.
Bronchial asthma is a disease with an allergic component of pathogenesis, the typical manifestation of which is episodes of suffocation. Depending on the frequency and duration of their repetition, the severity of the course is determined. The hyperreactivity of the airways is of leading importance - this means that in response to the influence of provoking factors, the lumen of the bronchi is significantly narrowed.
A variety of allergens, respiratory infections, and psychoemotional stress act as triggers for an asthma attack.
The patient is also worried about:
- Wheezing in the chest.
- Expiratory dyspnea, characterized by difficulty in exhaling.
During an asthma attack, the patient may also show signs of allergic rhinitis (nasal congestion), which aggravates the degree of respiratory distress. It is difficult for the patient to breathe through the nose and it is difficult to exhale air.
If breathing is difficult, the cause should be found out as soon as possible - pathological changes can progress quickly. People prone to allergic reactions should avoid contact with allergens provocateurs and, if possible, have emergency medications with them - for example, a pen with epinephrine (adrenaline). A gradual increase in shortness of breath against the background of a respiratory infection requires specialist advice, especially if there is reason to suspect diphtheria.