There are a number of heart diseases, without proper treatment of which there is a danger of myocardial infarction, hypertensive crisis, collapse. In the presence of congenital or acquired diseases, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the basics of the nursing process in acute cardiovascular failure. This will help prevent complications that often lead to the death of the patient.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Acute cardiovascular failure is a sudden lack of blood circulation caused by a violation of the contractile function of the heart. The cause of the disease is pathological conditions: myocardial infarction, heart disease, irregularities in the work of the heart rhythm. There are examples of the development of the disease in isolation: against the background of physical or psychological stress. The disease can develop in just a few hours.
Interesting fact! The main cause of the disease in women is arterial hypertension, and in men - coronary heart disease.

There are many reasons for the development of heart failure. These include diseases associated with blood circulation and heart function. This range is supplemented by:
- diabetes;
- arrhythmia;
- cardiac syndrome;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- hypertension.
The first symptoms in acute cardiovascular failure:
- weakness;
- sharp dizziness;
- severe shortness of breath;
- pallor of the skin;
- drop in temperature;
- pain in the chest and heart.
Acute cardiovascular failure can be manifested by severe clinical syndromes: pulmonary edema, cardiogenic shock and cardiac asthma, which develop within a couple of hours. Without proper care and further treatment, the disease can result in death.
To prevent attacks of acute cardiovascular failure, it is necessary to regularly conduct a complete medical examination, which can determine the disease in the early stages.
 There are two types of acute cardiovascular failure: left ventricular and right ventricular. The symptomatic picture changes, depending on the classification of the disease.
There are two types of acute cardiovascular failure: left ventricular and right ventricular. The symptomatic picture changes, depending on the classification of the disease.
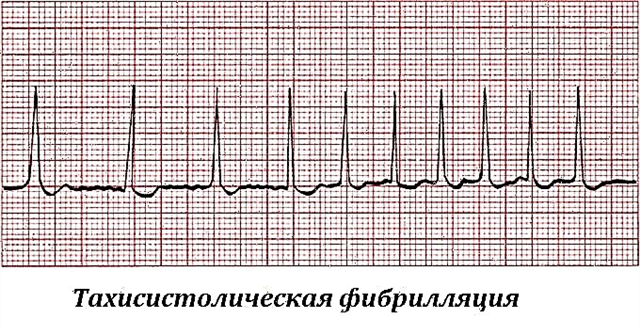
Left ventricular failure is characterized by hypotonic manifestations and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation, there is a left-sided expansion of the borders of the heart, heart palpitations (tachycardia attack) and a cardio-asthmatic surge, which turns into pulmonary edema. A clear sign of this disease, in addition to the main symptoms, is the release of frothy and bloody sputum from the oral cavity.
When the right heart ventricle is damaged, shortness of breath, painful sensations in the liver, cyanosis appear.
External manifestations
The main manifestations of acute cardiovascular failure are fainting, shock and collapse.
Fainting is a sudden loss of consciousness that has a short duration. It is caused by a disruption in the flow of blood to the brain. Fainting lasts up to a couple of minutes. This is not a separate disease, but only a sign of cardiovascular disease.
 The reasons for loss of consciousness are any actions leading to impaired blood circulation and oxygen deficiency. Closed stuffy rooms, nervous exhaustion or fear, prolonged standing are the main reasons leading to fainting.
The reasons for loss of consciousness are any actions leading to impaired blood circulation and oxygen deficiency. Closed stuffy rooms, nervous exhaustion or fear, prolonged standing are the main reasons leading to fainting.
Before fainting, dizziness, weakness are felt, extraneous noises are heard in the ears, a visible veil appears before the eyes, swelling of the limbs and nausea. When fainting, the patient falls unconscious, breathing is infrequent and shallow, and the pulse becomes weak.
This condition requires emergency assistance in the following sequence:
- Put the patient on a flat surface, slightly raise his legs.
- Provide free access to oxygen, relieving the body from the pressure of clothing in the area of the collar zone, belt.
- Apply a cold compress to the forehead of the unconscious person.
These actions contribute to vasoconstriction and improve blood flow to the brain.
If after a couple of minutes the patient does not wake up, this indicates an erroneous preliminary diagnosis. In this case, you will need urgent help from a specialized doctor.
Shock is a dangerous pathological process caused by physical or emotional shock. A state of shock implies a disruption in the work of the body's compensatory reaction (nervous system, respiratory tract, blood circulation, metabolism, and others).
Reasons for the state of shock:
- a number of cardiovascular diseases;
- critical dehydration of the body;
- great blood loss;
- severe allergic reaction;
- sepsis.
Signs of shock include dizziness, weakness, shallow breathing, bluish lips and nails, chest pain, unconsciousness, complete disorientation, pallor, rapid pulse, cold sweat.
The patient is forbidden to give any drink with obvious head injuries, abdominal injuries, internal bleeding.
