Normally, the heart muscle is forced to contract by an impulse from the sinus node. But in case of myocardial damage as a result of ischemia or inflammation, the lower parts of the conducting system begin to set the frequency. At the same time, the sequence of propagation of excitement also changes. This is how an ectopic heart rhythm arises, which I propose to talk about in more detail.
What is Atrial Rhythm
Myocardial contractions normally occur regularly and do not depend on consciousness: even when the brain dies, the heart still works for some time. This process is very important in maintaining life. Failures are due to serious damage to the structure of cells or metabolic disorders.
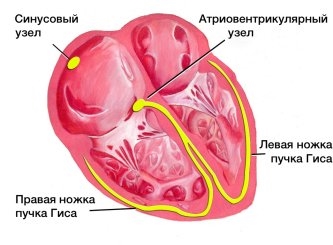
If the main pacemaker is affected, its function is transferred to the underlying departments located in the atria, atrioventricular zone, bundle branch. In this case, the normal impulse becomes too weak or absent. If the generation of myocardial contractions comes from the atria, then in this case an atrial ectopic rhythm is recorded on the ECG.
Reasons for appearance and types
The main causes of the atrial, as well as any ectopic (displaced) rhythm, are:
- Changes in the structure of the myocardium - as a result of inflammation, ischemia, cardiosclerosis, hypertrophy or dystrophy.
- Valvular defects and other congenital anomalies.
- Violation of electrolyte and water levels. This happens with a sharp loss of fluid (vomiting, diarrhea, taking diuretics).
- Metabolic changes in diseases of the endocrine organs.
- Internal or external intoxication (impaired renal and liver function, smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction, intake of heavy metal salts, etc.).
- Overdose of cardiac glycosides.
- Traumatic injury to the chest.
All these reasons are characteristic of ectopic atrial impulses in an adult. In children and adolescents, they most often occur against the background of a violation of autonomic innervation.
Depending on the frequency of contractions, slow and accelerated atrial rhythms are distinguished. The lower the pacemaker is in the conducting system, the less frequent the pulse - up to 45-60 beats per minute. An increase to 130 or more occurs when, under the influence of inflammation or other pathology, hyperexcitation and excessive activity of the ectopic focus develops.
The displaced rhythm can be permanent or temporary. By localization, it can be left or right atrial, but such a division has no particular clinical significance and does not affect the regimen of the prescribed treatment.
Ectopic impulses can vary in frequency, regularity, and strength. But in the absence of a normal sinus rhythm, they allow the heart to continue its work.
What is the danger
Active generation of heart rhythm from an atypical focus is most often a symptom of pathology of the myocardium or other organs and systems. I recommend that you definitely undergo additional examinations and identify the cause of the appearance of ectopia.
Arrhythmias and hemodynamic disturbances, especially with a high frequency of contractions and concomitant diseases, can lead to the formation of blood clots, angina attacks, the development of a heart attack, flickering, flutter and the gradual formation of heart failure.
Expert advice
In case of rhythm disturbance and a feeling of interruptions in the heart, you should:
- calm down, take a sedative;
- remember what preceded the onset of the attack;
- stop taking alcohol, tobacco, strong tea or coffee;
- if discomfort persists, consult a therapist;
- make a cardiogram, get tested, undergo other necessary examinations.
Possible Symptoms
Ectopic left and right atrial rhythms appear in the same way. A person often does not notice the changes, and the symptoms of the underlying disease, which caused the deviation, come first. The only way to detect a violation is to take an electrocardiogram.
In other cases, the patient makes the following complaints:
- a feeling of uneven heart rate and interruptions;
- sinking of the heart;
- dyspnea;
- weakness, decreased ability to work;
- pain or discomfort in the area of the heart.
In the presence of temporary pop-up atrial complexes, symptoms usually either do not appear or are transient. According to my observations, they do not pose a particular danger and do not affect hemodynamics.
With prolonged seizures, the patient's condition worsens, in addition to the main complaints, there are signs of circulatory disorders and cardialgia of ischemic origin.
Sometimes an ectopic rhythm occurs due to dysfunction of the autonomic system:
- If the influence of the sympathetic department prevails, the person's pulse quickens, the skin becomes cool and pale, hypertension is observed. This condition is characterized by chills, headache, and often there is a panic attack.
- When vagotonia (parasympathetic) comes first, the frequency of contractions decreases, sweat is released, pressure decreases, and digestion is disturbed.
How to make a diagnosis
At the moment, the only objective way to identify ectopic atrial rhythm is ECG. In the case when the impulses are temporary and interspersed with full-fledged contractions of the myocardium, Holter monitoring is used for diagnosis.

