A minor anomaly in the development of the heart, or dysplastic cardiopathy, is a pathology that is encountered equally in childhood and adulthood. For a long time, it manifests itself as many diseases of the cardiovascular system. If the diagnosis is not made on time, then serious complications develop. The disease, if untreated, can disrupt the rhythm of the heart. This leads to oxygen starvation of all body tissues. The pathology is complicated more often by angina pectoris, arterial hypertension and heart failure.
What it is?
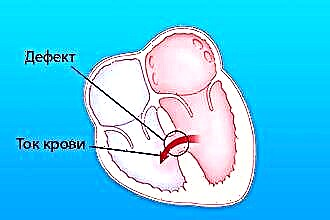
 The term "dysplastic cardiopathy" refers to a group of cardiac muscle disorders of non-inflammatory origin. Pathology is formed with insufficient metabolism in the myocardium. Cardiopathy is often diagnosed when there is a mitral valve defect or an extra chord (tendon) in the left ventricle.
The term "dysplastic cardiopathy" refers to a group of cardiac muscle disorders of non-inflammatory origin. Pathology is formed with insufficient metabolism in the myocardium. Cardiopathy is often diagnosed when there is a mitral valve defect or an extra chord (tendon) in the left ventricle.
The elastic fibers of the heart wall are gradually replaced by connective tissue that does not have this ability. The disease is accompanied by functional and structural changes in the myocardium.
Pathology of coronary arteries, valve cusps and arterial hypertension in the initial stage is not observed. Over time, with the weakening of the compensatory capabilities of the myocardium, complications join.
Characteristics of the disease
The main function of the heart muscle is rhythmic contraction, which ensures the expulsion of blood through the vessels and filling the cavities of the organ. This ability is provided by cardiomyocytes. Their continuous functioning supports the metabolism at the level necessary for work.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors, over time, the presented processes are disrupted. This is manifested by the formation of structural changes, which ends with a weakening of the contractile ability.
Symptoms of cardiopathy
Disease of the cardiovascular system can be asymptomatic for a long time. Then signs specific to cardiopathy appear. The characteristic of the disease consists of gradually increasing symptoms. Patients present with the following complaints:
- dyspnea;
- pain in the region of the heart;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- cyanosis;
- increased sweating;
- tachycardia;
- cough;
- an increase in the size of the spleen and liver;
- fast fatiguability;
The feeling of shortness of breath is associated with blood congestion in the lungs. Shortness of breath first occurs with excessive physical exertion. Then patients notice that they begin to suffocate already with a slight overexertion. Gradually, the symptoms increase and are observed at rest.
Some patients note one of the first symptoms - pain in the region of the heart. Dysplastic cardiopathy is characterized by stabbing or squeezing.
Against the background of heart failure, blood flow in the vascular bed slows down, and this is manifested by swelling of the lower extremities. They first appear in the evening. As the disease progresses, swelling becomes a permanent symptom. Violation of the outflow of fluid leads to its accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
Due to stagnation of blood in the veins, the appearance of a bluish tint is noted. Most often it is noted on the skin of the fingertips, earlobes, lips, nasolabial triangle. An increase in the liver and spleen is observed when the blood flow through the vessels is disturbed.
Complications
A minor anomaly in the development of the heart (cardiopathy) is dangerous not only for its manifestations, but also for complications. They are able to form if the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner and there is no treatment. With dysplastic cardiopathy, the following consequences are possible:
- angina pectoris;

- cardiac ischemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- pericarditis;
- pulmonary edema;
- arrhythmia;
- thrombosis;
- chronic heart failure.
The most common complication is arrhythmia. It appears in almost 10% of the total number of sick children. Cardiopathy leads to disruption of the normal conduction of electrical impulses in cardiomyocytes. As a result, heartbeats become irregular. Most often, there is an acceleration in the number of beats per minute.
With the expansion of the ventricles, when the disease lasts for a long time, the blood stagnates in the cavities. Conditions are created for the formation of clots.
