The normal functioning of all organs and systems of a person largely depends on blood pressure indicators. A decrease or increase in these indicators to critical levels can lead to death. If the pressure is normal, the body is fully supplied with blood, and with it - oxygen and other useful elements. Sudden pressure drops provoke the development of a dangerous brain disease, such as hypertensive encephalopathy.

Symptoms
Encephalopathy is a whole complex of pathological conditions, united by the destructive effect that they have on the brain: changes in its tissues (sometimes irreversible) occur, and the most important functions are disrupted. Hypertensive encephalopathy is a brain damage associated with increased blood pressure.
Even one-time cases of hypertension make themselves felt: the whole body suffers, it is especially hard for the kidneys, heart, and brain. If the pressure rises constantly, abruptly, then the negative impact on these organs increases many times. What happens in this case directly in the brain?
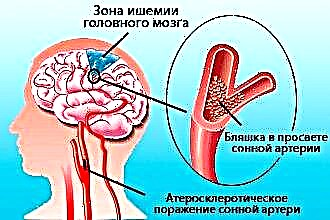
The vascular system has the ability to self-regulate, in other words, the vessels "adjust" to certain conditions: they narrow or expand as needed. When blood pressure rises slightly, the small vessels begin to constrict to prevent rupture of the walls. When the pressure drops below normal, the vessels expand.
A hypertensive crisis (a sharp jump in pressure to high levels) leads to damage to the vessels of the brain from the inside. First, a protective reflex is triggered, they sharply narrow, vasospasm occurs, and then paralysis, the capillaries lose their compensatory ability.
This leads to a passive expansion of small vessels, they overflow with blood and are damaged, blood cells and plasma begin to seep into nearby parts of the brain. In such a situation, one can state cerebral edema, accompanied by damage to its tissues and the extinction of functions.
In addition to hypertensive encephalopathy, a regular increase in pressure can cause brain hypoxia. In such a situation, the vessels of the brain are forced to constantly narrow, this leads to the compaction of their muscle tissues. As a result, the passage inside the vessel becomes very small, blood circulation deteriorates, and with this there is a lack of oxygen. Oxygen starvation has a very negative effect on the functions of the brain.
Hypertensive encephalopathy is a rare disease. Due to the high efficiency of existing medicinal products, arterial hypertension can be successfully treated. In addition, over time, the vessels begin to get used to the constantly increasing pressure, therefore, in most cases, they do not undergo pathological changes. The only danger is spasmodic hypertensive seizures.
Hypertensive encephalopathy has two forms of manifestation: chronic and acute. Each of them differs in its symptoms and course.
Acute manifestations
Acute hypertensive encephalopathy develops with the onset of a hypertensive crisis within a short time interval. This is a condition that occurs with a sharp increase in pressure. For each person, this indicator will be different: for someone, raising the pressure to the 140/90 mark may be critical (this applies to hypotonic patients).
Typical signs:
- excruciating pain in the back of the head;
- bouts of nausea or vomiting;
- seizures, similar to epileptic, accompanied by convulsions;
- significant vision problems appear;
- hearing loss;
- problems with the vestibular apparatus;
- inability to navigate in space and time;
- fainting;
- possible heart pain, interruptions in the heart rhythm;
- irritability and excitement will be replaced by lethargy and apathy;
- numbness and immobility of the limbs, decreased sensitivity of the facial tissues and tongue;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- a feeling of fear and anxiety;
- confused consciousness;
- hallucinations;
- paralysis and paresis.
The consequences of acute development of hypertensive encephalopathy can be very serious. Often the result of this form of the disease is a stroke. A person can become disabled, fall into a coma, or die. Therefore, assistance in such a situation should be provided immediately. The main task of doctors is to prevent the development of cerebral edema and to minimize the number of damaged areas of brain tissue.
Despite the severe course of the disease and life-threatening consequences, the timely administration of drugs to reduce pressure in a hypertensive crisis successfully prevents the development of irreversible processes in the cerebral cortex.
Chronic signs
When arterial hypertension becomes a constant companion of a person, there is a gradual increase in pathological processes in the brain. At the initial stage, hypertensive encephalopathy may have symptoms that are mild. The first noticeable signs occur when the patient can no longer do without drugs that lower blood pressure. There are three stages in the development of the chronic form of the disease.
- The first stage is characterized by the following symptoms: constant fatigue and weakness, dizziness, forgetfulness, distracted attention, tinnitus, frequent headaches. Usually, people do not attach much importance to these symptoms, mistaking them for age characteristics or considering them to be the result of insomnia and problems at work. Even a doctor's consultation does not save the situation: as a rule, a proper examination is not prescribed, and the emerging pathology remains unnoticed.
