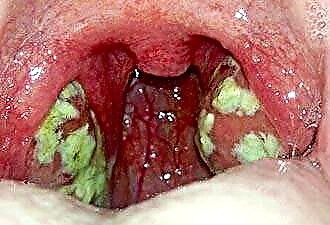
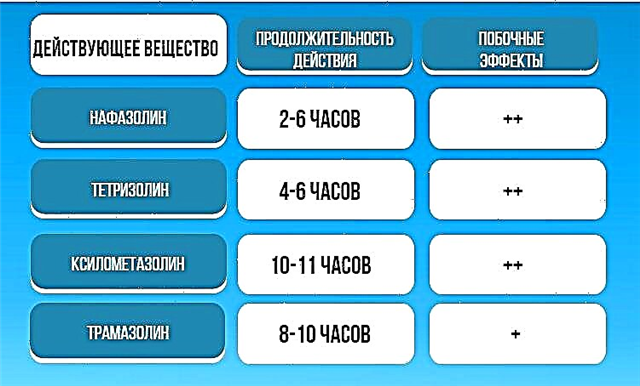
Throat irritation can be caused by exposure to a variety of pathogenic agents. Among the factors contributing to the development of the pathological process, there are pathogenic microorganisms, allergens, toxic substances in the inhaled air.
 The most common symptoms of an irritated throat are
The most common symptoms of an irritated throat are
- perspiration;
- scratching;
- sore throat;
- feeling of a lump;
- difficulty swallowing;
- a feeling of discomfort in the throat;
- cough.
These symptoms are combined into irritable throat syndrome.
Pathogenic microorganisms
Among the pathogens involved in the effect on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, viruses are the most common. The throat is the gateway to the entry of these infectious pathogens. The result of their exposure can be SARS, pharyngitis, laryngitis.
Dry and warm air of an unventilated room promotes the spread of diseases.
An obstacle to the spread of respiratory infections transmitted by airborne droplets is to ensure the required temperature regime of the inhaled air and its humidity. Room temperature not higher than 20 degrees and humidity 50-60% are optimal to prevent ARVI. Bacteria and fungi are also involved in the development of diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Disease factors
In addition to pathogens, throat irritation can be caused by:
- the presence of hazardous impurities in the air, chemical compounds;
- dustiness of the inhaled air;
- regularly eating spicy, acidic foods;
- the presence of bad habits, smoking, alcohol abuse;
- the effect of medicinal substances on the throat mucosa.
The influence of these factors increases the incidence of respiratory tract pathology. Patients who smoke and abuse alcohol are at risk for any disease involving the upper respiratory tract. The irritating factor in the form of nicotine leads to a negative effect on the mucous membrane of the throat and nose, reducing its protective properties. The consequence of this is an increase in the number of sick patients among smokers. No less dangerous is the effect of nicotine on the development of such serious diseases as chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis, throat cancer.
The danger of dustiness in the air for the development of pathology of the upper respiratory tract is evidenced by the increase in the number of cases among residents of large industrial centers, workers in hazardous workshops. In such cases, patients notice a deterioration in the condition, the appearance of signs of throat irritation at the end of the day. In most patients, the leading symptom is sneezing, sore throat, painful sensations when swallowing, dry cough.
Strong-smelling substances also have a pronounced irritant effect. Most often they are household chemical products, perfumed mixtures. Constant exposure to exogenous factors leads to the development of chronic pharyngitis in patients, an inflammatory process in the pharynx.
 If the larynx is involved in the pathological process, signs of damage to the vocal cords are added to these symptoms. The patient has a change in the timbre of his voice, the appearance of hoarseness. In severe cases, it can become silent. A factor contributing to the development of lesions of the vocal cords is also their overstrain. Acute laryngitis can develop as a result of a sharp cry or prolonged tension of the ligamentous apparatus during the professional activities of singers and teachers.
If the larynx is involved in the pathological process, signs of damage to the vocal cords are added to these symptoms. The patient has a change in the timbre of his voice, the appearance of hoarseness. In severe cases, it can become silent. A factor contributing to the development of lesions of the vocal cords is also their overstrain. Acute laryngitis can develop as a result of a sharp cry or prolonged tension of the ligamentous apparatus during the professional activities of singers and teachers.
Exogenous substances in the air are not the only irritating factor for the mucous membrane.
There are often cases when the parameters of the inhaled mixture themselves are unfavorable for the normal functioning of the body. Air, which does not contain dangerous impurities, but is characterized by low humidity, has an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. Dry air dries out the mucous membrane, reduces its protective properties, makes it susceptible to the effects of pathogens. With its irritating effect, it contributes to the development of inflammatory diseases.
Errors in diet, consumption of strong alcoholic beverages in large quantities also contribute to throat irritation and the development of a chronic inflammatory process in it. In this regard, for patients who neglect the recommendations for a healthy diet, hoarseness, constant tickling, and coughing are characteristic.
Topical drugs may have a similar effect. Most often, various aerosols used to treat diseases of the upper respiratory tract or oral mucosa have an irritating effect.
Individual intolerance to chlorhexidine, iodine preparations can irritate the mucous membrane, aggravating the course of the disease.
Reflux esophagitis
An irritating factor on the mucous membrane can also have the acidic content of gastric juice. Normally, it is not contained in the esophagus or throat.
 However, in a number of pathological processes, peptic ulcer, gastritis, hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, hydrochloric acid and other components of gastric juice can be thrown into the overlying sections, irritating the mucous membrane and causing an increase in acidity in them.
However, in a number of pathological processes, peptic ulcer, gastritis, hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, hydrochloric acid and other components of gastric juice can be thrown into the overlying sections, irritating the mucous membrane and causing an increase in acidity in them.
Sore throat syndrome in this case is characterized by sore throat, burning sensation along the throat and esophagus, belching, heartburn. The condition is aggravated in the horizontal position of the patient or when the trunk is tilted downward. It is this position that promotes the throwing of stomach contents.
Allergy
Exposure to allergens can also be irritating. The most characteristic symptom is a scratching sensation, perspiration, dry cough. Additional symptoms are shortness of breath, watery eyes, runny nose, and skin rashes. This symptomatology is due to the effect of allergens and the start of a pathological reaction.
Allergens can enter the body during breathing, through the use of hazardous substances in food, or direct contact. There are often cases when the use of a drug leads to an allergy. A severe course of allergy is the development of Quincke's edema, in which there is a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition, accompanied by disorders of the cardiovascular system. In this case, laryngeal edema develops, which can lead to suffocation.
The presence of irritated throat syndrome is a reason to contact an otolaryngologist for an appointment. In this case, it is important to determine the cause of the development of the pathological process. After conducting an objective examination, collecting an anamnesis of the disease and finding out the nature of irritating factors, the specialist will be able to prescribe the appropriate treatment, propose a set of measures to prevent this condition.