The greatest danger is represented by blood clots that enter the bloodstream (emboli) and over time they can penetrate into vessels of a narrow diameter. This feature is typical for the lung and brain tissue. Blockage of the lumen in them will lead to thromboembolism.
Features of pathology in children
Dysplastic cardiopathy in children is congenital and acquired. In the first case, it is found no later than 2 weeks from the moment of birth. Pathology at such an early age is associated with developmental defects that arose at the time of intrauterine life. In some cases, cardiopathy has an autoimmune origin, and it is associated with rheumatic organ damage.
Children from 7 to 12 years of age have to deal with the acquired form of the disease. This feature is associated with the active growth and development of the body. A repeated surge in the incidence among children is noted after 15 years, when there is a change in hormonal levels and active secretion of those responsible for sexual development.
Dysplastic cardiopathy in children has specific characteristics compared to adults. These include the following:
- In childhood, in almost 80% of children, pathology can be corrected, but not cured completely. Throughout life, it is possible to maintain the child's quality of life at a normal level.
- Most elderly patients have a poor prognosis when such a diagnosis is made.
- When selecting groups of drugs for treatment, there are age restrictions.
In childhood, dysplastic cardiopathy is manifested mainly by aching pains in the region of the heart, shortness of breath and rhythm disturbances. As the pathology progresses, there is a change in the color of the skin, excessive sweating. Some children experience short-term fainting, panic attacks. The latter symptoms sometimes resemble vegetative-vascular dystonia before the attachment of specific signs.
To suspect a disease in time, you need to pay attention to pain and fatigue. It is important to relate these symptoms to exercise. If these symptoms appear with slight overvoltage or at rest, you should consult a doctor. Instead of the term "dysplasia" in childhood, the diagnosis is "functional cardiopathy".
Children are considered the most susceptible to endocarditis (a complication of pathology). When bacteria penetrate through the bloodstream into the heart, the valves and walls of blood vessels become infected. Long-term course of the disease without treatment leads to serious damage to the heart muscle.
Causes
For the onset of the disease, the influence of one or more factors is necessary. These include:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious microorganisms;
- autoimmune pathology;
- fibrosis.
 Hereditary factors play one of the main roles in the appearance of pathology. The whole point lies in the proteins located in cardiomyocytes. Their main task is to maintain the constant functioning of the heart.When defects appear in the structure, the myocardium is disrupted.
Hereditary factors play one of the main roles in the appearance of pathology. The whole point lies in the proteins located in cardiomyocytes. Their main task is to maintain the constant functioning of the heart.When defects appear in the structure, the myocardium is disrupted.
Cardiopathy also occurs when infected with viral or fungal particles. The lack of a sufficient level of immunity makes it possible for them to easily penetrate the body and reproduce. The process leads to damage to the heart muscle and the appearance of symptoms of the disease. When examining the valves and blood vessels under the influence of infection, no changes are noted.
The predisposition to autoimmune pathology plays one of the main roles in the occurrence of cardiopathy. The body begins to attack its own cells, which it perceives as foreign.
Fibrosis is characterized by an active proliferation of connective tissue that replaces muscle cells. Over time, the walls lose their previous elasticity, which disrupts the contractile ability. Often in adults, myocardial infarction becomes a triggering factor for the disease.
Forecast
With the development of dysplastic cardiopathy, the prognosis is often poor. This is due to the emergence of difficulties in establishing a diagnosis. In most patients, it is almost impossible to detect the disease at an early stage. Some patients do not complain during the entire period of progression of cardiopathy (asymptomatic form). Establishing a diagnosis in them is possible only after the addition of complications.
By the time the pathology is detected, in most cases, cardiovascular failure proceeds for a long time. After confirming the diagnosis, the survival rate of such patients in 30% of cases does not exceed 5 years. If it was possible to achieve a heart transplant, then the rate increases to 10 years.
In childhood and adulthood, with early diagnosis, it is possible to stabilize the condition and achieve the absence of manifestations of pathology. To maintain the quality of life, all patients should be monitored by a cardiologist, independently monitor their well-being and constantly take medications according to the prescribed scheme.