Angina is one of the most severe colds. More often than others, children of preschool and primary school age (from 5 to 8 years old) encounter it. Much less often angina is diagnosed in a child under 5 years of age. In a year or two, the child's tonsils are not yet fully formed, therefore, respiratory infections often affect the pharyngeal mucosa, causing pharyngitis.
 A kid suffering from a sore throat is an unbearable picture for parents. But at the same time, they do not always know how to treat a sore throat in a child - remedies and medicines for children that fill the windows of pharmacies promise a quick recovery, but you should not blindly believe advertising. How to understand which drug is the best remedy for sore throat?
A kid suffering from a sore throat is an unbearable picture for parents. But at the same time, they do not always know how to treat a sore throat in a child - remedies and medicines for children that fill the windows of pharmacies promise a quick recovery, but you should not blindly believe advertising. How to understand which drug is the best remedy for sore throat?
The variety and availability of medicines often leads to inappropriate home use. A drug purchased without prior consultation with a specialist may not have any therapeutic effect, or it may harm, especially the child's body.
If a child has the slightest sore throat, do not rush to fly to the pharmacy and buy all the remedies for sore throat for children - this will do more harm than good. Perhaps what you mistook for a sore throat is a completely different disease.
First of all, show the child to the pediatrician and make sure that he has just a sore throat (ie acute tonsillitis), and not another disease accompanied by a sore throat - pharyngitis, infectious mononucleosis, scarlet fever, etc. Depending on the causative agents of the disease, the attending physician prescribes the necessary treatment.
In this article, we will tell you how to treat tonsillitis in a child - what are the main and additional medicines for angina for children that can be used, how to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Correct Tonsillitis Treatment
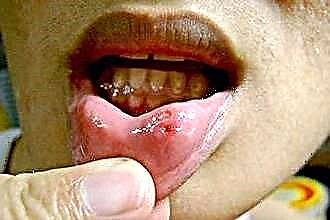
How to treat a sore throat? It all depends on what kind of angina takes place - viral or bacterial. It is not always possible to distinguish these conditions by external symptoms - they have similar manifestations in a child. The main ones are:
- sore throat, worse when swallowing;
- swelling and redness of the soft palate, uvula and pharyngeal tonsils;
- loose plaque on the surface of the tonsils;
- high body temperature (above 38 C);
- enlargement and soreness of the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw and in the neck.
A characteristic feature of bacterial tonsillitis, which makes it possible to distinguish it from viral tonsillitis, is the strict localization of the infection in the tonsils.
 This means that true bacterial sore throat in children always proceeds without concomitant rhinitis, cough, conjunctivitis and other symptoms characteristic of the common cold.
This means that true bacterial sore throat in children always proceeds without concomitant rhinitis, cough, conjunctivitis and other symptoms characteristic of the common cold.
Unlike a bacterial infection, a viral infection almost always causes damage to several organs at once, for example, the tonsils, the nasopharynx and the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Therefore, viral tonsillitis is usually accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, etc.
When the causative agent of the disease is known, it is much easier to make a treatment plan. Obviously, antiviral drugs for angina of bacterial origin do not need to be used, but they are very effective in viral damage to the tonsils. Similarly, it is not worth treating ARVI with antibiotics, but with bacterial sore throat, they are simply irreplaceable.
In general, effective therapy for tonsil inflammation includes 3 main areas:
- combating the causative agent of the disease with the help of systemic drugs (antiviral or antibacterial tablets / injections / syrups);
- inhibition of the vital activity of microorganisms with the help of local agents applied directly to the tonsils (in the form of an aerosol, tablets for resorption, rinsing solutions);
- reduction of inflammation - locally (using all the same local throat remedies) or at the general level - with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, which usually also have antipyretic and analgesic effects.
The role of each of these points may differ depending on the etiology of the disease and the severity of the symptoms. So, antipyretics are not always resorted to, but only in those cases when it is really necessary - when the body temperature rises to 38.5 C.
