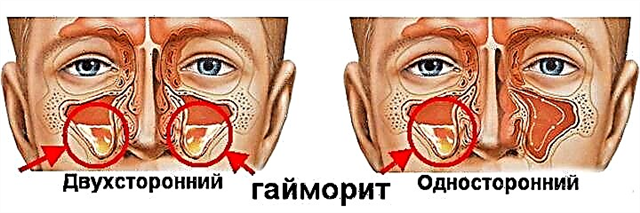
Changes in the normal rhythm of the heart muscle negatively affect the functioning of the body. Irregular (arrhythmic) or too frequent contractions lead to various complications, especially if they occur against the background of another pathology. But not everyone understands the difference between these phenomena. Let's see how arrhythmia differs from tachycardia.
What do these terms mean
Arrhythmia is a disorder of the cardiac conduction system with impaired formation and conduction of electrical impulses. As a result, irregular contractions of the myocardium occur. Tachycardia is characterized by a uniform frequency, but the heart rate increases, reaching 90 or more beats per minute. Normally, this reaction of the body can occur in response to stress or physical overload.
Depending on the place of origin of the impulse with arrhythmia or tachycardia, they can be:
- sinus;
- atrial;
- ventricular;
- atrioventricular.
Any deviation from the normal frequency and uniformity of heart contractions is considered an arrhythmia. This broad concept includes:
- increase or decrease, as well as uneven generation of an impulse from the main source (sinus brady-, tachycardia and arrhythmia);
- extrasystole;
- flutter, atrial or ventricular fibrillation;
- ectopic rhythms;
- conduction disturbances (asystole, blockade, premature ventricular excitation);
- sick sinus syndrome.
The concept of arrhythmia is broader and includes all types of cardiac arrhythmias, including tachycardia.
Difference in origin
Arrhythmia and tachycardia have a similar origin, so the reasons why they occur are usually the same. Physiological disturbance of the rhythm occurs in the following cases:
- strong emotional upheaval;
- hard physical labor;
- playing sports;
- eating disorder;
- lack of sleep;
- use of drinks with caffeine;
- lack of trace elements;
- sudden changes in ambient temperature.
All pathological causes of arrhythmia or increased frequency of myocardial contractions can be divided into cardiac and extracardiac. In the first case, the main disease is:
- Inflammatory processes (myocarditis, pericarditis).
- Ischemic disease (angina pectoris).
- The appearance of scars as a result of postinfarction or cardiomyopathic sclerosis.
- Valve defects.
- Chest trauma.
Deviation from the normal sinus rhythm can also occur in the case of other diseases or conditions:
- Excessive intake of cardiac glycosides, diuretics and antiarrhythmics.
- Diseases of the endocrine system with increased production of adrenaline, thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- Poisoning with heavy metals and other toxic substances.
- Severe infections with severe fever and intoxication.
- Excess in the blood of harmful substances in renal or hepatic insufficiency.
- Consuming drugs, alcohol, smoking.
In some cases, the violation of the rhythm of contractions occurs for an unknown reason, then they are considered idiopathic.
The main difference between arrhythmias is the unevenness of the intervals between contractions of the heart muscle. With tachycardia, the intervals are the same, but their frequency reaches 90 or more beats / min.
Signs and complaints
The subjective sensations of the patient with the development of both pathologies usually do not differ, he presents the following complaints:
- shortness of breath, shortness of breath;
- fatigue, darkening of the eyes, dizziness;
- pain behind the sternum on the left.
With arrhythmias, some patients experience individual beats or “freezing” of the heart. Tachycardia is perceived as strong and frequent tremors. In many cases, deviations occur without obvious symptoms and can only be determined with additional research methods.
Signs of violations are usually:
- uneven and / or rapid pulse;
- blanching of the skin;
- blue nasolabial triangle;
- decrease or increase in pressure.
The most objective way to detect pathology is ECG. In the case when a person's rhythm is disturbed episodically, in order to fix an attack, Holter monitoring is used.
Tachycardia from the sinus node on the cardiogram looks like this:
You can read a detailed description of the signs and symptoms of sinus tachycardia, as well as get specialist advice for this disorder, here.
Action tactics: what is the difference
If there are abnormalities in the physiological nature of the heart, treatment is usually not required. It is enough to eliminate the cause of their appearance, and everything returns to normal. It is another matter if the disease is the etiological factor. In this case, it is necessary to carry out a full-fledged treatment, the purpose of which will be the complete elimination of the disease or the transfer of pathology to a state of stable remission.
We remove provoking factors
To normalize the rhythm, it is recommended to remove the factors that contribute to the appearance of tachycardia or arrhythmia:
- Review nutrition. Eat often in small portions, exclude spicy, salty, caffeinated drinks from the diet.
- Try to avoid physical and psycho-emotional overload.
- Observe the mode of work and rest.
- Walk at an average pace and breathe clean air.
- Stop drinking alcohol and quit smoking.
Paroxysmal tachycardia can be stopped by exposure to the vagus nerve. For this, pressure is used on the eyeballs, massage of the carotid sinus zone.
You can get more detailed information about what tachycardia is, what its types are, and also find out ways to eliminate pathology here.
We use medications
Medication methods consist in the use of the following drugs:
- sedatives (motherwort, Valokordin);
- beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol);
- calcium antagonists (Amlodipine).
Herbal decoctions can be added to the general therapy. To improve cardiac activity, chamomile, valerian, hawthorn are used. But they should not be used as the primary treatment for an attack.
A detailed description of tablets and other medicines, as well as the features of their use for tachycardia, can be seen by clicking here.
Surgical treatment of severe pathology
Severe forms of rhythm and conduction disturbances require the use of surgical methods of treatment. Depending on the reason, the specialist recommends the following radical methods:
- radiofrequency ablation;
- installation of an artificial pacemaker;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- valve restoration;
- bypass surgery for impaired blood flow.
The prognosis for arrhythmia depends on the etiological factor of its appearance. But in general, in comparison with tachycardia, it is more severe and often leads to various complications and even death.
If you want to know everything about tachycardia, we advise you to watch the video below at the link. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and signs that it is time to see a doctor - about all this in 7 minutes. Happy viewing!