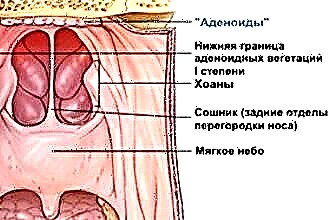
Adenoids - hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, which leads to impaired nasal breathing and decreased hearing acuity. Adenoid vegetation results from hyperplasia of lymphoid tissues.
 Periodic inflammation of the overgrown tonsils provokes frequent relapses of respiratory diseases, which can lead to the development of infectious complications.
Periodic inflammation of the overgrown tonsils provokes frequent relapses of respiratory diseases, which can lead to the development of infectious complications.
Laser removal of adenoids in children is a bloodless operation, during which hypertrophied tonsils are excised in whole or in part. The principle of operation of laser therapy is based on the ability of a monochromatic radiation flux to "evaporate" soft tissues, to accelerate lymph flow and blood circulation. In other words, laser reduction helps to reduce swelling and, accordingly, the volume of the pharyngeal tonsil, which leads to easier nasal breathing.
What are adenoids?
Adenoids are called pathological changes in the state of the lymphoid tissues, of which the palatine, tubal, lingual and pharyngeal tonsils are composed.
Hyperplasia is one of the key causes of dysfunction of the pharyngeal tonsil, which is involved in the formation of local and general immunity. A decrease in local immunity leads to the development of infectious diseases, which are often complicated by otitis media.
The pharyngeal tonsil is located in the fornix of the pharynx, so its increase leads to a narrowing of the lumen in the airways. Inflammatory processes in the lymphoid tissues cause swelling of the oropharyngeal mucosa, which provokes difficulty in nasal breathing. Typically, adenoid vegetation occurs in children aged 4 to 15 years. Untimely excision of a hypertrophied tonsil can cause deformation of the child's facial skull, which is associated with constant breathing through the mouth.
Indications for adenotomy
Adenotomy is a surgical operation involving partial or complete excision of the hyperplastic pharyngeal tonsil. In otolaryngology, there are more than 5 different ways to remove lymphoid formations, however, laser reduction is among the safest and least traumatic. Laser treatment of adenoids in children is carried out only if absolutely necessary, since the tonsils play an important role in the formation of immune defense.
Direct indications for adenotomy are:
- frequent relapses of infectious diseases, complicated by otitis media;
- regular bouts of snoring, accompanied by a holding of breath during sleep;
- insufficient physical and mental development caused by hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- adenoid vegetations almost completely block the airways;
 deviations in the development of the facial skull associated with the constant opening of the mouth.
deviations in the development of the facial skull associated with the constant opening of the mouth.
Untimely removal of a hypertrophied tonsil can cause enuresis, asthma, seizures and neuroses.
At the initial stage of the development of pathology, conservative treatment can be dispensed with, involving the use of anti-inflammatory and decongestants, physiotherapy, etc. And only in case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment, the doctor can prescribe a surgical removal of the adenoids.
Complications
Removal of adenoid vegetations can lead to a slight decrease in the body's resistance, but it is precisely inaction that leads to disastrous consequences much more often. Adenoiditis increases the risk of developing infectious pathologies, which does not exclude the possibility of chronicizing pathological processes.
Constant inflammation in the ENT organs provokes intoxication and deterioration of the child's well-being, which, ultimately, can lead to the development of systemic diseases.
Untimely performance of adenotomy is fraught with the following complications:
- decreased immunity - stagnation in the airways, caused by the proliferation of lymphoid tissues, create all conditions for the reproduction of pathogens and the development of otitis media, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc.;
- hearing impairment - hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil provokes a decrease in the elasticity of the tympanic membrane, which affects the quality of the conduction of sound signals and, accordingly, hearing acuity;
- allergy - general intoxication leads to sensitization and increased sensitivity of the body to the effects of surrounding allergens (dust, wool, food, medicines);
- deformation of the lower jaw - constant opening of the mouth caused by nasal congestion, leads to a violation of the uniform growth of bones, which contributes to the formation of an "elongated" lower jaw according to the adenoid type.
It should be understood that difficulty in nasal breathing affects the quality of sleep and rest of the child. It is during sleep that the body produces hormones that contribute to the normal development of the skeleton.
If the child's adenoids are not removed in time, in the future this may affect his mental and physical development.
Types of laser therapy
 If a child complains of persistent nasal congestion, headaches and chronic rhinitis for a long time, this may indicate the development of adenoiditis. Timely excision of hypertrophied lymphoid tissues makes breathing easier and prevents the development of respiratory diseases. Laser removal cannot be called a surgical operation - this is due to the absence of incisions, bleeding. Adenotomy is carried out in courses of 6 to 15 sessions, during which pathological tissues are destroyed, which helps to reduce the size of the amygdala.
