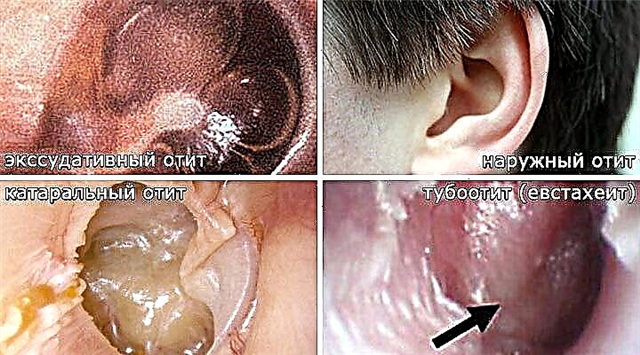
Otitis media is an ear pathology that develops as a result of inflammation of the main parts of the hearing organ. The disease can be of infectious or non-infectious origin, but in most cases it occurs against the background of a general infection of the body. Late therapy for otitis media affects the health of not only the woman, but also the unborn child.
During the period of gestation, a hormonal imbalance is observed in the female body, which affects the functioning of the immune system. A decrease in reactivity contributes to the development of opportunistic microorganisms in the upper respiratory tract, from where they enter the ear through the Eustachian tube. Antibacterial drugs are often included in the conservative treatment regimen for pathologies, but many of them cannot be taken during pregnancy due to the toxicity of the active ingredients.
Etiology

According to practical observations, the risk of developing ear pathologies in pregnant women increases at least 3 times. This is due to physiological changes in the body resulting from the development of the fetus. Excessive release of the hormone progesterone contributes to fluid retention in the body, as a result of which the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract swell. An increase in blood pressure associated with an increase in the amount of blood in the female body affects the tissue condition indirectly.
Swelling of the mucous epithelium lining the inner surface of the Eustachian tube leads to its narrowing. Subsequently, its ventilation function is disrupted, which leads to the accumulation of exudate in the ear cavity. With the development of a general infection, serous exudate turns into a purulent mass, which becomes the cause of purulent otitis media.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman should limit communication with others. During this period, taking medications can negatively affect the health of the unborn child.
It should be noted that the reactivity of the female body during gestation decreases, which is associated with the following reasons:
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- hormonal imbalance;
- common infections;
- intoxication of the body.
Timely diagnosis and therapy of ear pathology leads to rapid relief of the main manifestations of otitis media. However, experts warn that advanced forms of ENT disease are difficult to treat, due to the limited list of medications that can be taken during pregnancy.
Symptomatic picture
Otitis media during pregnancy is often almost asymptomatic, due to the reduced resistance of the body. For this reason, it is not easy to diagnose the disease at the initial stages of its development. The main symptoms of the onset of ENT disease include:
- ear congestion;
- aching pain in the ear;
- hearing impairment;
- serous or purulent discharge from the ear;
- general malaise and muscle weakness.
Infectious otitis media is a serious threat to the fetus. Some types of pathogens are able to penetrate the placental barrier and provoke hypoxia.
With the development of eustachitis, women complain of nasal congestion and a sensation of fluid transfusion inside the ear cavity. Such symptomatology is a direct indication for seeking help from an otolaryngologist.
Influence on the fetus
The development of otitis media during pregnancy does not affect the fetus, but only in the absence of severe complications. In about 35% of cases, the disease is complicated by purulent inflammation, which leads to the appearance of mastoiditis, myringitis, meningitis, sepsis, etc. Against the background of general intoxication of the body, the risk of developing pathologies in a child increases.
Experts say that the danger lies more in taking medications that help stop the symptoms of otitis media. This is especially true for pharmacotherapy in the first trimester of pregnancy. The active development of the vital organs and systems of the fetus occurs precisely during this period. The presence in the blood of toxic substances that are present in pharmacy products can cause pathologies.
By the beginning of the second trimester, the placenta surrounding the fetus is fully formed. It protects the developing organism from the effects of pathogens, which prevents it from becoming infected. In addition, the neural tube and most of the vital organs are already formed. This allows specialists to use a wider range of medications for the treatment of ear pathology.
The placental barrier prevents the penetration of pathogens, but not the active substances of medications. For this reason, only a specialist can deal with the selection of suitable pharmacotherapy agents.

Approved drugs
To eliminate local manifestations of otitis media, anti-edematous, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. The active ingredients in their composition are toxic and therefore cannot be used to treat women during pregnancy. For this reason, the following types of drugs can be included in the treatment regimen for pregnant women:
- "Otipax" - ear drops of combined action with analgesic, decongestant and antiseptic effect;
- "Sofradex" is an anti-allergic drug that helps to eliminate edema, inflammation and itching. Oppresses the development of gram-positive microorganisms that provoke the onset of otitis media;
- "Candibiotic" is an antibiotic of analgesic and anesthetic action, which kills pathogenic microbes and some types of fungi;
- "Amoxicillin" is an antibacterial drug of the penicillin series, which relieves inflammation and allergic manifestations in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract;
- "Biseptol" is a bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent that eliminates purulent foci of inflammation in the ear;
- "Amoxiclav" is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, the components of which are active against most bacterial pathogens of ear pathology.
Important! Vasoconstrictor drops increase the tone of the uterus, which is fraught with miscarriage at an early stage of pregnancy and premature birth at the latter.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is one of the main components of the treatment of otitis media in pregnant women, contributing to the regression of inflammatory processes in the organ of hearing. Thanks to physiotherapeutic procedures, tissue trophism is significantly improved, which contributes to the epithelialization of lesions of the mucous membrane, auditory ossicles, ear membrane, etc. For the treatment of women during the period of gestation, the following can be used:
during the period of gestation, the following can be used:
- phototherapy - leads to the elimination of bacteria in the foci of inflammation due to irradiation of the affected tissues with UV rays;
- UHF therapy - affects the affected tissues with ultra-high frequency currents, which restore blood microcirculation. Stimulates the production of specific antibodies that help eliminate inflammatory processes;
- blowing according to Politzer - restores the patency of the Eustachian tube, which facilitates the outflow of serous contents from the tympanic cavity.
Important! Physiotherapy procedures can be used in the inactive phase of otitis media, characterized by the absence of acute inflammation in the organ of hearing.
Preventive measures
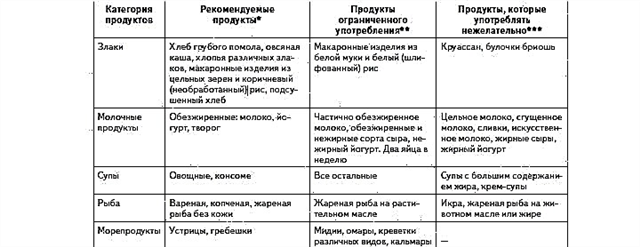
The treatment of ear pathology is complicated by the restrictions that are imposed on the list of drugs suitable for stopping the manifestations of the disease.In 90% of cases, otitis media in pregnant women occurs as a complication of an infectious disease. Therefore, strengthening the immune system plays a key role in the prevention of the disease. To increase the body's reactivity, experts recommend:
- avoid hypothermia;
- consume vitamins;
- timely treat acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections;
- ventilate the room daily;
- include in the diet foods rich in vitamins.
If you have the slightest signs of illness, you should immediately consult a doctor.