Extracapsular removal of the palatine tonsils (tonsillectomy) is a surgical procedure during which the doctor excises the lymphoid formations along with the peri-mucous tissue. The operation allows you to eliminate not only the organs affected by inflammation, but also paratonsillar foci together with abscesses.
 Not so long ago, tonsillectomy was used as a prophylactic measure to prevent severe post-infectious complications in children.
Not so long ago, tonsillectomy was used as a prophylactic measure to prevent severe post-infectious complications in children.
When is it necessary to remove tonsils? The tonsils are a protective barrier that prevents pathogens from entering the airways. In the lymphoid tissue, immune cells are synthesized, which protect the body from the pathogenic flora. For this reason, removal of the tonsils is performed only in the presence of serious ENT diseases and the risk of developing systemic complications.
A little about anatomy
Several years ago, the removal of the tonsils was considered a preventive measure preventing the development of complications after angina, pharyngitis, chronic rhinitis, etc. However, modern experts are confident that tonsillectomy should be performed only if there are serious indications. In the course of laboratory studies, it turned out that the tonsils are involved in the formation of immune defense, so their removal can negatively affect the body's resistance.
Tonsils (tonsils) are paired organs that consist of lymphoid tissue and perform hematopoietic and protective functions. Rollers penetrated by follicles and crypts (lacunae) are located deep in the throat behind the palatine arches. They are involved in the production of macrophages, which are capable of absorbing and neutralizing pathogens (protozoa, microbes, fungi, viruses).
Removing the tonsils leads to a decrease in general and local immunity, which increases the risk of developing infectious diseases. Experts say that even a half-dead gland synthesizes a large amount of immunoglobulin, which is involved in the formation of an immune response. For this reason, tonsillectomy is recommended only in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment or systemic complications.
Indications and contraindications
When do you need to remove tonsils? Surgical intervention is indicated in the event of toxic-allergic and infectious phenomena. The increasing intoxication of the body creates additional stress on the kidneys, liver, heart and joints, which can cause systemic complications. If the pathological processes in the palatine tonsils cannot be eliminated with medicines and physiotherapeutic measures, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
What are the main indications for tonsil removal?
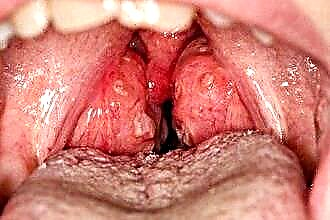 recurrent tonsillitis - chronic inflammation of lymphoid tissues indicates the accumulation of pathogens in the ENT organs, which in the future can lead to the development of severe local (sinusitis, retropharyngeal abscess) and systemic (pyelonephritis, rheumatism) complications;
recurrent tonsillitis - chronic inflammation of lymphoid tissues indicates the accumulation of pathogens in the ENT organs, which in the future can lead to the development of severe local (sinusitis, retropharyngeal abscess) and systemic (pyelonephritis, rheumatism) complications;- severe chronic tonsillitis - the presence of an acute allergic reaction to the metabolites of pathogens leads to an aggravation of the state of health: hyperthermia, fever, swelling of the mucous throat, etc., which is fraught with obstruction of the airways;
- a problem with breathing - swelling of the ciliated epithelium and hypertrophy of the glands provides for respiratory failure (apnea) and, as a result, the occurrence of malfunctions in the cardiovascular system;
- purulent processes - the formation of purulent masses inside the lymphoid tissues leads to their melting and generalization of inflammatory processes.
Failure to cut out tonsils in adults in time can be fatal. It should be noted that the reasons for the removal of the palatine tonsils are not limited to the list presented. Only a qualified specialist can determine the best way to solve the problem after passing the necessary tests. Sometimes, even in the presence of direct indications, it is impossible to carry out surgical treatment, which is associated with the risk of deteriorating the patient's health. It is not recommended to resort to tonsillectomy for:
- leukemia;
- hemophilia;
- diabetes mellitus;
- mental illness;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- pathological structure of blood vessels;
- chronic diseases at the stage of exacerbation.
Operation of patients in the presence of serious contraindications is fraught with serious blood loss, myocardial infarction, generalization of infectious processes, etc.
Tonsillectomy in children
Why are the tonsils cut out and removed - in what cases is it done? The need for an operation arises exclusively in the presence of infectious ENT diseases and hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils. Untimely removal of the affected organs affects not only the quality of life of the child, but also his appearance. The most common consequences of delayed removal of tonsils in children include:
- enuresis;
- snoring during sleep;
- nasal congestion;
- chronic rhinitis;
- poor appetite;
- sniffling during nasal breathing;
- change in the shape of the jaw.
Important! Prolonged asphyxia against the background of airway obstruction can cause the development of pulmonary hypertension.
With an increase in the size of the palatine tonsils, the patency of the airways is impaired. Regular shortage of air forces the baby to breathe through the open mouth, which can lead to deformation of the lower jaw. Poor sleep interferes with the production of necessary hormones, as a result of which there is a delay in growth and mental development.
Life-threatening complications
Why are tonsils cut out? Surgery may be required if complications develop that threaten the patient's life. Shortness of breath, provoked by hypertrophy or swelling of lymphoid formations, can cause sudden suffocation. If you experience unbearable sore throat and difficulty breathing through your mouth, you should immediately call an ambulance.
As a rule, severe complications in adults result from the development of chronic or hypertrophic tonsillitis. Intoxication of the body leads to malfunctions of vital organs and systems, as a result of which the following pathologies may occur:
- rheumatism;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- paratonsillar abscess;
- meningitis;
- mediastinitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis.
The onset of the above diseases is preceded by purulent inflammation in the tonsils, which leads to tissue melting and generalization of pathological processes. Therefore, if you experience severe sore throat, febrile fever and lymphadenitis, you must call a doctor.
Tonsillectomy: pros and cons
 In what cases are tonsils removed? Extracapsular excision of lymphoid formations inevitably leads to a decrease in immunity, but prevents the development of severe systemic complications. Tonsillectomy in adults is more often performed due to the development of chronic tonsillitis, which does not respond to drug treatment.
In what cases are tonsils removed? Extracapsular excision of lymphoid formations inevitably leads to a decrease in immunity, but prevents the development of severe systemic complications. Tonsillectomy in adults is more often performed due to the development of chronic tonsillitis, which does not respond to drug treatment.
Surgery is an indispensable step in resolving life-threatening situations for the patient. In all other cases, the decision to undergo tonsillectomy should be approached taking into account the following nuances:
Positive:
- absolute removal of the source of infection;
- elimination of chronic tonsillitis;
- no systemic complications
... Negative:
- decrease in the reactivity of the body;
- cicatricial changes in the throat mucosa;
- rapid development of ENT diseases in the event of their penetration into the oropharynx.
Removal of tonsils in adults is carried out only in extreme cases with direct indications.
If the patient is prone to allergies, which can lead to airway obstruction, or suffers an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis more often 4-5 times a year, the otolaryngologist may offer him surgical treatment.

 recurrent tonsillitis - chronic inflammation of lymphoid tissues indicates the accumulation of pathogens in the ENT organs, which in the future can lead to the development of severe local (sinusitis, retropharyngeal abscess) and systemic (pyelonephritis, rheumatism) complications;
recurrent tonsillitis - chronic inflammation of lymphoid tissues indicates the accumulation of pathogens in the ENT organs, which in the future can lead to the development of severe local (sinusitis, retropharyngeal abscess) and systemic (pyelonephritis, rheumatism) complications;