An electrocardiogram will reveal not only a violation of the rhythm, but also indicate the localization of pathological impulses, according to the state of the P wave. For clarity, you can give a table from which you can see how different types of ectopia manifest themselves:
Localization in the atria | Leads | Signs (P wave) |
Left | Right pectorals (V1-2) | biphasic, the first part is domed, the second is pointed, positive |
Left chest (V5-6) | negative | |
Standard (I, II) | smoothed out | |
Right (photo 2) | I, II | positive |
II, III | negative | |
V1-6 and aVF | smoothed out | |
Lower atrial rhythm (Fig. 1) | I, III, aVF | negative |
Atrial rhythm in its pure form is not accompanied by a change in the electrical axis of the heart (EOS), it is also not characterized by the appearance of deformation of the ventricular complexes.

As additional research methods and to identify the cause, I usually recommend:
- General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine. Laboratory results show the presence of inflammatory processes, problems in the functioning of the kidneys, and electrolyte imbalance.
- EchoCG. Ultrasound examination of the myocardium will help detect dilatation of the heart, valvular insufficiency, and the presence of structural changes.
- In case of chest trauma, chest x-rays are taken.

Treatment
If a problem occurs in a healthy person under the influence of external factors, then it is transient and is eliminated when their influence ceases. In this case, no treatment is required. In the presence of a pathological condition, the main therapy should be aimed at eliminating the cause. For direct relief of the ectopic rhythm from the atria, the following are used:
- beta blockers for frequent contractions (Anaprilin);
- stimulants for bradycardia (Atropine);
- with a lack of potassium and magnesium, Panangin is used;
- sedatives for vegetative disorder (Motherwort, Persen);
- soothing herbal decoctions.
In severe disorders with a pronounced decrease in the frequency of contractions and a high probability of developing a heart attack and other acute conditions, the issue of setting an artificial pacemaker is resolved.
Lifestyle restrictions
To prevent rhythm disturbances and the occurrence of ectopic atrial complexes, heart disease should be treated in time and the autonomic nervous system should be restored. Following the usual rules will help improve the condition with existing deviations and prevent their development:
- Nutrition plays an important role. It must be balanced and complete. It is necessary to drink 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day, exclude animal fat from the menu, and consume as many vegetables and fruits as possible. It should be eaten in small portions 4-5 times a day.
- Eliminate the possibility of overwork and normalize sleep.
- Breathe fresh air, go hiking, walk in a public garden or park.
- Exercise daily, visit the gym. Swimming, dancing, yoga will be beneficial.
- To develop stress resistance in oneself, classes with a psychologist, meditation practices help.
- Do not abuse alcohol, quit smoking.
Case from practice
A 48-year-old patient complained of a feeling of shortness of breath and heart failure. Two months ago he was treated for myocarditis. When taking an ECG, a lower atrial ectopic rhythm and single ventricular extrasystoles were detected. It was recommended: a diet with restriction of salt and fatty foods, avoiding coffee and alcohol. He took Corvalol and Asparkam for a month. At the time of the attack, I used Anaprilin. After 30 days, he notes an improvement in his condition, shortness of breath and interruptions in the heart do not bother.