- At the second stage, the disease progresses. It is already possible to notice impaired coordination of movements, signs of destruction of intelligence, changes in the patient's emotional well-being. The ability to work decreases, fatigue increases, a person loses the desire to do something, he has difficulty organizing any independent actions.
- The third stage is the most unpleasant. The existing symptoms intensify, convulsive seizures are added to them, and Parkinson's disease develops. At the same time, a sick person cannot do without outside help, he needs to be looked after. The patient does not remember anything, completely loses orientation in time and space, social skills and cognitive abilities fade away.
If you manage to "catch" the disease at an early stage, you can slow down the aggravation of pathological signs for a long time. It will no longer be possible to do this at the second and third stages.
Classification of pressure levels
Systemic blood pressure is the force of blood flow against the walls of blood vessels. Distinguish between pressure in veins, capillaries and arteries. It is customary to measure the pressure in the area of the passage of the artery due to the ease of the procedure.
The pressure measured with a special device (tonometer) on the arm is peripheral, its parameters are higher than that of the central blood pressure, which is recorded in the aorta.
The upper figure in the readings of the device is the systolic pressure or heart pressure, appears during the period of contractile movement of the heart muscle and the release of blood flows to the vessels. A high reading means an increased heart rate and strength.
The lower parameter is diastolic, or the pressure that is formed in the vessels.They fix it when the heart is in the resting phase. The readings indicate the strength of the vascular resistance.
 The values shown by the tonometer may vary during the day. Pressure fluctuations occur under the influence of various reasons: a person's mood, physical activity, medication, torso position, nutrition, time of day, conditions of the procedure. In old age, the systolic rate may be overestimated. Some people may not notice at all that their blood pressure has increased, so it is important to keep the situation under control and get your own blood pressure monitor for this.
The values shown by the tonometer may vary during the day. Pressure fluctuations occur under the influence of various reasons: a person's mood, physical activity, medication, torso position, nutrition, time of day, conditions of the procedure. In old age, the systolic rate may be overestimated. Some people may not notice at all that their blood pressure has increased, so it is important to keep the situation under control and get your own blood pressure monitor for this.
The table lists the readings for all blood pressure levels.
| Pressure levels | Systolic readings (in mm Hg) | Diastolic indicators (in mm. Art.) |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal | 120 | 80 |
| Normal | 120 – 130 | 80 – 85 |
| Normal elevated | 130 – 139 | 85 – 89 |
| Hypertension, grade 1 | 140 – 159 | 90 – 99 |
| Hypertension, grade 2 | 160 – 179 | 100 – 109 |
| Hypertension, grade 3 | 180 and above | 110 and higher |
| Systolic hypertension isolated | Above 140 | Below 90 |
| Hypotension | Below 90 | Below 60 |
To diagnose the hypertensive form of encephalopathy, a neurologist's examination is required. He must detect the first symptoms of the disease that occur at an early stage. The patient should also be examined by other narrow specialists: cardiologist, endocrinologist, therapist, nephrologist, ophthalmologist. The diagnosis is complicated by the fact that hypertensive encephalopathy is similar in its manifestations to other pathological conditions (cerebral tumor, stroke).
To get a more accurate picture, the doctor will need to examine the patient using different methods:
- blood pressure measurement;

- laboratory tests (blood test - biochemical and general, urinalysis);
- electroencephalography;
- echocardiography;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- spinal puncture.
In the early period of the disease, MRI and CT will not be able to reveal any pathologies in the patient. At the second stage, these studies will already show the areas of ischemia (lacunae).
Treatment
If the diagnosis is confirmed, especially when it is acute hypertensive encephalopathy, it is necessary to place the patient in a hospital and provide him with emergency assistance. The first step should be taken to eliminate a hypertensive attack. It is important that the pressure decreases gradually, a sharp drop in it will only worsen the situation, especially in the case of chronic hypertension.
The following drugs effectively normalize blood pressure: Diazoxide, Nitroglycerin, Hydralazine. Also use ganglion blockers ("Trimetafan", "Pentolinium", "Pentolamine") and diuretics.
Patients with a chronic form of the disease need to take metabolic drugs, vitamins, nootropics. The following medications are used: "Trenal", "Aspirin", "Dipyridamol". Such patients need to use antidepressants, drugs that have a sedative effect.
To increase the effectiveness of therapeutic agents, patients need to follow a diet low in cholesterol and completely get rid of bad habits.
To avoid the development of a disease such as acute hypertensive encephalopathy, it is necessary to treat hypertension in a timely manner. Every hypertensive person should have his own device for measuring blood pressure at home and be able to use it. Careful attention to the signals sent by the body, as well as sports, resistance to stress, positive emotions and good nutrition will help protect the vascular system from pathological changes and reduce the likelihood of problems. Being healthy isn't all that difficult.