Fever and sore throat are constant signs of many diseases of the upper respiratory tract and ENT pathology. The cause of the development of pathological conditions occurring with the development of this symptomatology can be viruses, bacteria, less often fungal pathogens.
 Exposure to allergens is also characterized by similar symptoms. A sore throat and an increase in temperature are characteristic of diseases of a tumor nature. Treatment methods for pathological conditions are different.
Exposure to allergens is also characterized by similar symptoms. A sore throat and an increase in temperature are characteristic of diseases of a tumor nature. Treatment methods for pathological conditions are different.
In order for therapeutic measures to be most effective, it is necessary to clarify the nature of the lesion in each specific case.
Timely prescribed treatment will improve the patient's condition in a shorter time frame, avoid complications of the disease.
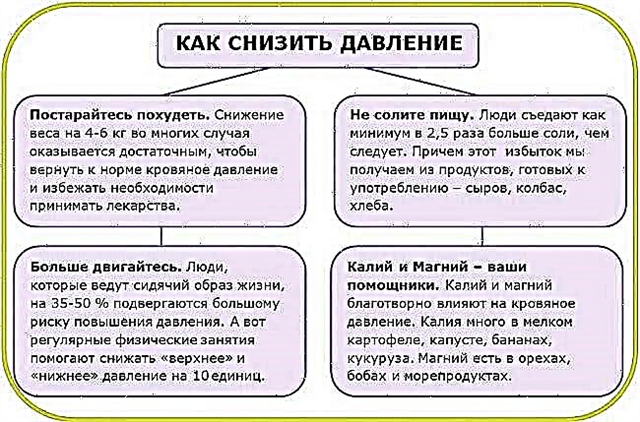
ARVI
The most common disease that affects the upper respiratory tract is ARVI. There are many viruses that can cause this infection. However, despite some differences in the clinical picture due to different strains of viruses, these signs are constant. In addition, symptoms that help clarify the diagnosis are
- acute development of symptoms;
- nasal congestion;
- profuse, mucous discharge from the nose;
- severe malaise, weakness;
- aching muscles and joints;
- dry cough.
With regard to temperature indicators, the most typical for ARVI is an increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees. However, with reduced immunity of the patient, old age, the presence of concomitant pathology, the disease can proceed at a lower temperature. Indicators 37-38 degrees are most characteristic if the development of the pathological process is caused not by a viral, but by a bacterial pathogen. Subfebrile temperature in this case will be the most typical.
Any acute respiratory disease, both viral and bacterial in nature, is characterized by a mild course.
The main therapeutic actions are detoxification measures and symptomatic treatment:
- drinking plenty of fluids;
- antipyretics when the temperature rises above 38 degrees;
- topical preparations aimed at reducing pain in the throat;
- local procedures, gargling, inhalation, rubbing, application of mustard plasters;
- expectorants in the form of tablets, syrups, herbal decoctions.
There is no single point of view among medical practitioners regarding the use of antiviral drugs. Most experts are of the opinion that they should be used at the stages of prevention, with a worsening epidemiological situation, or severe flu and other acute respiratory viral infections.
Laryngitis and pharyngitis
Among the ENT pathology, sore throat and cough are most characteristic of pharyngitis and laryngitis. The cause of these diseases can be viruses, bacteria, other pathogenic pathogens. In addition, the provoking factors in their development are:
- hypothermia;
- the presence of smoke, soot, and other impurities in the inhaled air;
- smoking;
- regular use of strong alcoholic beverages, spicy foods.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the clinical signs of the disease may differ slightly. With an inflammatory process in the pharynx, in addition to the sore throat, cough comes to the fore.
 By its nature, it is dry, paroxysmal, constant throughout the day. In this case, clinical symptoms are present for several weeks.
By its nature, it is dry, paroxysmal, constant throughout the day. In this case, clinical symptoms are present for several weeks.
Usually pharyngitis is characterized by a chronic course, with periods of remission and exacerbation, which is caused by the action of pathogenic microorganisms or exogenous factors. The general condition of the patient is usually not disturbed. Minor discomfort may occur. A temperature of 37 degrees is most typical for such a disease. An increase in it to 37.5-37.8 degrees can be noted only with an exacerbation of the process.
The main therapeutic measures are symptomatic treatment. Since the main symptom of the disease is the defeat of the throat and the development of pain in it, then they use the means of analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial action. These can be aerosols, lozenges, and throat rinses. According to otolaryngologists, Septefril, Strepsils, Faringosept and other popular drugs are ineffective in treating these conditions. In this regard, their use is indicated for milder forms of the disease.
In more severe cases, drugs with multidirectional effects are used. Bioparox has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also has a pronounced activity against many pathogens, both bacterial and viral. Imudon received a significant distribution in severe forms of pharyngitis. Its action is directed against the pathogenic agents that are most often involved in the development of pharyngitis.
Acute laryngitis is usually characterized by a sore throat and a temperature of 38 degrees. Since the inflammatory process affects the vocal cords, a change in voice is typical for the disease. It becomes rough, hoarse, and in some cases soundless. Attempts to reproduce sound are accompanied by an increase in sore throat, and therefore, patients spend most of their time in silence.
At the onset of the disease, the cough is dry. Over time, it becomes more humid, then regresses.
The duration of acute laryngitis and concomitant perspiration is approximately 10 days.
 The disease also has a chronic form. Exacerbation may be due to the action of adverse factors, including overstrain of the vocal cords. In this case, there is a local lesion of the larynx. The leading symptom is a change in the patient's voice. The phenomena of intoxication are not expressed. There may be a sore throat and a temperature of 37 degrees.
The disease also has a chronic form. Exacerbation may be due to the action of adverse factors, including overstrain of the vocal cords. In this case, there is a local lesion of the larynx. The leading symptom is a change in the patient's voice. The phenomena of intoxication are not expressed. There may be a sore throat and a temperature of 37 degrees.
The main factor contributing to the normalization of the situation is to provide rest to the organ, that is, the vocal cords. Patients are advised to spend as much time as possible in silence.
In addition, it is of great importance to provide gentle nutrition to such patients. It is recommended to avoid eating foods and foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Drinks consumed should be of moderate temperature.
From drugs of local action, agents with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory action are used. It is also shown carrying out local procedures, gargling, inhalations, applications of mustard plasters. With the development of the hypertrophic form of chronic laryngitis, epithelial growths form on the vocal cords, which determine the clinical picture, sore throat and hoarseness. In severe cases, the main method of treatment is a surgical operation to remove these formations.
Allergy
Low-grade fever and sore throat can be a sign of allergies. In this case, it is necessary to establish a connection between the effect of a pathogenic substance and the development of clinical symptoms. The defeat of the upper respiratory tract is most often the result of allergies to pollen, down and animal hair, strong odors.
By removing the hazardous substance, the patient will feel a significant improvement in his condition. In the event that it is not possible to clarify the allergen, the main method of treatment is the use of antihistamines, and in severe cases, corticosteroid drugs.Once an allergen is identified, specific immunotherapy is the most effective treatment.
Throat cancer and tuberculosis
Severe diseases, tuberculosis and tumor processes localized in the throat can also be accompanied by low-grade fever and sore throat.
 With the development of oncopathology, it is the larynx that is most often affected, which is characterized by a sore throat and a change in the timbre of the voice. Since the complaints are nonspecific, methods of objective examination, instrumental examinations, and laboratory diagnostics play an important role for diagnosis. It is possible to suspect this pathology due to the long course of the disease.
With the development of oncopathology, it is the larynx that is most often affected, which is characterized by a sore throat and a change in the timbre of the voice. Since the complaints are nonspecific, methods of objective examination, instrumental examinations, and laboratory diagnostics play an important role for diagnosis. It is possible to suspect this pathology due to the long course of the disease.
The presence of these clinical signs is a reason to consult an otolaryngologist and clarify the situation. Timely started treatment will prevent the protracted course of diseases, prevent serious complications.