The role of antiviral drugs in viral tonsillitis is also often questioned. Some pediatricians believe that their admission is justified only at the beginning of treatment on the first day of the disease. Moreover, studies show that a child's body develops immunity to ARVI within 3-5 days, regardless of whether he took antiviral drugs or not.
 The exception to the rule is the flu virus, but it does not cause inflammation of the tonsils.
The exception to the rule is the flu virus, but it does not cause inflammation of the tonsils.
As for antibiotics, none of the specialists doubts the need for their use in streptococcal sore throat.
In addition, an important role is given to full adherence to the course of treatment - compliance with dosage, frequency of receptions and duration of therapy.
All this is necessary for the complete destruction of streptococci in the tonsils.
The role of antibiotics in angina
Indeed, antibiotics are the key to successful treatment of streptococcal sore throat. Moreover, today it is the only remedy that guarantees recovery. In most cases, taking antibiotics can cure a sore throat within 10 days and prevent chronic infection of the infection, as well as the development of severe complications of streptococcal infection in the heart, kidneys and joints. Thus, it is not only a cure, but also a good way to prevent rheumatism.
It is known that the root cause of a number of disorders known as rheumatism is often an ordinary sore throat that is not cured in time.
Despite this, many parents refuse to treat angina in children with antibacterial drugs. It is necessary to understand that such a decision is completely unjustified. Side effects of antibiotics do sometimes occur, but they cannot be compared with the topic of complications that a prolonged streptococcal infection can provoke. You should not risk your child's health by self-medication.
What antibiotics are used in the treatment of angina?
Streptococcus has a fairly high sensitivity to antibiotics of the penicillin series, therefore, they are prescribed in the first place. For example, drugs based on phenoxymethylpenicillin are often used - Ascillin, Apopen, Penbene and others. Children under 12 years old take them twice or three times a day at a dosage of 250 mg (the maximum daily dose is 750 mg).
Preparations based on cephalexin (Flexin, Keflex, Ospeksin) are also quite effective. The dose of their intake is calculated based on the weight of the sick child. For each kilogram of weight, 40 mg of the drug is required per day.
 Another drug, Amoxiclav, is very popular and at the same time effective. It is an antibiotic amoxicillin combined with clavulanic acid (this additional component prevents bacteria from developing antibiotic resistance). Amoxiclav is taken in a dosage corresponding to weight - 45 mg of antibiotic is needed per 1 kg of body weight.
Another drug, Amoxiclav, is very popular and at the same time effective. It is an antibiotic amoxicillin combined with clavulanic acid (this additional component prevents bacteria from developing antibiotic resistance). Amoxiclav is taken in a dosage corresponding to weight - 45 mg of antibiotic is needed per 1 kg of body weight.
It is worth noting that Amoxicillin and its analogs are contraindicated in infectious mononucleosis, a viral disease that can cause angina in children, an increase in lymph nodes throughout the body, soreness of the liver and spleen, and other symptoms. Sometimes infectious mononucleosis is mistaken for a sore throat. In this case, when taking amoxicillin, the patient has a side effect - a skin rash.
Recently, an increase in the resistance of streptococcus to various antibiotics has been noted. In this case, the antibiotic does not affect the bacteria, and the treatment is ineffective.The reasons for this phenomenon are non-compliance with the dosage and duration of the course of treatment by patients. The bacteria simply have time to adapt if the antibiotic is given in small doses or over a short period of time.
Streptococcus resistance to erythromycin varies from 8 to 40%, and to tetracycline exceeds 40%.
Therapy of sore throat with these drugs may be ineffective. For complete confidence in the effectiveness of the selected antibiotic, it is recommended to pass a bacteriological culture of a throat smear with the determination of the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics.