If a child complains of persistent nasal congestion, headaches and chronic rhinitis for a long time, this may indicate the development of adenoiditis. Timely excision of hypertrophied lymphoid tissues makes breathing easier and prevents the development of respiratory diseases. Laser removal cannot be called a surgical operation - this is due to the absence of incisions, bleeding. Adenotomy is carried out in courses of 6 to 15 sessions, during which pathological tissues are destroyed, which helps to reduce the size of the amygdala.
During therapy, the tonsils are exposed to a powerful stream of healing, which "evaporates" the tissue. High-precision bloodless surgeries can reduce the size of the adenoids and, consequently, facilitate nasal breathing. The choice of a specific method of laser therapy is determined by the size of the adenoid vegetations and the state of the tissues:
- carbon dioxide laser with slight hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil; vaporization of small growths allows you to "evaporate" excess moisture from the amygdala and normalize its functioning;
- laser coagulation leads to necrotization and detachment of lymphoid tissues; used in the therapy of extensive adenoid vegetations;
- interstitial coagulation is aimed at “evaporation” of the submucosal membranes without damaging the outer surface of the adenoids;
- the classic operation in combination with laser destruction involves the removal of the tonsil with a scalpel, after which the remaining tissue is "evaporated" by laser radiation.
The advantage of laser reduction is the virtual absence of postoperative complications.
During therapy, small-sized wound surfaces are formed, which prevents the further occurrence of septic inflammation.
Features of laser adenotomy
How is adenoiditis laser treated? Gentle therapy is used to remove adenoids at any stage of the development of pathology. However, the procedure involves passing preliminary training, which consists in passing the appropriate tests:
- CT of the nasopharynx;
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
 X-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
Operations should not be performed in the presence of acute inflammatory processes in the ENT organs, which is associated with the possibility of infection spreading to the operated tissues.
In most cases, surgery is performed under local anesthesia. A few hours before the procedure, the patient should not eat or drink.How is laser treatment carried out?
- sanitation of the nasal passages and oropharynx is carried out;
- the tissues of the hypertrophied tonsil are anesthetized;
- adenoids are irradiated with a laser in several approaches.
It should be understood that after 3-4 laser reduction sessions the child's nasal breathing is normalized. However, premature discontinuation of therapy may lead to a repeated increase in the size of the pharyngeal tonsil. To prevent complications, you need to undergo a full course of therapy recommended by a specialist.
Benefits of the procedure
Laser therapy is one of the most gentle, non-contact methods of removing adenoid vegetations in children. A high-precision effect on lymphadenoid tissues with a powerful flux of radiation minimizes the likelihood of bleeding and, accordingly, septic inflammation. If unbearable pain and swelling occur during the classical excision of the pharyngeal tonsil, then after laser reduction there are practically no postoperative side effects.
The obvious advantages of laser adenotomy include:
- short rehabilitation period;
- absence of blood loss during therapy;
- low probability of recurrence of pathology;
- no delayed bleeding;
- absence of pain syndrome and, as a result, postoperative stress;
- preservation of the main functions of the pharyngeal tonsil in the event of its partial excision;
- the possibility of performing an operation under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis.
The effectiveness of therapy largely depends on the qualifications of a specialist and the accuracy of performing surgical procedures.
In the course of treatment, the doctor can adjust the intensity of the laser radiation and the depth of "evaporation" of soft tissues.
 Too intense flow of coherent laser radiation can lead to damage to the deep layers of the mucous membrane, which is fraught with an increase in the rehabilitation period.
Too intense flow of coherent laser radiation can lead to damage to the deep layers of the mucous membrane, which is fraught with an increase in the rehabilitation period.
To make sure that there are no lymphoid accumulations on the mucosal surface, the doctor should conduct an endoscopic examination of the tissues. Visualization of the oropharyngeal mucosa surface using optical equipment makes it possible to determine the presence of adenoid vegetations at the site of the pharyngeal tonsil. Incomplete removal of lymphadenoid formations can lead to re-proliferation of the adenoids and impaired nasal breathing.
Treatment after adenotomy
Laser removal of adenoids in children reduces the likelihood of recurrence of inflammation and hyperplasia of lymphoid tissues by up to 15%. However, the risk of re-growth of adenoid vegetation still remains. If during the operation the specialist left at least 2-3 mm of lymphoid tissue, this can provoke the re-development of the pathology.
After undergoing laser reduction, there are practically no side effects, which is associated with the absence of blood loss and the formation of minor wound surfaces. To prevent a deterioration in well-being, the child must adhere to the following rules for 1-2 weeks:
- eat only liquid food that does not injure the mucous membrane of the oropharynx; refrain from sports, going to the pool and social events;
- at least 2-3 times a day, instill drops with a vasoconstrictor effect into the nose;
- avoid contact with allergens: dust, pollen, animal hair, etc .;
- ventilate the room at least 1-2 times a day and periodically do wet cleaning.
During rehabilitation, it is advisable to exclude contact with a large number of people. The development of infectious diseases can cause an aggravation of the state of health and the formation of abscesses in the area of the operated tissues.

 deviations in the development of the facial skull associated with the constant opening of the mouth.
deviations in the development of the facial skull associated with the constant opening of the mouth. X-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses.