Sanitation of the glands is a therapeutic and prophylactic procedure designed to cleanse lymphadenoid tissues from purulent exudate and pathological flora. Cleansing soft tissues from detritus and pathogens accelerates the regeneration of the ciliated epithelium, which has a positive effect on tissue reactivity and, accordingly, local immunity.
 The palatine tonsils are washed with antiseptic solutions, which include antibacterial components.
The palatine tonsils are washed with antiseptic solutions, which include antibacterial components.
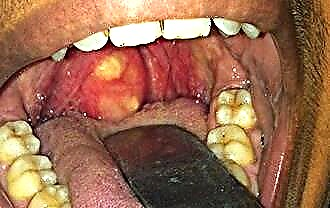
The tonsils are paired organs that perform protective and hematopoietic functions, which prevents the development of pathogens in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx. Getting into the lacunae of the tonsils, pathogenic bacteria and viruses are destroyed by neutrophils and T-lymphocytes in the process of phagocytosis. But in the case of a decrease in the body's resistance, the pathogenic flora is localized in the tissues, which can lead to the chronicization of pathological processes.
Sanitation - what is it?
Sanitation of palatine tonsils is the process of cleansing lymphadenoid formations from pathological secretions. Septic inflammation of the ENT organs leads to tissue edema, as a result of which the drainage of lacunae is impaired. Over time, detritus and purulent masses accumulate in them, which lead to disruption of the basic functions of the tonsils. If the foci of inflammation in the glands are not eliminated in time, this will contribute to the generalization of pathological processes and the occurrence of complications.
Washing the oropharynx and palatine tonsils at the stage of acute tissue inflammation contributes to the destruction of most pathogens and, accordingly, the regression of inflammation. Direct indications for the procedure are:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- hypertrophic tonsillitis;
- deformation of crypts (lacunae);
- diffuse inflammation in the oropharynx.
Important! Purulent inflammation in the glands leads to tissue destruction and the appearance of a paratonsillar abscess.
Sanitation of tonsils
Self-cleansing of the tonsils can be carried out only on the recommendation of a specialist, subject to the prescribed rules. Purulent plugs (tonsilloliths) in crypts are not easy to remove due to their high density, which is due to the presence of calcium salts in the pathological masses. To soften them, the outer surface of the lymphoid tissues from time to time needs to be treated with "Lugol" or a gel antiseptic.
 How to properly handle tonsils?
How to properly handle tonsils?
- gargle with saline;
- soak a cotton swab in an antiseptic solution;
- treat the inflamed gaps;
- apply an antiseptic spray to the mucous membrane of the oropharynx.
During the debridement of the tonsils, you need to change at least 4-5 sticks to prevent the spread of infection in the oral cavity.
Instead of a cotton swab, you can use sterile gauze wrapped around your finger to cleanse your tonsils. It is undesirable to press on the tissues during the cleansing of the tonsils, as this can lead to mechanical damage to the tonsils and aggravate the state of health.
Syringing
Syringe - washing of lymphoid tissues under high pressure with antiseptic solutions. The purpose of the procedure is to cleanse the lacunae from purulent plugs and pathogenic flora. To clear the tonsils, you need to take a regular or laboratory 20 ml syringe with a rounded thick needle. As an antiseptic solution, it is more advisable to use a liquid that is neutral in terms of pH and has pronounced bactericidal and antiphlogistic properties.
To prevent aspiration of fluid, flushing is performed while holding the breath while exhaling.
During the debridement of the oropharynx, the solution is injected under high pressure through a narrow hole in the needle. Systematic injection of tonsils helps to eliminate purulent plugs in lymphoid tissues, which accelerates the process of recovery or the onset of long-term remission. Reusable syringes are disinfected with antiseptics before use: Chlorhexidine, Betadine, Azulan, Benzamycin, etc.
Specialist recommendations
To achieve the desired therapeutic results, sanitizing procedures must be performed at least 3-4 times a day for at least 10 days. Regular cleansing of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx from the pathogenic flora not only accelerates the healing process, but prevents the spread of foci of inflammation. Unlike systemic antibiotics, local treatment of ENT pathologies rarely causes adverse reactions.
How to flush tonsils without assistance?
 draw an antiseptic solution into a syringe;
draw an antiseptic solution into a syringe;- direct the nozzle of the syringe to the purulent plug;
- holding your breath, sharply press your finger on the syringe plunger;
- spit the solution out and repeat the rinsing.
Some patients are not able to independently carry out sanitizing procedures due to the occurrence of a gag reflex. In this case, rinsing can be replaced by resorption of antiseptic and anti-inflammatory tablets. As drugs can be used "Strepsils", "Septolete", "Faringosept", "Lizobakt", etc.
Drug overview
Self-rehabilitation of the tonsils should be performed only on the instructions of a doctor using the recommended drugs. The composition of the antiseptic should include components that have anti-edematous, antiphlogistic and antimicrobial effects. The presence of tonsillolitis in the gaps in 98% of cases indicates the development of bacterial flora in the foci of inflammation, which can be eliminated only with the help of antibiotics.
It should be understood that local treatment of chronic inflammation of the ENT organs cannot replace systemic therapy. To stop pathological processes throughout the body, drugs of etiotropic action should be used, i.e. antibiotics. The following antiseptic solutions will help to eliminate the symptoms of an infectious disease:
- "Geksoral" is an antiseptic of hemostatic, analgesic and disinfecting action, which is used to sanitize the mucous membrane of the throat with the development of tonsillitis, stomatitis, pharyngitis and other septic inflammations in the oral cavity;
- "Furacilin" - a solution of antimicrobial action, which is used to eliminate purulent-inflammatory reactions in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx;
- Miramistin is an antiseptic with antiflogistic, analgesic and enveloping effect; used in the treatment of acute tonsillitis, gingivitis, pharyngitis and other ENT pathologies;
- "Chlorhexidine" is a bactericidal and antiseptic solution that has a pronounced fungicidal and anti-edema effect; used to disinfect the mucous membrane of the throat and treat fungal infections;
- "Chlorophyllipt" is an antibacterial, wound-healing and anti-inflammatory drug that is used to treat trophic ulcers and purulent inflammation in the throat mucosa.

The regularity of the procedure is the main rule that must be observed during the local treatment of inflammation in the tonsils. Only in the case of creating a high concentration of drugs in the lacunae of lymphoid tissues can regression of pathological processes be achieved. Even with a visual decrease in the hyperemia of the tonsils, sanitation should be continued for 4-5 days in order to prevent recurrence of inflammation.

 draw an antiseptic solution into a syringe;
draw an antiseptic solution into a syringe;