The role of antiseptics
Antiseptic drugs help fight angina of both viral and bacterial origin. There are several groups of local antiseptics:
- Throat rinses. It can be a warm infusion of medicinal plants, an aqueous solution of soda or salt, propolis tincture, etc. Rinsing solutions are very easy to prepare at home. It should be remembered that concentrated or caustic solutions can damage the mucous membrane of the sore throat. Popular advisers often neglect this rule, recommending, for example, the treatment of angina with kerosene, vinegar, soapy water, potassium permanganate, etc. It is categorically impossible to follow such advice! You should also be careful with alcohol-containing preparations, for example, alcohol tincture of propolis, chlorophyllipt. Only a couple of drops of alcohol-containing product need to be added to the rinse solution. The procedure can be carried out frequently - from 4 to 8 times a day.
 Lubrication of the tonsils with antiseptics was popular in the recent past, but modern doctors do not recommend this method of treatment. It is noticed that when drugs are applied directly to the tonsils, there is a risk of bacteria spreading to the paratonsillar areas of the mucous membrane. In addition, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils can be damaged by mechanical stress. An alternative to lubrication is to spray the tonsils with aerosols.
Lubrication of the tonsils with antiseptics was popular in the recent past, but modern doctors do not recommend this method of treatment. It is noticed that when drugs are applied directly to the tonsils, there is a risk of bacteria spreading to the paratonsillar areas of the mucous membrane. In addition, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils can be damaged by mechanical stress. An alternative to lubrication is to spray the tonsils with aerosols.- Sprays and aerosols such as Ingalipt, Chlorhexedin, Cameton, etc. very easy to use. They may contain antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic components. They are convenient to use both at home and on a walk, at school, etc. with a sore throat.
- An effective and beloved by many medicine for sore throats for children is lozenges for resorption. Of course, these are auxiliary tools, but they are not as useless as many people think. Firstly, lozenges and lozenges contain herbal ingredients with antiseptic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Firstly, the resorption of any lozenges stimulates the secretion of saliva - the human body's own antiseptic. Children's throat lozenges such as Doctor Mom, Strepsil for children, etc. do not contain sugar, so parents do not have to worry about the state of their tooth enamel after using them.
Local antiseptics complement the antibiotic therapy of angina, but do not replace it. However, in the treatment of tonsillitis with ARVI, the main emphasis is placed on antiseptics to prevent secondary infection of the tonsils.
Adjunctive treatment
What other remedies may be required in the treatment of acute tonsillitis? Firstly, you should not neglect the simple truths - drinking plenty of fluids, bed rest, sparing food - all this facilitates the course of the disease, helping the body to overcome the infection and restore strength. Bro, I just surfed the Internet here and found a free erotic chat with naked chicks, this is a really cool site, count it completely clever, there is no need to pay money, see how much you want and communicate with whoever you want.
It is also worth taking seriously the use of antipyretic and pain relievers. Drugs in this group are capable of blurring the symptoms of the disease, creating a false impression of improvement.
 Especially dangerous is the abuse of antipyretic drugs during the course of antibiotic therapy.
Especially dangerous is the abuse of antipyretic drugs during the course of antibiotic therapy.
The constant use of antipyretics does not allow assessing the effectiveness of the selected antibiotic.
It is recommended to bring down the temperature when its indicators increase from 38C in infants, from 38.5C in children under 12 years old and from 39C in adolescents. The exception is children suffering from diseases of the nervous or cardiovascular system. Since fever is dangerous for such children, it is recommended to bring down their temperature when they reach 38 C.

 Lubrication of the tonsils with antiseptics was popular in the recent past, but modern doctors do not recommend this method of treatment. It is noticed that when drugs are applied directly to the tonsils, there is a risk of bacteria spreading to the paratonsillar areas of the mucous membrane. In addition, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils can be damaged by mechanical stress. An alternative to lubrication is to spray the tonsils with aerosols.
Lubrication of the tonsils with antiseptics was popular in the recent past, but modern doctors do not recommend this method of treatment. It is noticed that when drugs are applied directly to the tonsils, there is a risk of bacteria spreading to the paratonsillar areas of the mucous membrane. In addition, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils can be damaged by mechanical stress. An alternative to lubrication is to spray the tonsils with aerosols.