Shock is a condition that requires immediate medical attention, including emergency nursing. It includes the provision of anti-shock measures.
- The patient who is in the consciousness must be reassured.
- The body, even in the summer, should be wrapped in a warm blanket or put on warm clothes on the patient.
- If there are no injuries to the head, neck or spine, you need to lay the patient on his back and slightly raise his legs.
- Give the victim some sweet tea.
- Regularly record blood pressure and heart rate indicators before the arrival of the doctor.

Follow-up nursing activities should be supervised by a qualified physician.
Collapse is a sharp drop in vascular tone and a decrease in the amount of circulating blood. Collapse attacks are accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and lead to a decline in all working processes of the body.
The reasons for the state of collapse are:
- Sudden large blood loss associated with external injuries or rupture of internal organs.
- Sharp attacks of arrhythmia.
- Violations of the contractile function of the myocardium.
- Expansion of peripheral vessels (occurs in conditions of high humidity and temperature in acute infectious diseases).
- An increased emotional state (often manifested in adolescents, against the background of strong experiences).
The causes that caused the collapse do not affect the main symptoms of the disease. There is a sudden deterioration in the condition. The patient complains of headache, tinnitus, darkening in the eyes. The main symptom is aching pain in the chest area, severe weakness and lethargy. Also, clear symptoms of collapse are paleness, dull eyes, and rapid breathing. If you do not provide first aid, the patient may lose consciousness.
Nursing process
| Action | Justification |
|---|---|
| Put the patient on a flat and hard surface, lifting the lower limbs with a pillow or chair. | Facilitates blood flow to the brain. |
| Provide complete rest. | The degree of oxygen starvation decreases. |
| Place heating pads on the limbs, wrap the body in a warm blanket. If possible, give the patient hot tea. | The degree of oxygen starvation decreases. |
| Free the patient from tight clothing. Inhale oxygen. | The blood supply to the brain improves, the vascular tone rises. |
| Measure blood pressure and pulse every 5 minutes until the doctor arrives. | This will show the dynamics of the patient's condition to the doctor. |
In the event of a loss of consciousness in a patient, a number of resuscitation actions are required, which include indirect heart massage and artificial respiration. With a slowdown in the provision of medical intensive care, an attack can result in death.
Follow-up by a physician is mandatory. In most cases, the collapse is caused by a serious illness. At home, cardiac malfunctions can be recorded with a conventional tonometer - mechanical or automatic. By regularly checking your blood pressure and heart rate, a number of heart diseases and death can be prevented.
As soon as the syndrome is arrested, the patient is referred for treatment in a hospital. There, an experienced cardiologist will prescribe a course of treatment that will prevent the recurrence of an acute condition. If the patient's condition was stabilized in time, and the patient is recovering, after a while he is sent home. Unfortunately, the treatment does not end there.
In addition to the fact that the patient must strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician regarding the regimen of activity and rest, nutrition and lifestyle in general, medical services will come to him every day. Her task is to monitor the patient's condition, because even if he misses the appearance of some dangerous symptoms, she will be able to notice them. The duties of a nurse also include injections, measurement of the patient's blood pressure, and a survey.
Helping children
Acute cardiovascular insufficiency in children can occur as a result of infectious-toxic and allergic diseases, acute poisoning and hypoxia - this is an energetic-dynamic insufficiency. A decrease in heart function also occurs due to myocardial overload and exhaustion of compensatory capabilities - this is hemodynamic insufficiency. The division of the disease into these types is considered conditional.
In therapeutic studies of heart failure in childhood, a direct relationship was found between the onset of the disease and direct lesions of the heart muscle (congenital or acquired heart disease, myocarditis, poisoning with cardiotoxic poisons).
The main signs of deficiency in children are:
- cyanosis;
- dyspnea;
- dry wheezing and coughing.
 The provision of first aid for acute cardiovascular failure in a child should be carried out when the first symptoms appear. To do this, hold the child in a semi-sitting position. Hands and feet should be immersed in warm water. If possible, inhale oxygen. These actions help to stabilize the level of blood pressure and improve the supply of oxygen to the brain.
The provision of first aid for acute cardiovascular failure in a child should be carried out when the first symptoms appear. To do this, hold the child in a semi-sitting position. Hands and feet should be immersed in warm water. If possible, inhale oxygen. These actions help to stabilize the level of blood pressure and improve the supply of oxygen to the brain.
Attacks of heart failure in children are an indicator of the need for a complete examination. This disease is treated by eliminating the causes of the disease.
Quitting smoking and alcohol will have a positive effect on the functioning of the heart and other organs. Proper nutrition and exercise will strengthen the heart muscle. Any prevention of heart disease prevents the occurrence of acute cardiovascular failure. Any self-medication can have negative consequences. Before taking any preventive measures or therapeutic effects on the body, it is imperative to consult a doctor.